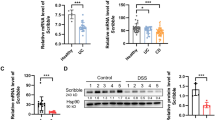
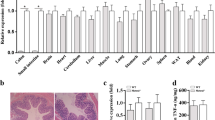
Abstract
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a critical regulator of barrier integrity during colonic mucosal injury. Previous works have shown that the absence of autophagy is implicated in the development of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Additionally, changes in bacterial profiles in the gut are intimately associated with IBD. Although HIF-1α, autophagy, microbiota, and their metabolites are all involved in the pathogenesis of IBD, their roles are not known. In this study, we investigated the relationship between HIF-1α and autophagy in healthy and inflammatory states using transgenic mice, colitis models, and cell culture models. We confirmed that the absence of intestinal epithelial HIF-1α changed the composition of the intestinal microbes and increased the susceptibility of mice to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis. In addition, autophagy levels in the intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) were significantly reduced in IEC-specific HIF-1α-deficient (HIF-1α∆IEC) mice. Moreover, in the cell culture models, butyrate treatment significantly increased autophagy in HT29 cells under normal conditions, whereas butyrate had little effect on autophagy after HIF-1α ablation. Furthermore, in the DSS-induced colitis model, butyrate administration relieved the colonic injury and suppressed inflammation in Cre-/HIF-1α- (HIF-1αloxP/loxP) mice. However, the butyrate-mediated protection against colonic injury was considerably diminished in the HIF-1α∆IEC mice. These results show that HIF-1α, autophagy, and intestinal microbes are essential for the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Butyrate can alleviate DSS-induced colitis by regulating autophagy via HIF-1α. These insights may have important implications for the development of therapeutic strategies for IBD.
Key messages
• The absence of intestinal epithelial HIF-1α leads to downregulation of autophagy in mice.
• The absence of intestinal epithelial HIF-1α exacerbates DSS-induced colitis.
• Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) can alleviate DSS-induced colitis by regulating autophagy via HIF-1α.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maloy KJ, Powrie F (2011) Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 474:298–306
Larabi A, Barnich N, Nguyen H (2019) New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD. Autophagy:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1635384
Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, Lee JC, Schumm LP, Sharma Y, Anderson CA, Essers J, Mitrovic M, Ning K, Cleynen I, Theatre E, Spain SL, Raychaudhuri S, Goyette P, Wei Z, Abraham C, Achkar JP, Ahmad T, Amininejad L, Ananthakrishnan AN, Andersen V, Andrews JM, Baidoo L, Balschun T, Bampton PA, Bitton A, Boucher G, Brand S, Buning C, Cohain A, Cichon S, D'Amato M, De Jong D, Devaney KL, Dubinsky M, Edwards C, Ellinghaus D, Ferguson LR, Franchimont D, Fransen K, Gearry R, Georges M, Gieger C, Glas J, Haritunians T, Hart A, Hawkey C, Hedl M, Hu X, Karlsen TH, Kupcinskas L, Kugathasan S, Latiano A, Laukens D, Lawrance IC, Lees CW, Louis E, Mahy G, Mansfield J, Morgan AR, Mowat C, Newman W, Palmieri O, Ponsioen CY, Potocnik U, Prescott NJ, Regueiro M, Rotter JI, Russell RK, Sanderson JD, Sans M, Satsangi J, Schreiber S, Simms LA, Sventoraityte J, Targan SR, Taylor KD, Tremelling M, Verspaget HW, De Vos M, Wijmenga C, Wilson DC, Winkelmann J, Xavier RJ, Zeissig S, Zhang B, Zhang CK, Zhao H, Silverberg MS, Annese V, Hakonarson H, Brant SR, Radford-Smith G, Mathew CG, Rioux JD, Schadt EE, Daly MJ, Franke A, Parkes M, Vermeire S, Barrett JC, Cho JH (2012) Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 491:119–124
Chu H, Khosravi A, Kusumawardhani IP, Kwon AH, Vasconcelos AC, Cunha LD, Mayer AE, Shen Y, Wu WL, Kambal A, Targan SR, Xavier RJ, Ernst PB, Green DR, McGovern DP, Virgin HW, Mazmanian SK (2016) Gene-microbiota interactions contribute to the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Science 352:1116–1120
Mizushima N (2018) A brief history of autophagy from cell biology to physiology and disease. Nat Cell Biol 20:521–527
Lassen KG, Xavier RJ (2018) Mechanisms and function of autophagy in intestinal disease. Autophagy 14:216–220
Nguyen HT, Lapaquette P, Bringer MA, Darfeuille-Michaud A (2013) Autophagy and Crohn's disease. J Innate Immun 5:434–443
Deretic V, Master S, Singh S (2008) Autophagy gives a nod and a wink to the inflammasome and Paneth cells in Crohn's disease. Dev Cell 15:641–642
Thachil E, Hugot JP, Arbeille B, Paris R, Grodet A, Peuchmaur M, Codogno P, Barreau F, Ogier-Denis E, Berrebi D, Viala J (2012) Abnormal activation of autophagy-induced crinophagy in Paneth cells from patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 142:1097–1099
