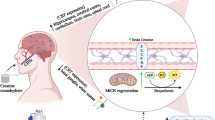
Abstract
The brain lacks a classic lymphatic drainage system. How it is cleansed of damaged proteins, cellular debris, and molecular by-products has remained a mystery for decades. Recent discoveries have identified a hybrid system that includes cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-filled perivascular spaces and classic lymph vessels in the dural covering of the brain and spinal cord that functionally cooperate to remove toxic and non-functional trash from the brain. These two components functioning together are referred to as the glymphatic system. We propose that the high levels of melatonin secreted by the pineal gland directly into the CSF play a role in flushing pathological molecules such as amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) from the brain via this network. Melatonin is a sleep-promoting agent, with waste clearance from the CNS being highest especially during slow wave sleep. Melatonin is also a potent and versatile antioxidant that prevents neural accumulation of oxidatively-damaged molecules which contribute to neurological decline. Due to its feedback actions on the suprachiasmatic nucleus, CSF melatonin rhythm functions to maintain optimal circadian rhythmicity, which is also critical for preserving neurocognitive health. Melatonin levels drop dramatically in the frail aged, potentially contributing to neurological failure and dementia. Melatonin supplementation in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) defers Aβ accumulation, enhances its clearance from the CNS, and prolongs animal survival. In AD patients, preliminary data show that melatonin use reduces neurobehavioral signs such as sundowning. Finally, melatonin controls the mitotic activity of neural stem cells in the subventricular zone, suggesting its involvement in neuronal renewal.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Klostranec JM, Vucevic D, Bhatia KD, Kortman HGJ, Krings T, Murphy KP et al (2021) Current concepts in intracranial interstitial fluid transport and the glymphatic system: part II-imaging techniques and clinical applications. Radiology 301:516–532. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2021204088
Liu J, Guo Y, Zhang C, Zeng Y, Luo Y, Wang G (2021) Clearance systems in the brain, from structure to function. Front Cell Neurosci 15:729706. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.729706
Yankova G, Bogomyakova O, Tulupov A (2021) The glymphatic system and meningeal lymphatics of the brain: new understanding of brain clearance. Rev Neurosci 32:693–705. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2020-0106
Gordleeva S, Kanakov O, Ivanchenko M, Zaikin A, Franceschi C (2020) Brain aging and garbage cleaning : modelling the role of sleep, glymphatic system, and microglia senescence in the propagation of inflammaging. Semin Immunopathol 42:647–665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-020-00816-x
Kylkilahti TM, Berends E, Ramos M, Shanbhag NC, Toger J, Markenroth Bloch K et al (2021) Achieving brain clearance and preventing neurodegenerative diseases-A glymphatic perspective. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 41:2137–2149. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X20982388
Yamada S, DePasquale M, Patlak CS, Cserr HF (1991) Albumin outflow into deep cervical lymph from different regions of rabbit brain. Am J Physiol 261:H1197-1204. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.H1197
Benveniste H, Lee H, Ozturk B, Chen X, Koundal S, Vaska P et al (2021) Glymphatic cerebrospinal fluid and solute transport quantified by MRI and PET imaging. Neuroscience 474:63–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.11.014
Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, Wardlaw JM (2015) Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability. Cerebrovasc Dis 39:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1159/000375153
Hladky SB, Barrand MA (2022) The glymphatic hypothesis: the theory and the evidence. Fluids Barriers CNS 19:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12987-021-00282-z
Hedlund L, Lischko MM, Rollag MD, Niswender GD (1977) Melatonin: daily cycle in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of calves. Science 195:686–687. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.841305
Reppert SM, Coleman RJ, Heath HW, Keutmann HT (1982) Circadian properties of vasopressin and melatonin rhythms in cat cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Physiol 243:E489-498. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.6.E489
Skinner DC, Malpaux B (1999) High melatonin concentrations in third ventricular cerebrospinal fluid are not due to Galen vein blood recirculating through the choroid plexus. Endocrinology 140:4399–4405. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.140.10.7074
Bitar RD, Torres-Garza JL, Reiter RJ, Phillips WT (2021) Neural glymphatic system: clinical implications and potential importance of melatonin. Melatonin Res 4:551–565. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr112500111
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Rosales-Corral S, de Mange J, Phillips WT, Tan DX et al (2022) Melatonin in ventricular and subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid: its function in the neural glymphatic network and biological significance for neurocognitive health. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 605:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.03.025
Hardeland R (2015) Melatonin and circadian oscillators in aging–a dynamic approach to the multiply connected players. Interdiscip Top Gerontol 40:128–140. https://doi.org/10.1159/000364975
Perez-Lloret S, Cardinali DP (2021) Melatonin as a chronobiotic and cytoprotective agent in Parkinson’s disease. Front Pharmacol 12:650597. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.650597
Spector R, Robert Snodgrass S, Johanson CE (2015) A balanced view of the cerebrospinal fluid composition and functions: focus on adult humans. Exp Neurol 273:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.07.027
Quintela T, Goncalves I, Silva M, Duarte AC, Guedes P, Andrade K et al (2018) Choroid plexus is an additional source of melatonin in the brain. J Pineal Res 65:e12528. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12528
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Reiter RJ (2016) CSF generation by pineal gland results in a robust melatonin circadian rhythm in the third ventricle as an unique light/dark signal. Med Hypotheses 86:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2015.11.018
Brown PD, Davies SL, Speake T, Millar ID (2004) Molecular mechanisms of cerebrospinal fluid production. Neuroscience 129:957–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.003
