Abstract
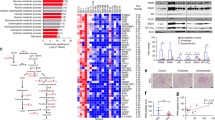
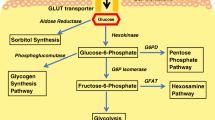
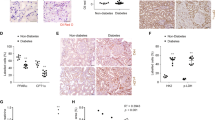
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) affects approximately 30–40% of patients with type 1 (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes (T2DM). It is a major cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) for the developed world. Hyperglycemia and genetics are major causal factors for the initiation and progression of DN. Multiple abnormalities in glucose and mitochondrial metabolism induced by diabetes likely contribute to the severity of DN. Recent clinical studies in people with extreme duration of T1DM (> 50 years, Joslin Medalist Study) have supported the importance of endogenous protective factors to neutralize the toxic effects of hyperglycemia on renal and other vascular tissues. Using renal glomeruli from these patients (namely Medalists) with and without DN, we have shown the importance of increased glycolytic flux in decreasing the accumulation of glucose toxic metabolites, improving mitochondrial function, survival of glomerular podocytes, and reducing glomerular pathology. Activation of a key glycolytic enzyme, pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), resulted in the normalization of renal hemodynamics and mitochondrial and glomerular dysfunction, leading to the mitigation of glomerular pathologies in several mouse models of DN.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breyer MD, Susztak K (2016) The next generation of therapeutics for chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15:568–588
Pambianco G, Costacou T, Ellis D, Becker DJ, Klein R, Orchard TJ (2006) The 30-year natural history of type 1 diabetes complications: the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study experience. Diabetes 55:1463–1469
Gregg EW, Li Y, Wang J, Burrows NR, Ali MK, Rolka D, Williams DE, Geiss L (2014) Changes in diabetes-related complications in the United States, 1990-2010. N Engl J Med 370:1514–1523
United States Renal Data System (2015) USRDS Annual Data Report. USRDS; 2015
Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, Davis M, Rand L, Siebert C (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329:977–986
de Boer IH, Sun W, Cleary PA, Lachin JM, Molitch ME, Steffes MW, Zinman B (2011) Intensive diabetes therapy and glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 365:2366–2376
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR (2003) Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int 63:225–232
Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Bain RP, Rohde RD (1993) The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 329:1456–1462
Strippoli GF, Craig M, Deeks JJ, Schena FP, Craig JC (2004) Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists on mortality and renal outcomes in diabetic nephropathy: systematic review. BMJ 329:828
Mauer M, Zinman B, Gardiner R, Suissa S, Sinaiko A, Strand T, Drummond K, Donnelly S, Goodyer P, Gubler MC, Klein R (2009) Renal and retinal effects of enalapril and losartan in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 361:40–51
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE (2015) Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 373:2117–2128
Dunlop M (2000) Aldose reductase and the role of the polyol pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl 77:S3–12
Wendt TM, Tanji N, Guo J, Kislinger TR, Qu W, Lu Y, Bucciarelli LG, Rong LL, Moser B, Markowitz GS, Stein G, Bierhaus A, Liliensiek B, Arnold B, Nawroth PP, Stern DM, D'Agati VD, Schmidt AM (2003) RAGE drives the development of glomerulosclerosis and implicates podocyte activation in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Pathol 162:1123–1137
Yao D, Brownlee M (2010) Hyperglycemia-induced reactive oxygen species increase expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and RAGE ligands. Diabetes 59:249–255
Wang SN, LaPage J, Hirschberg R (2000) Role of glomerular ultrafiltration of growth factors in progressive interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 57:1002–1014
Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, Yamagishi S, Matsumura T, Kaneda Y, Yorek MA, Beebe D, Oates PJ, Hammes HP, Giardino I, Brownlee M (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404:787–790