Wehkamp J, Wang G, Kubler I, Nuding S, Gregorieff A, Schnabel A, Kays RJ, Fellermann K, Burk O, Schwab M, Clevers H, Bevins CL, Stange EF (2007) The Paneth cell alpha-defensin deficiency of ileal Crohn's disease is linked to Wnt/Tcf-4. J Immunol 179:3109–3118
Adolph TE, Tomczak MF, Niederreiter L, Ko HJ, Bock J, Martinez-Naves E, Glickman JN, Tschurtschenthaler M, Hartwig J, Hosomi S, Flak MB, Cusick JL, Kohno K, Iwawaki T, Billmann-Born S, Raine T, Bharti R, Lucius R, Kweon MN, Marciniak SJ, Choi A, Hagen SJ, Schreiber S, Rosenstiel P, Kaser A, Blumberg RS (2013) Paneth cells as a site of origin for intestinal inflammation. Nature 503:272–276
Albenberg L, Esipova TV, Judge CP, Bittinger K, Chen J, Laughlin A, Grunberg S, Baldassano RN, Lewis JD, Li H, Thom SR, Bushman FD, Vinogradov SA, Wu GD (2014) Correlation between intraluminal oxygen gradient and radial partitioning of intestinal microbiota. Gastroenterology 147:1055–1063
Kelly CJ, Zheng L, Campbell EL, Saeedi B, Scholz CC, Bayless AJ, Wilson KE, Glover LE, Kominsky DJ, Magnuson A, Weir TL, Ehrentraut SF, Pickel C, Kuhn KA, Lanis JM, Nguyen V, Taylor CT, Colgan SP (2015) Crosstalk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and intestinal epithelial HIF augments tissue barrier function. Cell Host Microbe 17:662–671
Colgan SP, Taylor CT (2010) Hypoxia: an alarm signal during intestinal inflammation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:281–287
Fang Y, Tan J, Zhang Q (2015) Signaling pathways and mechanisms of hypoxia-induced autophagy in the animal cells. Cell Biol Int 39:891–898
Sun L, Li T, Tang H, Yu K, Ma Y, Yu M, Qiu Y, Xu P, Xiao W, Yang H (2019) Intestinal epithelial cells-derived hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha is essential for the homeostasis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Front Immunol 10:806
Goncalves P, Araujo JR, Di Santo JP (2018) A cross-talk between microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids and the host mucosal immune system regulates intestinal homeostasis and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 24:558–572
Ploger S, Stumpff F, Penner GB, Schulzke JD, Gabel G, Martens H, Shen Z, Gunzel D, Aschenbach JR (2012) Microbial butyrate and its role for barrier function in the gastrointestinal tract. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1258:52–59
Hamer HM, Jonkers D, Venema K, Vanhoutvin S, Troost FJ, Brummer RJ (2008) Review article: the role of butyrate on colonic function. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27:104–119
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P, Chiche J, Roux D, Pouyssegur J, Mazure NM (2009) Hypoxia-induced autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol 29:2570–2581
Ji T, Xu C, Sun L, Yu M, Peng K, Qiu Y, Xiao W, Yang H (2015) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation down-regulates IL-7 and reduces inflammation in a mouse model of DSS-induced colitis. Dig Dis Sci 60:1958–1966
Hamamoto N, Maemura K, Hirata I, Murano M, Sasaki S, Katsu K (1999) Inhibition of dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice by intracolonically administered antibodies against adhesion molecules (endothelial leucocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) or intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1)). Clin Exp Immunol 117:462–468
Wu S, Zhang YG, Lu R, Xia Y, Zhou D, Petrof EO, Claud EC, Chen D, Chang EB, Carmeliet G, Sun J (2015) Intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor deletion leads to defective autophagy in colitis. GUT 64:1082–1094
Kornbluth A, Sachar DB (2010) Ulcerative colitis practice guidelines in adults: American College of Gastroenterology, Practice Parameters Committee. Am J Gastroenterol 105(501–523):524
Qiu Y, Pu A, Zheng H, Liu M, Chen W, Wang W, Xiao W, Yang H (2016) TLR2-dependent signaling for IL-15 production is essential for the homeostasis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Mediat Inflamm 2016:4281865
Sanz ML, Polemis N, Morales V, Corzo N, Drakoularakou A, Gibson GR, Rastall RA (2005) In vitro investigation into the potential prebiotic activity of honey oligosaccharides. J Agric Food Chem 53:2914–2921
Shen T, Li S, Cai LD, Liu JL, Wang CY, Gan WJ, Li XM, Wang JR, Sun LN, Deng M, Liu YH, Li JM (2018) Erbin exerts a protective effect against inflammatory bowel disease by suppressing autophagic cell death. Oncotarget 9:12035–12049
Santos S, Andrade DJ (2017) HIF-1alpha and infectious diseases: a new frontier for the development of new therapies. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 59:e92
Zeitouni NE, Chotikatum S, von Kockritz-Blickwede M, Naim HY (2016) The impact of hypoxia on intestinal epithelial cell functions: consequences for invasion by bacterial pathogens. Mol Cell Pediatr 3:14