Tricoire H, Locatelli A, Chemineau P, Malpaux B (2002) Melatonin enters the cerebrospinal fluid through the pineal recess. Endocrinology 143:84–90. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.143.1.8585
Mestre H, Mori Y, Nedergaard M (2020) The Brain’s glymphatic system: current controversies. Trends Neurosci 43:458–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2020.04.003
Lewis LD (2021) The interconnected causes and consequences of sleep in the brain. Science 374:564–568. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abi8375
Vaughan GM, Pelham RW, Pang SF, Loughlin LL, Wilson KM, Sandock KL et al (1976) Nocturnal elevation of plasma melatonin and urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in young men: attempts at modification by brief changes in environmental lighting and sleep and by autonomic drugs. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 42:752–764. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-42-4-752
Korf HW (2018) Signaling pathways to and from the hypophysial pars tuberalis, an important center for the control of seasonal rhythms. Gen Comp Endocrinol 258:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.05.011
Wehr TA (1991) The durations of human melatonin secretion and sleep respond to changes in daylength (photoperiod). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 73:1276–1280. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-73-6-1276
Hull JT, Czeisler CA, Lockley SW (2018) Suppression of melatonin secretion in totally visually blind people by ocular exposure to white light: clinical characteristics. Ophthalmology 125:1160–1171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.01.036
Skene DJ, Arendt J (2007) Circadian rhythm sleep disorders in the blind and their treatment with melatonin. Sleep Med 8:651–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2006.11.013
Barboni MTS, Bueno C, Nagy BV, Maia PL, Vidal KSM, Alves RC et al (2018) Melanopsin system dysfunction in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59:362–369. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-22612
Potocki L, Glaze D, Tan DX, Park SS, Kashork CD, Shaffer LG et al (2000) Circadian rhythm abnormalities of melatonin in Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Med Genet 37:428–433. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.37.6.428
Lockley SW, Arendt J, Skene DJ (2007) Visual impairment and circadian rhythm disorders. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 9:301–314
Kanematsu N, Mori Y, Hayashi S, Hoshino K (1989) Presence of a distinct 24-hour melatonin rhythm in the ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of the goat. J Pineal Res 7:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1989.tb00662.x
Leston J, Harthe C, Mottolese C, Mertens P, Sindou M, Claustrat B (2015) Is pineal melatonin released in the third ventricle in humans? A study in movement disorders. Neurochirurgie 61:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2013.04.004
Legros C, Chesneau D, Boutin JA, Barc C, Malpaux B (2014) Melatonin from cerebrospinal fluid but not from blood reaches sheep cerebral tissues under physiological conditions. J Neuroendocrinol 26:151–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12134
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Kim SJ, Cruz MH (2014) Delivery of pineal melatonin to the brain and SCN: role of canaliculi, cerebrospinal fluid, tanycytes and Virchow-Robin perivascular spaces. Brain Struct Funct 219:1873–1887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0719-7
Bruce J, Tamarkin L, Riedel C, Markey S, Oldfield E (1991) Sequential cerebrospinal fluid and plasma sampling in humans: 24-hour melatonin measurements in normal subjects and after peripheral sympathectomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:819–823. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-72-4-819
Iliff JJ, Lee H, Yu M, Feng T, Logan J, Nedergaard M et al (2013) Brain-wide pathway for waste clearance captured by contrast-enhanced MRI. J Clin Invest 123:1299–1309. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI67677
Tricoire H, Malpaux B, Moller M (2003) Cellular lining of the sheep pineal recess studied by light-, transmission-, and scanning electron microscopy: morphologic indications for a direct secretion of melatonin from the pineal gland to the cerebrospinal fluid. J Comp Neurol 456:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.10477
Moore RY, Rapport RL (1971) Pineal and gonadal function in the rat following cervical sympathectomy. Neuroendocrinology 7:361–374. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121983
Reiter RJ, Hester RJ (1966) Interrelationships of the pineal gland, the superior cervical ganglia and the photoperiod in the regulation of the endocrine systems of hamsters. Endocrinology 79:1168–1170. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-79-6-1168
Acuna-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Venegas C, Diaz-Casado ME, Lima-Cabello E, Lopez LC et al (2014) Extrapineal melatonin: sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell Mol Life Sci 71:2997–3025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1579-2
Loh D, Reiter RJ (2021) Melatonin: regulation of biomolecular condensates in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxidants (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10091483
Pablos MI, Agapito MT, Gutierrez R, Recio JM, Reiter RJ, Barlow-Walden L et al (1995) Melatonin stimulates the activity of the detoxifying enzyme glutathione peroxidase in several tissues of chicks. J Pineal Res 19:111–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1995.tb00178.x
Reiter RJ, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Sainz RM, Alatorre-Jimenez M, Qin L (2016) Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers. J Pineal Res 61:253–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12360
Wang J, Xia Z, Sheng P, Rui Y, Cao J, Zhang J et al (2022) Targeting MicroRNA-144/451-AKT-GSK3beta axis affects the proliferation and differentiation of radial glial cells in the mouse hippocampal dentate gyrus. ACS Chem Neurosci 13:897–909. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00636
Shi C, Zeng J, Li Z, Chen Q, Hang W, Xia L et al (2018) Melatonin mitigates kainic acid-induced neuronal tau hyperphosphorylation and memory deficits through alleviating ER stress. Front Mol Neurosci 11:5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00005
Zhang Y, Chen X, Zhao Y, Ponnusamy M, Liu Y (2017) The role of ubiquitin proteasomal system and autophagy-lysosome pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Neurosci 28:861–868. https://doi.org/10.1515/revneuro-2017-0013