Doria A, Krolewski AS (2011) Diabetes: lowering serum uric acid levels to prevent kidney failure. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:495–496
Zhu Y, Usui HK, Sharma K (2007) Regulation of transforming growth factor beta in diabetic nephropathy: implications for treatment. Semin Nephrol 27:153–160
Sedeek M, Callera G, Montezano A, Gutsol A, Heitz F, Szyndralewiez C, Page P, Kennedy CR, Burns KD, Touyz RM, Hebert RL (2010) Critical role of Nox4-based NADPH oxidase in glucose-induced oxidative stress in the kidney: implications in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F1348–F1358
Koya D, Lee IK, Ishii H, Kanoh H, King GL (1997) Prevention of glomerular dysfunction in diabetic rats by treatment with d-alpha-tocopherol. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:426–435
Navarro-Gonzalez JF, Mora-Fernandez C, Muros de Fuentes M, Garcia-Perez J (2011) Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 7:327–340
Brosius FC, Tuttle KR, Kretzler M (2016) JAK inhibition in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 59:1624–1627
Ruiz S, Pergola PE, Zager RA, Vaziri ND (2013) Targeting the transcription factor Nrf2 to ameliorate oxidative stress and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 83:1029–1041
Shahzad K, Bock F, Al-Dabet MM, Gadi I, Nazir S, Wang H, Kohli S, Ranjan S, Mertens PR, Nawroth PP, Isermann B (2016) Stabilization of endogenous Nrf2 by minocycline protects against Nlrp3-inflammasome induced diabetic nephropathy. Sci Rep 6:34228
Sun W, Liu X, Zhang H, Song Y, Li T, Liu X, Liu Y, Guo L, Wang F, Yang T, Guo W, Wu J, Jin H, Wu H (2017) Epigallocatechin gallate upregulates NRF2 to prevent diabetic nephropathy via disabling KEAP1. Free Radic Biol Med 108:840–857
Keenan HA, Costacou T, Sun JK, Doria A, Cavellerano J, Coney J, Orchard TJ, Aiello LP, King GL (2007) Clinical factors associated with resistance to microvascular complications in diabetic patients of extreme disease duration: the 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care 30:1995–1997
Sun JK, Keenan HA, Cavallerano JD, Asztalos BF, Schaefer EJ, Sell DR, Strauch CM, Monnier VM, Doria A, Aiello LP, King GL (2011) Protection from retinopathy and other complications in patients with type 1 diabetes of extreme duration: the joslin 50-year medalist study. Diabetes Care 34:968–974
Tinsley LJ, Kupelian V, D'Eon SA, Pober D, Sun JK, King GL, Keenan HA (2017) Association of glycemic control with reduced risk for large-vessel disease after more than 50 years of type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 102:3704–3711
Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma K, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Zoungas S, Rossing P, Groop PH, Cooper ME (2015) Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1:15018
Fioretto P, Steffes MW, Brown DM, Mauer SM (1992) An overview of renal pathology in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in relationship to altered glomerular hemodynamics. Am J Kidney Dis 20:549–558
Osterby R (1992) Glomerular structural changes in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus: causes, consequences, and prevention. Diabetologia 35:803–812
Dalla Vestra M, Saller A, Mauer M, Fioretto P (2001) Role of mesangial expansion in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. J Nephrol 14(Suppl 4):S51–S57
Fioretto P, Mauer M (2007) Histopathology of diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27:195–207
Najafian B, Kim Y, Crosson JT, Mauer M (2003) Atubular glomeruli and glomerulotubular junction abnormalities in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:908–917
Najafian B, Mauer M (2012) Morphologic features of declining renal function in type 1 diabetes. Semin Nephrol 32:415–422
Gerich JE, Meyer C, Woerle HJ, Stumvoll M (2001) Renal gluconeogenesis: its importance in human glucose homeostasis. Diabetes Care 24:382–391
Castellino P, DeFronzo RA (1990) Glucose metabolism and the kidney. Semin Nephrol 10:458–463
Coward RJ, Welsh GI, Yang J, Tasman C, Lennon R, Koziell A, Satchell S, Holman GD, Kerjaschki D, Tavare JM, Mathieson PW, Saleem MA (2005) The human glomerular podocyte is a novel target for insulin action. Diabetes 54:3095–3102
Brownlee M (2005) The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54:1615–1625
