Abstract
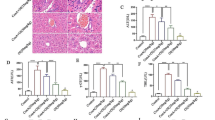
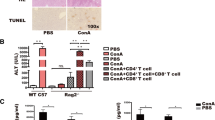
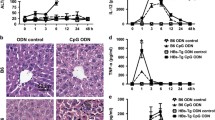
IL-33, a recently described member of the IL-1 family, has been identified as a cytokine endowed with pro-Th2 type functions. To date, there are only limited data on its role in physiological and pathological hepatic immune responses. In this study, we examined the role of IL-33 in immune-mediated liver injury by exploring the model of concanavalin A (Con A)-induced hepatitis. We observed that the level of IL-33 expression in the liver was dramatically increased at 12 h after Con A injection. Meanwhile, ST2L, the receptor of IL-33, was significantly up-regulated in lymphocytes including T and natural killer T (NKT) cells, especially in NKT cells. Moreover, administration of recombinant IL-33 exacerbated Con A-induced hepatitis, while pretreatment of IL-33-blocking antibody or psST2-Fc plasmids showed a protective effect probably by inhibiting the activation of late stage of T cells and NKT cells and also decreasing the production of the cytokine IFN-γ. Furthermore, depletion of NKT cells abolished the protective effect of IL-33-blocking antibody, and IL-33 failed to exacerbate Con A-induced hepatitis in IFN-γ−/− mice. These data suggested the critical roles of NKT cells and IFN-γ in the involvement of IL-33 in Con A-induced hepatitis. Blockade of IL-33 may represent a novel therapeutic strategy through IL-33/ST2L signal to prevent immune-mediated liver injury.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest 90:196–203
Torisu T, Nakaya M, Watanabe S, Hashimoto M, Yoshida H, Chinen T, Yoshida R, Okamoto F, Hanada T, Torisu K et al (2008) Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 protects mice against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis by inhibiting apoptosis. Hepatology 47:1644–1654
Nakashima H, Kinoshita M, Nakashima M, Habu Y, Shono S, Uchida T, Shinomiya N, Seki S (2008) Superoxide produced by Kupffer cells is an essential effector in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Hepatology 48:1979–1988
Louis H, Le Moine A, Flamand V, Nagy N, Quertinmont E, Paulart F, Abramowicz D, Le Moine O, Goldman M, Deviere J (2002) Critical role of interleukin 5 and eosinophils in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 122:2001–2010
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Van Kaer L, Matsuda H, Yagita H, Okumura K (2000) Critical contribution of liver natural killer T cells to a murine model of hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5498–5503
Jaruga B, Hong F, Sun R, Radaeva S, Gao B (2003) Crucial role of IL-4/STAT6 in T cell-mediated hepatitis: up-regulating eotaxins and IL-5 and recruiting leukocytes. J Immunol 171:3233–3244
Mizuhara H, O’Neill E, Seki N, Ogawa T, Kusunoki C, Otsuka K, Satoh S, Niwa M, Senoh H, Fujiwara H (1994) T cell activation-associated hepatic injury: mediation by tumor necrosis factors and protection by interleukin 6. J Exp Med 179:1529–1537
Kusters S, Gantner F, Kunstle G, Tiegs G (1996) Interferon gamma plays a critical role in T cell-dependent liver injury in mice initiated by concanavalin A. Gastroenterology 111:462–471
Kaneko Y, Harada M, Kawano T, Yamashita M, Shibata Y, Gejyo F, Nakayama T, Taniguchi M (2000) Augmentation of Valpha14 NKT cell-mediated cytotoxicity by interleukin 4 in an autocrine mechanism resulting in the development of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Exp Med 191:105–114
Li B, Sun R, Wei H, Gao B, Tian Z (2006) Interleukin-15 prevents concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice via NKT cell-dependent mechanism. Hepatology 43:1211–1219
Radaeva S, Sun R, Pan HN, Hong F, Gao B (2004) Interleukin 22 (IL-22) plays a protective role in T cell-mediated murine hepatitis: IL-22 is a survival factor for hepatocytes via STAT3 activation. Hepatology 39:1332–1342
Van Kaer L (2007) NKT cells: T lymphocytes with innate effector functions. Curr Opin Immunol 19:354–364
Mercer JC, Ragin MJ, August A (2005) Natural killer T cells: rapid responders controlling immunity and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1337–1343
Wu L, Van Kaer L (2009) Natural killer T cells and autoimmune disease. Curr Mol Med 9:4–14
Xu D, Jiang HR, Kewin P, Li Y, Mu R, Fraser AR, Pitman N, Kurowska-Stolarska M, McKenzie AN, McInnes IB et al (2008) IL-33 exacerbates antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10913–10918
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, H’Ng SC, Pitman N, Xu D, McKenzie A, Liew FY, Melendez AJ (2009) The cytokine interleukin-33 mediates anaphylactic shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:9773–9778
Liew FY, Pitman NI, McInnes IB (2010) Disease-associated functions of IL-33: the new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat Rev Immunol 10:103–110