Chinchalongporn V, Shukla M, Govitrapong P (2018) Melatonin ameliorates Abeta42 -induced alteration of betaAPP-processing secretases via the melatonin receptor through the Pin1/GSK3beta/NF-kappaB pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. J Pineal Res 64:e12470. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12470
Matsubara E, Bryant-Thomas T, Pacheco Quinto J, Henry TL, Poeggeler B, Herbert D et al (2003) Melatonin increases survival and inhibits oxidative and amyloid pathology in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 85:1101–1108. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01654.x
Rathnasamy G, Ling EA, Kaur C (2014) Therapeutic implications of melatonin in cerebral edema. Histol Histopathol 29:1525–1538. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-29.1525
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M et al (2013) Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 342:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Fultz NE, Bonmassar G, Setsompop K, Stickgold RA, Rosen BR, Polimeni JR et al (2019) Coupled electrophysiological, hemodynamic, and cerebrospinal fluid oscillations in human sleep. Science 366:628–631. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax5440
Holth JK, Fritschi SK, Wang C, Pedersen NP, Cirrito JR, Mahan TE et al (2019) The sleep-wake cycle regulates brain interstitial fluid tau in mice and CSF tau in humans. Science 363:880–884. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav2546
Shokri-Kojori E, Wang GJ, Wiers CE, Demiral SB, Guo M, Kim SW et al (2018) Beta-Amyloid accumulation in the human brain after one night of sleep deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:4483–4488. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721694115
Hablitz LM, Vinitsky HS, Sun Q, Staeger FF, Sigurdsson B, Mortensen KN et al (2019) Increased glymphatic influx is correlated with high EEG delta power and low heart rate in mice under anesthesia. Sci Adv 5:eaav5447. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav5447
Iadecola C (2017) The neurovascular unit coming of age: a journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron 96:17–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.07.030
Mateo C, Knutsen PM, Tsai PS, Shih AY, Kleinfeld D (2017) Entrainment of arteriole vasomotor fluctuations by neural activity is a basis of blood-oxygenation-level-dependent “resting-state” connectivity. Neuron 96:936-948e933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.012
van Veluw SJ, Hou SS, Calvo-Rodriguez M, Arbel-Ornath M, Snyder AC, Frosch MP et al (2020) Vasomotion as a driving force for paravascular clearance in the awake mouse brain. Neuron 105:549-561e545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.10.033
Kress BT, Iliff JJ, Xia M, Wang M, Wei HS, Zeppenfeld D et al (2014) Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann Neurol 76:845–861. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24271
Wolkove N, Elkholy O, Baltzan M, Palayew M (2007) Sleep and aging: 1. Sleep disorders commonly found in older people. CMAJ 176:1299–1304. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.060792
Reiter RJ, Richardson BA, Johnson LY, Ferguson BN, Dinh DT (1980) Pineal melatonin rhythm: reduction in aging Syrian hamsters. Science 210:1372–1373. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7434032
Sack RL, Lewy AJ, Erb DL, Vollmer WM, Singer CM (1986) Human melatonin production decreases with age. J Pineal Res 3:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1986.tb00760.x
Grigg-Damberger M, Foldvary-Schaefer N (2022) Sleep biomarkers help predict the development of Alzheimer disease. J Clin Neurophysiol. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNP.0000000000000818
Nous A, Engelborghs S, Smolders I (2021) Melatonin levels in the Alzheimer’s disease continuum: a systematic review. Alzheimers Res Ther 13:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-021-00788-6
Wu YH, Swaab DF (2005) The human pineal gland and melatonin in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J Pineal Res 38:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00196.x
Chen D, Zhang T, Lee TH (2020) Cellular mechanisms of melatonin: insight from neurodegenerative diseases. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081158
Shukla M, Govitrapong P, Boontem P, Reiter RJ, Satayavivad J (2017) Mechanisms of melatonin in alleviating Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 15:1010–1031. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X15666170313123454
Cardinali DP (2021) Melatonin and healthy aging. Vitam Horm 115:67–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2020.12.004
Mishima K, Tozawa T, Satoh K, Matsumoto Y, Hishikawa Y, Okawa M (1999) Melatonin secretion rhythm disorders in patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer’s type with disturbed sleep-waking. Biol Psychiatry 45:417–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-3223(97)00510-6
Skene DJ, Vivien-Roels B, Sparks DL, Hunsaker JC, Pevet P, Ravid D et al (1990) Daily variation in the concentration of melatonin and 5-methoxytryptophol in the human pineal gland: effect of age and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 528:170–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(90)90214-v
He H, Dong W, Huang F (2010) Anti-amyloidogenic and anti-apoptotic role of melatonin in Alzheimer disease. Curr Neuropharmacol 8:211–217. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015910792246137
Liu RY, Zhou JN, van Heerikhuize J, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (1999) Decreased melatonin levels in postmortem cerebrospinal fluid in relation to aging, Alzheimer’s disease, and apolipoprotein E-epsilon4/4 genotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84:323–327. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.1.5394
Wu YH, Feenstra MG, Zhou JN, Liu RY, Torano JS, Van Kan HJ et al (2003) Molecular changes underlying reduced pineal melatonin levels in Alzheimer disease: alterations in preclinical and clinical stages. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:5898–5906. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-030833
Galano A, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2013) On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin’s metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J Pineal Res 54:245–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12010
Bromme HJ, Ebelt H, Peschke D, Peschke E (1999) Alloxan acts as a prooxidant only under reducing conditions: influence of melatonin. Cell Mol Life Sci 55:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s000180050305