Kaelin WG (2005) Proline hydroxylation and gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem 74:115–128
Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2005) Signalling hypoxia by HIF hydroxylases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 338:617–626
Cosin-Roger J, Simmen S, Melhem H, Atrott K, Frey-Wagner I, Hausmann M, de Valliere C, Spalinger MR, Spielmann P, Wenger RH, Zeitz J, Vavricka SR, Rogler G, Ruiz PA (2017) Hypoxia ameliorates intestinal inflammation through NLRP3/mTOR downregulation and autophagy activation. Nat Commun 8:98
D'Arcy MS (2019) Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int 43:582–592
Galluzzi L, Green DR (2019) Autophagy-independent functions of the autophagy machinery. Cell 177:1682–1699
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN, Bhutia SK (2014) Autophagy and apoptosis: where do they meet? Apoptosis 19:555–566
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU, Kimchi A (2009) Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ 16:966–975
Wei Y, Sinha S, Levine B (2008) Dual role of JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 in autophagy and apoptosis regulation. Autophagy 4:949–951
Parkes M (2012) Evidence from genetics for a role of autophagy and innate immunity in IBD pathogenesis. Dig Dis 30:330–333
Randall-Demllo S, Chieppa M, Eri R (2013) Intestinal epithelium and autophagy: partners in gut homeostasis. Front Immunol 4:301
Baxt LA, Xavier RJ (2015) Role of autophagy in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Gastroenterology 149:553–562
Glover LE, Colgan SP (2011) Hypoxia and metabolic factors that influence inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 140:1748–1755
Ortiz-Masia D, Cosin-Roger J, Calatayud S, Hernandez C, Alos R, Hinojosa J, Apostolova N, Alvarez A, Barrachina MD (2014) Hypoxic macrophages impair autophagy in epithelial cells through Wnt1: relevance in IBD. Mucosal Immunol 7:929–938
Parada VD, De la Fuente MK, Landskron G, Gonzalez MJ, Quera R, Dijkstra G, Harmsen H, Faber KN, Hermoso MA (2019) Short chain fatty acids (SCFAs)-mediated gut epithelial and immune regulation and its relevance for inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Immunol 10:277
Wu H, Huang S, Chen Z, Liu W, Zhou X, Zhang D (2015) Hypoxia-induced autophagy contributes to the invasion of salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma through the HIF-1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 12:6467–6474
Zhang Y, Liu D, Hu H, Zhang P, Xie R, Cui W (2019) HIF-1α/BNIP3 signaling pathway-induced-autophagy plays protective role during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Pharmacother 120:109464
Zhou J, Yao W, Li C, Wu W, Li Q, Liu H (2017) Administration of follicle-stimulating hormone induces autophagy via upregulation of HIF-1α in mouse granulosa cells. Cell Death Dis 8:e3001
Sun Y, Xing X, Liu Q, Wang Z, Xin Y, Zhang P, Hu C, Liu Y (2015) Hypoxia-induced autophagy reduces radiosensitivity by the HIF-1α/miR-210/Bcl-2 pathway in colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol 46:750–756
Song L, Liu S, Zhang L, Yao H, Gao F, Xu D, Li Q (2016) MiR-21 modulates radiosensitivity of cervical cancer through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/HIF-1α feedback loop and the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Tumour Biol 37:12161–12168
Kelly CJ, Colgan SP (2016) Breathless in the gut: implications of luminal O2 for microbial pathogenicity. Cell Host Microbe 19:427–428
Acknowledgements
We thank professor Lin Chen for technical assistance with the HIF-1α∆IEC mice.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81873551 to HY), the Basic Science and Frontier Technology Project of Chongqing (cstc2017jcyjAX0234 to YQ), the Open Project of the State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burn and Combined Injury, Third Military Medical University(No. SKLKF201904 to YQ), and the Innovative Research Team of Ministry of Education of China (IRT_17R16 to HY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YQ and HY.
Analysis and interpretation: CZ, LZL, TML, LHS, and JHY.
Data collection: HDG, LCW, HBZ, PX, XF, and WDX.
Writing the article: CZ, YQ, and HY.
Final approval of the article: CZ, YQ, and HY.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All animal procedures were performed following the guidelines of the Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee Of the Third Military Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1379 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Li, L., Li, T. et al. SCFAs induce autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells and relieve colitis by stabilizing HIF-1α. J Mol Med 98, 1189–1202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01947-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01947-2