Prefontaine D, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Foley S, Audusseau S, Olivenstein R, Halayko AJ, Lemiere C, Martin JG, Hamid Q (2009) Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: evidence of expression by airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol 183:5094–5103
Marvie P, Lisbonne M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Turlin B, Preisser L, Bourd-Boittin K, Theret N, Gascan H, Piquet-Pellorce C et al (2010) Interleukin-33 overexpression is associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans. J Cell Mol Med 14:1726–1739
Le Goffic R, Arshad MI, Rauch M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Delmas B, Piquet-Pellorce C, Samson M (2011) Infection with influenza virus induces IL-33 in murine lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45:1125–1132
Moussion C, Ortega N, Girard JP (2008) The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: a novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS One 3:e3331
Nile CJ, Barksby E, Jitprasertwong P, Preshaw PM, Taylor JJ (2010) Expression and regulation of interleukin-33 in human monocytes. Immunology 130:172–180
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X et al (2005) IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 23:479–490
Arend WP, Palmer G, Gabay C (2008) IL-1, IL-18, and IL-33 families of cytokines. Immunol Rev 223:20–38
Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA (2007) IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J Immunol 179:2551–2555
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A, Tominaga S (2007) Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic airway inflammation. J Biol Chem 282:26369–26380
Bourgeois E, Van LP, Samson M, Diem S, Barra A, Roga S, Gombert JM, Schneider E, Dy M, Gourdy P et al (2009) The pro-Th2 cytokine IL-33 directly interacts with invariant NKT and NK cells to induce IFN-gamma production. Eur J Immunol 39:1046–1055
Arshad MI, Rauch M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Julia V, Leite-de-Moraes MC, Lucas-Clerc C, Piquet-Pellorce C, Samson M (2011) NKT cells are required to induce high IL-33 expression in hepatocytes during ConA-induced acute hepatitis. Eur J Immunol 41:2341–2348
Yin H, Li XY, Jin XB, Zhang BB, Gong Q, Yang H, Zheng F, Gong FL, Zhu JY (2010) IL-33 prolongs murine cardiac allograft survival through induction of TH2-type immune deviation. Transplantation 89:1189–1197
Yin H, Huang BJ, Yang H, Huang YF, Xiong P, Zheng F, Chen XP, Chen YF, Gong FL (2006) Pretreatment with soluble ST2 reduces warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 351:940–946
Liu W, Hou Y, Chen H, Wei H, Lin W, Li J, Zhang M, He F, Jiang Y (2011) Sample preparation method for isolation of single-cell types from mouse liver for proteomic studies. Proteomics 11:3556–3564. doi:10.1002/pmic.201100157
Gong Q, Zhang H, Li JH, Duan LH, Zhong S, Kong XL, Zheng F, Tan Z, Xiong P, Chen G et al (2010) High-mobility group box 1 exacerbates concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury in mice. J Mol Med (Berl) 88:1289–1298
Duan L, Wang CY, Chen J, Gong Q, Zhu P, Zheng F, Tan Z, Gong F, Fang M (2010) High-mobility group box 1 promotes early acute allograft rejection by enhancing IL-6-dependent Th17 alloreactive response. Lab Invest 91:43–53
Haraldsen G, Balogh J, Pollheimer J, Sponheim J, Kuchler AM (2009) Interleukin-33—cytokine of dual function or novel alarmin? Trends Immunol 30:227–233
Wang J, Sun R, Wei H, Dong Z, Gao B, Tian Z (2006) Poly I:C prevents T cell-mediated hepatitis via an NK-dependent mechanism. J Hepatol 44:446–454
Dong Z, Wei H, Sun R, Tian Z (2007) The roles of innate immune cells in liver injury and regeneration. Cell Mol Immunol 4:241–252
Kunstle G, Hentze H, Germann PG, Tiegs G, Meergans T, Wendel A (1999) Concanavalin A hepatotoxicity in mice: tumor necrosis factor-mediated organ failure independent of caspase-3-like protease activation. Hepatology 30:1241–1251
Tagawa Y, Sekikawa K, Iwakura Y (1997) Suppression of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in IFN-gamma(-/-) mice, but not in TNF-alpha(−/−) mice: role for IFN-gamma in activating apoptosis of hepatocytes. J Immunol 159:1418–1428
Tamaru M, Nishioji K, Kobayashi Y, Watanabe Y, Itoh Y, Okanoue T, Murai M, Matsushima K, Narumi S (2000) Liver-infiltrating T lymphocytes are attracted selectively by IFN-inducible protein-10. Cytokine 12:299–308
Volarevic V, Mitrovic M, Milovanovic M, Zelen I, Nikolic I, Mitrovic S, Pejnovic N, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML (2012) Protective role of IL-33/ST2 axis in Con A-induced hepatitis. J Hepatol 56(1):26–33
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81072440) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant 2007CB512402).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Duan, L., Xiong, A. et al. Blockade of IL-33 ameliorates Con A-induced hepatic injury by reducing NKT cell activation and IFN-γ production in mice. J Mol Med 90, 1505–1515 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0938-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0938-4