Hardeland R (2021) Melatonin, its metabolites and their interference with reactive nitrogen compounds. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134105
Tan D-X, Chen LD, Poeggeler B, Manchester LC, Reiter R (1993) Melatonin: a potent endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J 1:57–60
Agapito MT, Redondo I, Plaza R, Lopez-Burillo S, Recio JM, Pablos MI (1999) Relationships between melatonin, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and catalase. Endogenous rhythms on cerebral cortex in Gallus domesticus. Adv Exp Med Biol 460:377–381
Ma Z, Xin Z, Di W, Yan X, Li X, Reiter RJ et al (2017) Melatonin and mitochondrial function during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:3989–3998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2618-6
Ikram M, Park HY, Ali T, Kim MO (2021) Melatonin as a potential regulator of oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation: mechanisms and implications for the management of brain injury-induced neurodegeneration. J Inflamm Res 14:6251–6264. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S334423
Mukherjee R, Desai F, Singh S, Gajaria T, Singh PK, Baxi DB et al (2010) Melatonin protects against alterations in hippocampal cholinergic system, trace metals and oxidative stress induced by gestational and lactational exposure to cadmium. Excli J 9:119–132
Salman M, Kaushik P, Tabassum H, Parvez S (2021) melatonin provides neuroprotection following traumatic brain injury-promoted mitochondrial perturbation in Wistar rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41:765–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00884-5
Abolhasanpour N, Alihosseini S, Golipourkhalili S, Badalzadeh R, Mahmoudi J, Hosseini L (2021) Effect of melatonin on endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial crosstalk in stroke. Arch Med Res 52:673–682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.04.002
Reiter RJ, Ma Q, Sharma R (2020) Melatonin in mitochondria: mitigating clear and present dangers. Physiology (Bethesda) 35:86–95. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00034.2019
Ebanks B, Chakrabarti L (2022) Mitochondrial ATP synthase is a target of oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Mol Biosci 9:854321. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.854321
Lahiri DK (1999) Melatonin affects the metabolism of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in different cell types. J Pineal Res 26:137–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1999.tb00575.x
Pappolla M, Bozner P, Soto C, Shao H, Robakis NK, Zagorski M et al (1998) Inhibition of Alzheimer beta-fibrillogenesis by melatonin. J Biol Chem 273:7185–7188. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.13.7185
Pappolla MA, Sos M, Omar RA, Bick RJ, Hickson-Bick DL, Reiter RJ et al (1997) Melatonin prevents death of neuroblastoma cells exposed to the Alzheimer amyloid peptide. J Neurosci 17:1683–1690
Pappolla MA, Chyan YJ, Poeggeler B, Frangione B, Wilson G, Ghiso J et al (2000) An assessment of the antioxidant and the antiamyloidogenic properties of melatonin: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 107:203–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050018
Pappolla MA, Simovich MJ, Bryant-Thomas T, Chyan YJ, Poeggeler B, Dubocovich M et al (2002) The neuroprotective activities of melatonin against the Alzheimer beta-protein are not mediated by melatonin membrane receptors. J Pineal Res 32:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079x.2002.1o838.x
Pappolla MA, Matsubara E, Vidal R, Pacheco-Quinto J, Poeggeler B, Zagorski M et al (2018) Melatonin treatment enhances abeta lymphatic clearance in a transgenic mouse model of amyloidosis. Curr Alzheimer Res 15:637–642. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567205015666180411092551
Hatterer E, Touret M, Belin MF, Honnorat J, Nataf S (2008) Cerebrospinal fluid dendritic cells infiltrate the brain parenchyma and target the cervical lymph nodes under neuroinflammatory conditions. PLoS One 3:e3321. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003321
Kozhevnikova OS, Korbolina EE, Stefanova NA, Muraleva NA, Orlov YL, Kolosova NG (2013) Association of AMD-like retinopathy development with an Alzheimer’s disease metabolic pathway in OXYS rats. Biogerontology 14:753–762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9439-2
Rudnitskaya EA, Maksimova KY, Muraleva NA, Logvinov SV, Yanshole LV, Kolosova NG et al (2015) Beneficial effects of melatonin in a rat model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Biogerontology 16:303–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9547-7
Scholtens RM, van Munster BC, van Kempen MF, de Rooij SE (2016) Physiological melatonin levels in healthy older people: a systematic review. J Psychosom Res 86:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2016.05.005
Hardeland R (2019) Aging, melatonin, and the pro- and anti-inflammatory networks. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051223
Mehrzadi S, Hemati K, Reiter RJ, Hosseinzadeh A (2020) Mitochondrial dysfunction in age-related macular degeneration: melatonin as a potential treatment. Expert Opin Ther Targets 24:359–378. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2020.1737015
Chen C, Yang C, Wang J, Huang X, Yu H, Li S et al (2021) Melatonin ameliorates cognitive deficits through improving mitophagy in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Pineal Res 71:e12774. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12774
Mihardja M, Roy J, Wong KY, Aquili L, Heng BC, Chan YS et al (2020) Therapeutic potential of neurogenesis and melatonin regulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1478:43–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14436
Da Mesquita S, Louveau A, Vaccari A, Smirnov I, Cornelison RC, Kingsmore KM et al (2018) Functional aspects of meningeal lymphatics in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 560:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0368-8
McClean C, Davison GW (2022) Circadian clocks, redox homeostasis, and exercise: time to connect the dots? Antioxidants (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11020256
Gilley RR (2022) The role of sleep in cognitive function: the value of a good night’s rest. Clin EEG Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1177/15500594221090067
Poeggeler B (2005) Melatonin, aging, and age-related diseases: perspectives for prevention, intervention, and therapy. Endocrine 27:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:27:2:201