Kramer H, Luke A, Bidani A, Cao G, Cooper R, McGee D (2005) Obesity and prevalent and incident CKD: the Hypertension Detection and Follow-Up Program. Am J Kidney Dis 46:587–594
Kuboki K, Jiang ZY, Takahara N, Ha SW, Igarashi M, Yamauchi T, Feener EP, Herbert TP, Rhodes CJ, King GL (2000) Regulation of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase gene expression in endothelial cells and in vivo: a specific vascular action of insulin. Circulation 101:676–681
Mima A, Kitada M, Geraldes P, Li Q, Matsumoto M, Mizutani K, Qi W, Li C, Leitges M, Rask-Madsen C, King GL (2012) Glomerular VEGF resistance induced by PKCdelta/SHP-1 activation and contribution to diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J 26:2963–2974
Hale LJ, Hurcombe J, Lay A, Santamaria B, Valverde AM, Saleem MA, Mathieson PW, Welsh GI, Coward RJ (2013) Insulin directly stimulates VEGF-A production in the glomerular podocyte. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305:F182–F188
Klisic J, Hu MC, Nief V, Reyes L, Fuster D, Moe OW, Ambuhl PM (2002) Insulin activates Na(+)/H(+) exchanger 3: biphasic response and glucocorticoid dependence. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F532–F539
Mima A, Ohshiro Y, Kitada M, Matsumoto M, Geraldes P, Li C, Li Q, White GS, Cahill C, Rask-Madsen C, King GL (2011) Glomerular-specific protein kinase C-beta-induced insulin receptor substrate-1 dysfunction and insulin resistance in rat models of diabetes and obesity. Kidney Int 79:883–896
Saudek CD, Boulter PR, Knopp RH, Arky RA (1974) Sodium retention accompanying insulin treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 23:240–246
Catena C, Cavarape A, Novello M, Giacchetti G, Sechi LA (2003) Insulin receptors and renal sodium handling in hypertensive fructose-fed rats. Kidney Int 64:2163–2171
Qi W, Keenan HA, Li Q, Ishikado A, Kannt A, Sadowski T, Yorek MA, Wu IH, Lockhart S, Coppey LJ, Pfenninger A, Liew CW, Qiang G, Burkart AM, Hastings S, Pober D, Cahill C, Niewczas MA, Israelsen WJ, Tinsley L, Stillman IE, Amenta PS, Feener EP, Vander Heiden MG, Stanton RC, King GL (2017) Pyruvate kinase M2 activation may protect against the progression of diabetic glomerular pathology and mitochondrial dysfunction. Nat Med 23:753–762
Kang HM, Ahn SH, Choi P, Ko YA, Han SH, Chinga F, Park AS, Tao J, Sharma K, Pullman J, Bottinger EP, Goldberg IJ, Susztak K (2015) Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat Med 21:37–46
Qi W, Chen X, Gilbert RE, Zhang Y, Waltham M, Schache M, Kelly DJ, Pollock CA (2007) High glucose-induced thioredoxin-interacting protein in renal proximal tubule cells is independent of transforming growth factor-beta1. Am J Pathol 171:744–754
Qi W, Poronnik P, Young B, Jackson CJ, Field MJ, Pollock CA (2004) Human cortical fibroblast responses to high glucose and hypoxia. Nephron Physiol 96:p121–p129
Artunc F, Schleicher E, Weigert C, Fritsche A, Stefan N, Haring HU (2016) The impact of insulin resistance on the kidney and vasculature. Nat Rev Nephrol 12:721–737
Kaiser N, Sasson S, Feener EP, Boukobza-Vardi N, Higashi S, Moller DE, Davidheiser S, Przybylski RJ, King GL (1993) Differential regulation of glucose transport and transporters by glucose in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Diabetes 42:80–89
Muzi M, Freeman SD, Burrows RC, Wiseman RW, Link JM, Krohn KA, Graham MM, Spence AM (2001) Kinetic characterization of hexokinase isoenzymes from glioma cells: implications for FDG imaging of human brain tumors. Nucl Med Biol 28:107–116
Vander Jagt DL, Kolb NS, Vander Jagt TJ, Chino J, Martinez FJ, Hunsaker LA, Royer RE (1995) Substrate specificity of human aldose reductase: identification of 4-hydroxynonenal as an endogenous substrate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1249:117–126
Hodgkinson AD, Sondergaard KL, Yang B, Cross DF, Millward BA, Demaine AG (2001) Aldose reductase expression is induced by hyperglycemia in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 60:211–218
Koya D, Jirousek MR, Lin YW, Ishii H, Kuboki K, King GL (1997) Characterization of protein kinase C beta isoform activation on the gene expression of transforming growth factor-beta, extracellular matrix components, and prostanoids in the glomeruli of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest 100:115–126
