Abstract
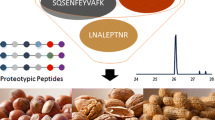
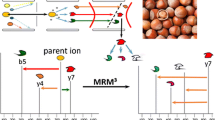
A liquid chromatography–electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry (LC–ESI-MS–MS) method based on the detection of biomarker peptides from allergenic proteins was devised for confirming and quantifying peanut allergens in foods. Peptides obtained from tryptic digestion of Ara h 2 and Ara h 3/4 proteins were identified and characterized by LC–MS and LC–MS–MS with a quadrupole-time of flight mass analyzer. Four peptides were chosen and investigated as biomarkers taking into account their selectivity, the absence of missed cleavages, the uniform distribution in the Ara h 2 and Ara h 3/4 protein isoforms together with their spectral features under ESI-MS–MS conditions, and good repeatability of LC retention time. Because of the different expression levels, the selection of two different allergenic proteins was proved to be useful in the identification and univocal confirmation of the presence of peanuts in foodstuffs. Using rice crispy and chocolate-based snacks as model food matrix, an LC–MS–MS method with triple quadrupole mass analyzer allowed good detection limits to be obtained for Ara h2 (5 μg protein g−1 matrix) and Ara h3/4 (1 μg protein g−1 matrix). Linearity of the method was established in the 10–200 μg g−1 range of peanut proteins in the food matrix investigated. Method selectivity was demonstrated by analyzing tree nuts (almonds, pecan nuts, hazelnuts, walnuts) and food ingredients such as milk, soy beans, chocolate, cornflakes, and rice crispy.

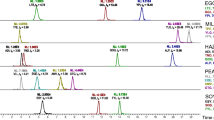
ESI-QTOF-MS mass spectrum of Ara h3/4 triptig digest


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grundy J, Matthews S, Bateman B, Dean T, Arshad SH (2002) J Allergy Clin Immunol 110:784–789
Bock SA, Munoz-Furlong A, Sampson HA (2001) J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:191–193
Rangaraj S, Ramanathan V, Tuthill DP, Spear E, Hourihane JO, Alfaham M (2004) Pediatr Allergy Immunol 15:449–453
Sicherer SH, Leung DY (2005) J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:153–163
Hourihane JB, Kilburn SA, Nordlee JA, Hefle SL, Taylor SL, Warner JO (1997) J Allergy Clin Immunol 100:596–600
Kemp SF, Lockey RF (1996) JAMA 275:1636–1637
Vierk K, Falci K, Wolyniak C, Klontz KC (2002) J Allergy Clin Immunol 109:1022–1026
Joshi P, Mofidi S, Sicherer SH (2002) J Allergy Clin Immunol 109:1019–1021
Directive 2003/89/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 10 November 2003 amending Directive 2000/13/EC, Official Journal of the European Union 25.11.2003, L 308/15
Humieres J, Wal JM (2004) Allergy 59:1259–1261
Mills EN, Valovirta E, Madsen C, Taylor SL, Vieths S, Anklam E (2004) Allergy 59:1262–1268
Schmitt D, Cheng H, Maleki J (2004) JAOAC Int 87:1492–1497
Whitaker TB, Williams KM, Trucksess MW, Slate AB (2005) JAOAC Int 88:161–174
Hird H, Lloyd J, Goodier R, Brown J, Reece P (2003) Eur Food Res Technol 217:265–268
Careri M, Elviri L, Mangia A, Mucchino C (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1851–1854
de Jong EC, Van Zijverden M, Spanhaak S (1998) Clin Exp Allergy 28:743–751
Clarke MC, Kilburn SA, Hourihane JO (1998) Clin Exp Allergy 28:1251–1257
Shefcheck KJ, Musser SM (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:2785–2790
Shefcheck KJ, Callahan JH, Musser SM (2006) J Agric Food Chem 54:7953–7959
Chassaigne H, Nørgaard JV, van Hengel A (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:4461–4473
Chatel JM, Bernard H, Orson FM (2003) Int Arch Allergy Immunol 131:14–18
Stanley JS, King N, Burks AW, Huang SK, Sampson H, Cockrell G, Helm RM, West CM, Bannon GA (1997) Arch Biochem Biophys 342:244–253
Xiang P, Beardslee TA, Zeece MG, Markwell J, Saratha G (2002) Arch Biochem Biophys 408:51–57
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding support from MIUR (Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca, Italy), PRIN 2004 Project “Identification of allergenic proteins from peanuts and hazelnuts in foods as a consequence of process contamination or adulteration; determination by mass spectrometry-based methods”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Careri, M., Costa, A., Elviri, L. et al. Use of specific peptide biomarkers for quantitative confirmation of hidden allergenic peanut proteins Ara h 2 and Ara h 3/4 for food control by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 389, 1901–1907 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1595-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1595-2