Li L, Ding G, Zhang L, Davoodi-Bojd E, Chopp M, Li Q et al (2022) Aging-related alterations of glymphatic transport in rat: in vivo magnetic resonance imaging and kinetic study. Front Aging Neurosci 14:841798. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.841798
Cardinali DP, Esquifino AI, Srinivasan V, Pandi-Perumal SR (2008) Melatonin and the immune system in aging. NeuroImmunoModulation 15:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1159/000156470
Prodhan A, Cavestro C, Kamal MA, Islam MA (2021) Melatonin and sleep disturbances in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 20:736–754. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527320666210804155617
Novais AA, Chuffa LGA, Zuccari D, Reiter RJ (2021) Exosomes and melatonin: where their destinies intersect. Front Immunol 12:692022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.692022
Cho JH, Bhutani S, Kim CH, Irwin MR (2021) Anti-inflammatory effects of melatonin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Brain Behav Immun 93:245–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.034
Cardinali DP, Vigo DE, Olivar N, Vidal MF, Furio AM, Brusco LI (2012) Therapeutic application of melatonin in mild cognitive impairment. Am J Neurodegener Dis 1:280–291
Chang YT, Chang WN, Tsai NW, Huang CC, Kung CT, Su YJ et al (2014) The roles of biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidant in Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int 2014:182303. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/182303
Liu WC, Wang X, Zhang X, Chen X, Jin X (2017) Melatonin supplementation, a strategy to prevent neurological diseases through maintaining integrity of blood brain barrier in old people. Front Aging Neurosci 9:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2017.00165
Mukda S, Panmanee J, Boontem P, Govitrapong P (2016) Melatonin administration reverses the alteration of amyloid precursor protein-cleaving secretases expression in aged mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 621:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.013
Tarasoff-Conway JM, Carare RO, Osorio RS, Glodzik L, Butler T, Fieremans E et al (2015) Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 11:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC et al (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 330:1774. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1197623
Li Y, Zhang J, Wan J, Liu A, Sun J (2020) Melatonin regulates Abeta production/clearance balance and Abeta neurotoxicity: a potential therapeutic molecule for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 132:110887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110887
Sbai O, Djelloul M, Auletta A, Ieraci A, Vascotto C, Perrone L (2022) AGE-TXNIP axis drives inflammation in Alzheimer’s by targeting Abeta to mitochondria in microglia. Cell Death Dis 13:302. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04758-0
Iqbal K, Liu F, Gong CX, Grundke-Iqbal I (2010) Tau in Alzheimer disease and related tauopathies. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:656–664. https://doi.org/10.2174/156720510793611592
Ali T, Kim MO (2015) Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3beta pathway in the mouse hippocampus. J Pineal Res 59:47–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12238
Zhu L, Gong Y, Lju H, Sun G, Zhang Q, Qian Z (2021) Mechanisms of melatonin binding and destabilizing the protofilament and filament of tau R3–R4 domains revealed by molecular dynamics simulation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23:20615–20626. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cp03142b
Oishi A, Gbahou F, Jockers R (2021) Melatonin receptors, brain functions, and therapies. Handb Clin Neurol 179:345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819975-6.00022-4
Yao K, Zhao YF, Zu HB (2019) Melatonin receptor stimulation by agomelatine prevents Abeta-induced tau phosphorylation and oxidative damage in PC12 cells. Drug Des Devel Ther 13:387–396. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S182684
Roy J, Wong KY, Aquili L, Uddin MS, Heng BC, Tipoe GL et al (2022) Role of melatonin in Alzheimer’s disease: from preclinical studies to novel melatonin-based therapies. Front Neuroendocrinol 65:100986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2022.100986
Wei Z, Li X, Li X, Liu Q, Cheng Y (2018) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Mol Neurosci 11:236. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00236
Wang Z, Bai Z, Qin X, Cheng Y (2019) Aberrations in oxidative stress markers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1712323. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1712323
Trigo D, Avelar C, Fernandes M, Sa J, da Cruz ESO (2022) Mitochondria, energy, and metabolism in neuronal health and disease. FEBS Lett. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14298
Manchester LC, Coto-Montes A, Boga JA, Andersen LP, Zhou Z, Galano A et al (2015) Melatonin: an ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J Pineal Res 59:403–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12267
Yildirim S, Ozkan A, Aytac G, Agar A, Tanriover G (2022) Role of melatonin in TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway in the MTPT-induced mouse model. Neurotoxicology 88:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2021.11.011
Khaldy H, Escames G, Leon J, Vives F, Luna JD, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2000) Comparative effects of melatonin, L-deprenyl, Trolox and ascorbate in the suppression of hydroxyl radical formation during dopamine autoxidation in vitro. J Pineal Res 29:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079x.2000.290206.x
Gitto E, Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Karbownik M, Manchester LC, Cuzzocrea S et al (2001) Individual and synergistic antioxidative actions of melatonin: studies with vitamin E, vitamin C, glutathione and desferrioxamine (desferoxamine) in rat liver homogenates. J Pharm Pharmacol 53:1393–1401. https://doi.org/10.1211/0022357011777747
Brown GM, Young SN, Gauthier S, Tsui H, Grota LJ (1979) Melatonin in human cerebrospinal fluid in daytime; its origin and variation with age. Life Sci 25:929–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(79)90498-3
Benot S, Goberna R, Reiter RJ, Garcia-Maurino S, Osuna C, Guerrero JM (1999) Physiological levels of melatonin contribute to the antioxidant capacity of human serum. J Pineal Res 27:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1999.tb00597.x
McCleery J, Cohen DA, Sharpley AL (2016) Pharmacotherapies for sleep disturbances in dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD009178. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009178.pub3