Brouwers O, Niessen PM, Haenen G, Miyata T, Brownlee M, Stehouwer CD, De Mey JG, Schalkwijk CG (2010) Hyperglycaemia-induced impairment of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in rat mesenteric arteries is mediated by intracellular methylglyoxal levels in a pathway dependent on oxidative stress. Diabetologia 53:989–1000
Kim KM, Kim YS, Jung DH, Lee J, Kim JS (2012) Increased glyoxalase I levels inhibit accumulation of oxidative stress and an advanced glycation end product in mouse mesangial cells cultured in high glucose. Exp Cell Res 318:152–159
Eid AA, Gorin Y, Fagg BM, Maalouf R, Barnes JL, Block K, Abboud HE (2009) Mechanisms of podocyte injury in diabetes: role of cytochrome P450 and NADPH oxidases. Diabetes 58:1201–1211
Igarashi M, Wakasaki H, Takahara N, Ishii H, Jiang ZY, Yamauchi T, Kuboki K, Meier M, Rhodes CJ, King GL (1999) Glucose or diabetes activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase via different pathways. J Clin Invest 103:185–195
Dugan LL, You YH, Ali SS, Diamond-Stanic M, Miyamoto S, DeCleves AE, Andreyev A, Quach T, Ly S, Shekhtman G, Nguyen W, Chepetan A, Le TP, Wang L, Xu M, Paik KP, Fogo A, Viollet B, Murphy A, Brosius F, Naviaux RK, Sharma K (2013) AMPK dysregulation promotes diabetes-related reduction of superoxide and mitochondrial function. J Clin Invest 123:4888–4899
Sharma K, Karl B, Mathew AV, Gangoiti JA, Wassel CL, Saito R, Pu M, Sharma S, You YH, Wang L, Diamond-Stanic M, Lindenmeyer MT, Forsblom C, Wu W, Ix JH, Ideker T, Kopp JB, Nigam SK, Cohen CD, Groop PH, Barshop BA, Natarajan L, Nyhan WL, Naviaux RK (2013) Metabolomics reveals signature of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 24:1901–1912
Long J, Badal SS, Ye Z, Wang Y, Ayanga BA, Galvan DL, Green NH, Chang BH, Overbeek PA, Danesh FR (2016) Long noncoding RNA Tug1 regulates mitochondrial bioenergetics in diabetic nephropathy. J Clin Invest 126:4205–4218
Frank RN (1994) The aldose reductase controversy. Diabetes 43:169–172
Lunt SY, Muralidhar V, Hosios AM, Israelsen WJ, Gui DY, Newhouse L, Ogrodzinski M, Hecht V, Xu K, Acevedo PN, Hollern DP, Bellinger G, Dayton TL, Christen S, Elia I, Dinh AT, Stephanopoulos G, Manalis SR, Yaffe MB, Andrechek ER, Fendt SM, Vander Heiden MG (2015) Pyruvate kinase isoform expression alters nucleotide synthesis to impact cell proliferation. Mol Cell 57:95–107
Cooper ME, El-Osta A (2010) Epigenetics: mechanisms and implications for diabetic complications. Circ Res 107:1403–1413
Chen Z, Miao F, Paterson AD, Lachin JM, Zhang L, Schones DE, Wu X, Wang J, Tompkins JD, Genuth S, Braffett BH, Riggs AD, Natarajan R (2016) Epigenomic profiling reveals an association between persistence of DNA methylation and metabolic memory in the DCCT/EDIC type 1 diabetes cohort. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E3002–E3011
El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao D, Pocai A, Jones PL, Roeder RG, Cooper ME, Brownlee M (2008) Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia. J Exp Med 205:2409–2417
Young JI, Zuchner S, Wang G (2015) Regulation of the epigenome by vitamin C. Annu Rev Nutr 35:545–564
Hayden MR, Sowers JR, Tyagi SC (2005) The central role of vascular extracellular matrix and basement membrane remodeling in metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: the matrix preloaded. Cardiovasc Diabetol 4:9
Siperstein MD, Unger RH, Madison LL (1968) Studies of muscle capillary basement membranes in normal subjects, diabetic, and prediabetic patients. J Clin Invest 47:1973–1999
Funding
W.Q. was supported by JDRF Fellowship. G.L.K. was funded by NIH 1DP3DK112192-01, NIH P30DK036836, JDRF 8-2005-358, JDRF 18-2008-363, and JDRF 17-2011-47. This work was supported in part by Mary K. Iacocca Fellowship provided by the Iacocca Foundation (D.G.). D.G. was also supported by grants from the Medical Society of Finland (Finska Läkaresällskapet), the Wilhelm and Else Stockmann Foundation, the Biomedicum Helsinki Foundation, the Finnish Medical Foundation, the Swedish Cultural Foundation in Finland, and the Dorothea Olivia, Karl Walter och Jarl Walter Perkléns Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, W., Li, Q., Gordin, D. et al. Preservation of renal function in chronic diabetes by enhancing glomerular glucose metabolism. J Mol Med 96, 373–381 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1630-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1630-0