Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis
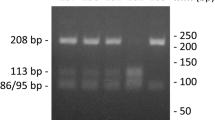
Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is in part attributed to qualitative and quantitative changes in connective tissue of the urogenital tract. We examined the association of collagen type I a1 (COLIA 1) Sp1 polymorphism with the risk of SUI.
Methods
Forty-five postmenopausal women suffering from urodynamically verified SUI (study group) were compared to 45 healthy volunteers (control). DNA was extracted from peripheral blood. The genotyping concerning the type 1 a1 collagen gene Sp1 polymorphism was performed with polymerase chain reaction.
Results
The polymorphic T allele was overrepresented in the SUI patients (63.2% versus 36.8%, p = 0.016). Odds ratio for SUI in women harboring the T allele was 2.19 (95% CI 1.149–4.176) compared to women with the wild-type genotype.
Conclusions
The COLIA1 Sp1 polymorphism is associated with increased prevalence of stress urinary incontinence in postmenopausal women.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hannestad YS, Rortveit G, Sandvik H, Hunskaar S (2000) Norwegian EPINCONT study. Epidemiology of incontinence in the county of Nord-Trøndelag. A community- based epidemiological survey of female urinary incontinence: the Norwegian EPINCONTstudy. Epidemiology of incontinence in the county of Nord-Trøndelag. J Clin Epidemiol 53(11):1150–1157
Melville JL, Katon W, Delaney K, Newton K (2005) Urinary incontinence in US women: a population-based study. Arch Intern Med 165(5):537–542
DeLancey JO, Starr RA (1990) Histology of the connection between the vagina and levator ani muscles. Implications for urinary tract function. J Reprod Med 35(8):765–771
Petros PE, Ulmsten UI (1993) An integral theory and its method for the diagnosis and management of female urinary incontinence. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 153:1–93
Rechberger T, Postawski K, Jakowicki JA, Gunja-Smith Z, Woessner JF Jr (1998) Role of fascial collagen in stress urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 179(6 Pt 1):1511–1514
Ulmsten U, Ekman G, Giertz G, Malmström A (1987) Different biochemical composition of connective tissue in continent and stress incontinent women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 66(5):455–457
Falconer C, Ekman G, Malmström A, Ulmsten U (1994) Decreased collagen synthesis in stress-incontinent women. Obstet Gynecol 84(4):583
Keane DP, Sims TJ, Abrams P, Bailey AJ (1997) Analysis of collagen status in premenopausal nulliparous women with genuine stress incontinence. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 104(9):994–998
Grant SF, Reid DM, Blake G, Herd R, Fogelman I, Ralston SH (1996) Reduced bone density and osteoporosis associated with a polymorphic Sp1 binding site in the collagen type I alpha 1 gene. Nat Genet 14(2):203–5
Mann V, Hobson EE, Li B, Stewart TL, Grant SF, Robins SP et al (2001) A COL1A1 Sp1 binding site polymorphism predisposes to osteoporotic fracture by affecting bone density and quality. J Clin Invest 107(7):899–907
Skorupski P, Król J, Starega J, Adamiak A, Jankiewicz K, Rechberger T (2006) An alpha-1 chain of type I collagen Sp1-binding site polymorphism in women suffering from stress urinary incontinence. Am J Obstet Gynecol 194(2):346–350
Feiner B, Fares F, Azam N, Auslender R, David M, Abramov Y (2009) Does COLIA1 SP1-binding site polymorphism predispose women to pelvic organ prolapse? Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 20(9):1061–1065
Schäfer W, Abrams P, Liao L, Mattiasson A, Pesce F, Spangberg A et al (2002) International Continence Society. Good urodynamic practices: uroflowmetry, filling cystometry, and pressure-flow studies. Neurourol Urodyn 21(3):261–274
Ghoniem G, Stanford E, Kenton K, Achtari C, Goldberg R, Mascarenhas T, Parekh M, Tamussino K, Tosson S, Lose G, Petri E (2008) Evaluation and outcome measures in the treatment of female urinary stress incontinence: International Urogynecological Association (IUGA) guidelines for research and clinical practice. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 19(1):5–33
Liapis A, Bakas P, Pafiti A, Hassiakos D, Frangos-Plemenos M, Creatsas G (2000) Changes in the quantity of collagen type I in women with genuine stress incontinence. Urol Res 28(5):323–326
Ralston SH, Uitterlinden AG, Brandi ML, Balcells S, Langdahl BL, Lips P, Lorenc R et al (2006) GENOMOS investigators. Large-scale evidence for the effect of the COLIA1 Sp1 polymorphism on osteoporosis outcomes: the GENOMOS study. PLoS Med 3(4):e90
Ji GR, Yao M, Sun CY, Zhang L, Han Z (2009) Association of collagen type I alpha1 (COLIA1) Sp1 polymorphism with osteoporotic fracture in Caucasian post-menopausal women: a meta-analysis. J Int Med Res 37(6):1725–1732
Lambrinoudaki I, Kung AW (2001) Absence of high-risk “s” allele associated with osteoporosis at the intronic SP1 binding-site of collagen Ialpha1 gene in Southern Chinese. J Endocrinol Investig 24(7):499–502
Rodrigues AM, Girão MJ, da Silva ID, Sartori MG, Martins Kde F, Castro Rde A (2008) COL1A1 Sp1-binding site polymorphism as a risk factor for genital prolapse. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 19(11):1471–1475
Cho HJ, Jung HJ, Kim SK, Choi JR, Cho NH, Bai SW (2009) Polymorphism of a COLIA1 gene Sp1 binding site in Korean women with pelvic organ prolapse. Yonsei Med J 50(4):564–568
Skorupski P, Miotła P, Jankiewicz K, Rechberger T (2007) Polymorphism of the gene encoding alpha-1 chain of collagen type I and a risk of pelvic organ prolapse—a preliminary study. Ginekol Pol 78(11):852–5
Goepel C, Hefler L, Methfessel HD, Koelbl H (2003) Periurethral connective tissue status of postmenopausal women with genital prolapse with and without stress incontinence. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 82(7):659–664
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sioutis, D., Economou, E., Lambrinoudaki, I. et al. Sp1 collagen I A1 polymorphism in women with stress urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 22, 835–839 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-011-1372-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-011-1372-9