Jansen SL, Forbes D, Duncan V, Morgan DG, Malouf R (2006) Melatonin for the treatment of dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003802.pub3
Majidazar R, Rezazadeh-Gavgani E, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Naseri A (2022) Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease: an overview of systematic reviews. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 78:1567–1587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-022-03363-6
De Crescenzo F, D’Alo GL, Ostinelli EG, Ciabattini M, Di Franco V, Watanabe N et al (2022) Comparative effects of pharmacological interventions for the acute and long-term management of insomnia disorder in adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 400:170–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00878-9
Kim JH, Duffy JF (2018) Circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders in older adults. Sleep Med Clin 13:39–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.004
Zhang B, Chen T, Cao M, Yuan C, Reiter RJ, Zhao Z et al (2022) Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by decreasing endogenous melatonin mediates the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and obesity. Front Immunol 13:900132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.900132
Coelho LA, Peres R, Amaral FG, Reiter RJ, Cipolla-Neto J (2015) Daily differential expression of melatonin-related genes and clock genes in rat cumulus-oocyte complex: changes after pinealectomy. J Pineal Res 58:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12234
Garcia-Rios A, Ordovas JM (2022) Chronodisruption and cardiovascular disease. Clin Investig Arterioscler. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arteri.2021.12.004
Zhou L, Zhang Z, Nice E, Huang C, Zhang W, Tang Y (2022) Circadian rhythms and cancers: the intrinsic links and therapeutic potentials. J Hematol Oncol 15:21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-022-01238-y
Hattar S, Kumar M, Park A, Tong P, Tung J, Yau KW et al (2006) Central projections of melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cells in the mouse. J Comp Neurol 497:326–349. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.20970
La Morgia C, Carelli V, Sadun AA (2021) Retina and melanopsin neurons. Handb Clin Neurol 179:315–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819975-6.00020-0
Contreras E, Nobleman AP, Robinson PR, Schmidt TM (2021) Melanopsin phototransduction: beyond canonical cascades. J Exp Biol. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.226522
Hattar S, Liao HW, Takao M, Berson DM, Yau KW (2002) Melanopsin-containing retinal ganglion cells: architecture, projections, and intrinsic photosensitivity. Science 295:1065–1070. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1069609
Esquiva G, Hannibal J (2019) Melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cells in aging and disease. Histol Histopathol 34:1299–1311. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-18-138
Vartanian GV, Li BY, Chervenak AP, Walch OJ, Pack W, Ala-Laurila P et al (2015) Melatonin suppression by light in humans is more sensitive than previously reported. J Biol Rhythms 30:351–354. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748730415585413
Abe M, Kawaguchi H, Miura N, Akioka K, Ushikai M, Oi S et al (2018) Diurnal variation of melatonin concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid of unanesthetized microminipig. In Vivo 32:583–590. https://doi.org/10.21873/invivo.11279
Reiter RJ (1993) The melatonin rhythm: both a clock and a calendar. Experientia 49:654–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01923947
Hardeland R (2013) Chronobiology of melatonin beyond the feedback to the suprachiasmatic nucleus-consequences to melatonin dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci 14:5817–5841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14035817
Quera Salva MA, Hartley S (2012) Mood disorders, circadian rhythms, melatonin and melatonin agonists. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis 4:15–26. https://doi.org/10.4137/JCNSD.S4103
Buijs RM, Kalsbeek A (2001) Hypothalamic integration of central and peripheral clocks. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:521–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/35081582
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Korkmaz A, Rosales-Corral SA (2014) Melatonin and stable circadian rhythms optimize maternal, placental and fetal physiology. Hum Reprod Updat 20:293–307. https://doi.org/10.1093/humupd/dmt054
Klosen P, Lapmanee S, Schuster C, Guardiola B, Hicks D, Pevet P et al (2019) MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors are expressed in nonoverlapping neuronal populations. J Pineal Res 67:e12575. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12575
Pevet P (2016) Melatonin receptors as therapeutic targets in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Expert Opin Ther Targets 20:1209–1218. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2016.1179284
Waly NE, Hallworth R (2015) Circadian pattern of melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptor localization in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. J Circadian Rhythms 13:1. https://doi.org/10.5334/jcr.ab
Vriend J, Reiter RJ (2015) Melatonin feedback on clock genes: a theory involving the proteasome. J Pineal Res 58:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12189
Pevet P, Challet E, Felder-Schmittbuhl MP (2021) Melatonin and the circadian system: keys for health with a focus on sleep. Handb Clin Neurol 179:331–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819975-6.00021-2
Stehle JH, von Gall C, Korf HW (2002) Organisation of the circadian system in melatonin-proficient C3H and melatonin-deficient C57BL mice: a comparative investigation. Cell Tissue Res 309:173–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-002-0583-2
Rusak B, Yu GD (1993) Regulation of melatonin-sensitivity and firing-rate rhythms of hamster suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons: pinealectomy effects. Brain Res 602:200–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(93)90683-e
Torres-Farfan C, Mendez N, Abarzua-Catalan L, Vilches N, Valenzuela GJ, Seron-Ferre M (2011) A circadian clock entrained by melatonin is ticking in the rat fetal adrenal. Endocrinology 152:1891–1900. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2010-1260
Robinson AG, Zimmerman EA (1973) Cerebrospinal fluid and ependymal neurophysin. J Clin Invest 52:1260–1267. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI107293
Rodriguez E, Guerra M, Peruzzo B, Blazquez JL (2019) Tanycytes: a rich morphological history to underpin future molecular and physiological investigations. J Neuroendocrinol 31:e12690. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12690
Cardinali DP, Brown GM, Pandi-Perumal SR (2021) Chronotherapy. Handb Clin Neurol 179:357–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819975-6.00023-6
Fernandez FX, Kaladchibachi S, Negelspach DC (2021) Resilience in the suprachiasmatic nucleus: implications for aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Gerontol 147:111258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111258
Nassan M, Videnovic A (2022) Circadian rhythms in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 18:7–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-021-00577-7
Van Erum J, Van Dam D, De Deyn PP (2018) Sleep and Alzheimer’s disease: a pivotal role for the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Sleep Med Rev 40:17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2017.07.005
Tomasello U, Klingler E, Niquille M, Mule N, Santinha AJ, de Vevey L et al (2022) miR-137 and miR-122, two outer subventricular zone non-coding RNAs, regulate basal progenitor expansion and neuronal differentiation. Cell Rep 38:110381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110381
Wang F, Xia Z, Sheng P, Ren Y, Liu J, Ding L et al (2022) Targeting the Erk1/2 and autophagy signaling easily improved the neurobalst differentiation and cognitive function after young transient forebrain ischemia compared to old gerbils. Cell Death Discov 8:87. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-022-00888-8
Hinojosa-Godinez A, Jave-Suarez LF, Flores-Soto M, Galvez-Contreras AY, Luquin S, Oregon-Romero E et al (2019) Melatonin modifies SOX2(+) cell proliferation in dentate gyrus and modulates SIRT1 and MECP2 in long-term sleep deprivation. Neural Regen Res 14:1787–1795. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.257537
Sotthibundhu A, Ekthuwapranee K, Govitrapong P (2016) Comparison of melatonin with growth factors in promoting precursor cells proliferation in adult mouse subventricular zone. Excli J 15:829–841. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2016-606
Arias-Carrion O, Drucker-Colin R (2007) Neurogenesis as a therapeutic strategy to regenerate central nervous system. Rev Neurol 45:739–745
Arias-Carrion O, Freundlieb N, Oertel WH, Hoglinger GU (2007) Adult neurogenesis and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6:326–335. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152707783220875
Singhakumar R, Boontem P, Ekthuwapranee K, Sotthibundhu A, Mukda S, Chetsawang B et al (2015) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced inhibition of neurogenesis in the adult mouse hippocampus: an in vivo study. Neurosci Lett 606:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2015.09.011
Mendivil-Perez M, Soto-Mercado V, Guerra-Librero A, Fernandez-Gil BI, Florido J, Shen YQ et al (2017) Melatonin enhances neural stem cell differentiation and engraftment by increasing mitochondrial function. J Pineal Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12415
Codega P, Silva-Vargas V, Paul A, Maldonado-Soto AR, Deleo AM, Pastrana E et al (2014) Prospective identification and purification of quiescent adult neural stem cells from their in vivo niche. Neuron 82:545–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.039
Gengatharan A, Malvaut S, Marymonchyk A, Ghareghani M, Snapyan M, Fischer-Sternjak J et al (2021) Adult neural stem cell activation in mice is regulated by the day/night cycle and intracellular calcium dynamics. Cell 184:709-722e713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.026
Chu J, Tu Y, Chen J, Tan D, Liu X, Pi R (2016) Effects of melatonin and its analogues on neural stem cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 420:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2015.10.012
Anderson G (2020) The effects of melatonin on signaling pathways and molecules involved in glioma: melatonin and glioblastoma: pathophysiology and treatment. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 34:189–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12538
Anderson G, Reiter RJ (2019) Glioblastoma: role of mitochondria N-acetylserotonin/melatonin ratio in mediating effects of miR-451 and aryl hydrocarbon receptor and in coordinating wider biochemical changes. Int J Tryptophan Res 12:1178646919855942. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178646919855942
Moretti E, Favero G, Rodella LF, Rezzani R (2020) Melatonin’s antineoplastic potential against glioblastoma. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030599
Yan Z, Zhang X, Hua L, Huang L (2022) Melatonin inhibits the malignant progression of glioblastoma via regulating miR-16-5p/PIM1. Curr Neurovasc Res. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567202619666220406084947
Kinker GS, Ostrowski LH, Ribeiro PAC, Chanoch R, Muxel SM, Tirosh I et al (2021) MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors play opposite roles in brain cancer progression. J Mol Med (Berl) 99:289–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-02023-5
Beiriger J, Habib A, Jovanovich N, Kodavali CV, Edwards L, Amankulor N et al (2022) The subventricular zone in glioblastoma: genesis, maintenance, and modeling. Front Oncol 12:790976. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.790976
Ghareghani M, Zibara K, Rieter RJ, Rivest S (2022) Reduced melatonin levels may facilitate glioblastoma initiation in the subventricular zone. Expert Rev Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2022.15
Samantaray S, Das A, Thakore NP, Matzelle DD, Reiter RJ, Ray SK et al (2009) Therapeutic potential of melatonin in traumatic central nervous system injury. J Pineal Res 47:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00703.x
Yang X, Chen J, Ma Y, Huang M, Qiu T, Bian H et al (2022) Function, mechanism, and application of plant melatonin: an update with a focus on the cereal crop, Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Antioxidants (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040634
Suofu Y, Li W, Jean-Alphonse FG, Jia J, Khattar NK, Li J et al (2017) Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:E7997–E8006. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705768114
Venegas C, Garcia JA, Escames G, Ortiz F, Lopez A, Doerrier C et al (2012) Extrapineal melatonin: analysis of its subcellular distribution and daily fluctuations. J Pineal Res 52:217–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00931.x
Amstrup AK, Sikjaer T, Heickendorff L, Mosekilde L, Rejnmark L (2015) Melatonin improves bone mineral density at the femoral neck in postmenopausal women with osteopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Pineal Res 59:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12252
Blackman J, Swirski M, Clynes J, Harding S, Leng Y, Coulthard E (2021) Pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions to enhance sleep in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J Sleep Res 30:e13229. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.13229
Zetner D, Andersen LPK, Alder R, Jessen ML, Tolstrup A, Rosenberg J (2021) Pharmacokinetics and safety of intravenous, intravesical, rectal, transdermal, and vaginal melatonin in healthy female volunteers: a cross-over study. Pharmacology 106:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1159/000510252
Castillo RR, Quizon GRA, Junco MJM, Roman ADE, De Leon DG, Punzalan FER et al (2020) Melatonin as adjuvant treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia patients requiring hospitalization (MAC-19 PRO): a case series. Melatonin Res 3:297–310. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250063
Nordlund JJ, Lerner AB (1977) The effects of oral melatonin on skin color and on the release of pituitary hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 45:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-45-4-768
Nopparat C, Chaopae W, Boontem P, Sopha P, Wongchitrat P, Govitrapong P (2021) Melatonin attenuates high glucose-induced changes in beta amyloid precursor protein processing in human neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03290-5
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Sanchez-Barcelo E, Mediavilla MD, Reiter RJ (2010) Significance of high levels of endogenous melatonin in Mammalian cerebrospinal fluid and in the central nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol 8:162–167. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015910792246182
Cardinali DP, Vigo DE, Olivar N, Vidal MF, Brusco LI (2014) Melatonin therapy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 3:245–277. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox3020245
Liguori C, Fernandes M, Cerroni R, Ludovisi R, Mercuri NB, Stefani A et al (2022) Effects of melatonin prolonged-release on both sleep and motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: a preliminary evidence. Neurol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-022-06111-x
Zeviani M, Viscomi C (2022) Mitochondrial neurodegeneration. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11040637
Nissanka N, Moraes CT (2018) Mitochondrial DNA damage and reactive oxygen species in neurodegenerative disease. FEBS Lett 592:728–742. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12956
Wallace DC, Fan W, Procaccio V (2010) Mitochondrial energetics and therapeutics. Annu Rev Pathol 5:297–348. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092314
Reiter RJ, Sharma R, Rosales-Corral S, de Campos Zuccari DAP, de Almeida Chuffa LG (2022) Melatonin: a mitochondrial resident with a diverse skill set. Life Sci 301:120612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120612
Tan DX, Manchester LC, Qin L, Reiter RJ (2016) Melatonin: a mitochondrial targeting molecule involving mitochondrial protection and dynamics. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122124
Acuna-Castroviejo D, Rahim I, Acuna-Fernandez C, Fernandez-Ortiz M, Solera-Marin J, Sayed RKA et al (2017) Melatonin, clock genes and mitochondria in sepsis. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:3965–3987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2610-1
Ericson T, Singla P, Kohan L (2022) Intrathecal pumps. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 33:409–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2022.01.004
William J, Roehmer C, Mansy L, Kennedy DJ (2022) Epidural steroid injections. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 33:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmr.2022.01.009
Kuthati Y, Lin SH, Chen IJ, Wong CS (2019) Melatonin and their analogs as a potential use in the management of neuropathic pain. J Formos Med Assoc 118:1177–1186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2018.09.017
Chaudhry SR, Stadlbauer A, Buchfelder M, Kinfe TM (2021) Melatonin moderates the triangle of chronic pain, sleep architecture and immunometabolic traffic. Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9080984
Iram T, Kern F, Kaur A, Myneni S, Morningstar AR, Shin H et al (2022) Young CSF restores oligodendrogenesis and memory in aged mice via Fgf17. Nature 605:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-04722-0
Abo Taleb HA, Alghamdi BS (2020) Neuroprotective effects of melatonin during demyelination and remyelination stages in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci 70:386–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01425-6
Kumar RR, Singh L, Thakur A, Singh S, Kumar B (2021) Role of vitamins in neurodegenerative diseases: a review. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527320666211119122150
Uthaiah CA, Beeraka NM, Rajalakshmi R, Ramya CM, Madhunapantula SV (2022) Role of neural stem cells and vitamin D receptor (VDR)-mediated cellular signaling in the mitigation of neurological diseases. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02837-z
Louveau A, Plog BA, Antila S, Alitalo K, Nedergaard M, Kipnis J (2017) Understanding the functions and relationships of the glymphatic system and meningeal lymphatics. J Clin Invest 127:3210–3219. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90603
Krstic R (1975) Scanning electron microscope observations of the canaliculi in the rat pineal gland. Experientia 31:1072–1074. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02326967
Matsushima S, Sakai Y, Hira Y (1989) Twenty-four-hour changes in pinealocytes, capillary endothelial cells and pericapillary and intercellular spaces in the pineal gland of the mouse. Semiquantitative electron-microscopic observations. Cell Tissue Res 255:323–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224115
Quay WB (1974) Pineal canaliculi: demonstration, twenty-four-hour rhythmicity and experimental modification. Am J Anat 139:81–93. https://doi.org/10.1002/aja.1001390105
Arias-Carrion O (2008) Basic mechanisms of rTMS: implications in Parkinson’s disease. Int Arch Med 1:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-7682-1-2
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant funding from agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors declare a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Reiter, R.J., Sharma, R., Cucielo, M.S. et al. Brain washing and neural health: role of age, sleep, and the cerebrospinal fluid melatonin rhythm. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 80, 88 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04736-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04736-5