Abstract
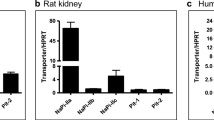
This review summarizes the physiological roles of the renal sulfate transporters NaS1 (Slc13a1) and Sat1 (Slc26a1). NaS1 and Sat1 encode renal anion transporters that mediate proximal tubular sulfate reabsorption and thereby regulate blood sulfate levels. Targeted disruption of murine NaS1 and Sat1 leads to hyposulfatemia and hypersulfaturia. Sat1 null mice also exhibit hyperoxalemia, hyperoxaluria and calcium oxalate urolithiasis. Dysregulation of NaS1 and Sat1 leads to hypersulfaturia, hyposulfatemia and liver damage. Loss of Sat1 leads additionally to hyperoxaluria with hyperoxalemia, nephrocalcinosis and calcium oxalate urolithiasis. These data indicate that the renal anion transporters NaS1 and Sat1 are essential for sulfate and oxalate homeostasis, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NaS1:
-
Sodium sulfate cotransporter-1
- Sat1:
-
Sulfate anion transporter-1
- BBM:
-
Brush-border membrane
- BLM:
-
Basolateral membrane
- DIDS:
-
4,4′-Diisothiocyanato-2,2′-disulfonate
- SITS:
-
4-Acetamido-4′-isothiocyanato-2,2′-disulfonate
References
Bastlein C, Burckhardt G (1986) Sensitivity of rat renal luminal and contraluminal sulfate transport to DIDS. Am J Physiol 250:F226–F234
Beck L, Markovich D (2000) The mouse Na(+)–sulfate cotransporter gene Nas1. Cloning, tissue distribution, gene structure, chromosomal assignment, and transcriptional regulation by vitamin D. J Biol Chem 275:11880–11890
Bissig M, Hagenbuch B, Stieger B et al (1994) Functional expression cloning of the canalicular sulfate transport system of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 269:3017–3021
Brazy PC, Dennis VW (1981) Sulfate transport in rabbit proximal convoluted tubules: presence of anion exchange. Am J Physiol 241:F300–F307
Busch AE, Waldegger S, Herzer T et al (1994) Electrogenic cotransport of Na+ and sulfate in Xenopus oocytes expressing the cloned Na+SO4(2−) transport protein NaSi-1. J Biol Chem 269:12407–12409
David C, Ullrich KJ (1992) Substrate specificity of the luminal Na+-dependent sulphate transport system in the proximal renal tubule as compared to the contraluminal sulphate exchange system. Pflugers Arch 421:455–465
Dawson PA, Markovich D (2002) Regulation of the mouse Nas1 promoter by vitamin D and thyroid hormone. Pflugers Arch 444:353–359
Dawson PA, Markovich D (2005) Pathogenetics of the human SLC26 transporters. Curr Med Chem 12:385–396
Dawson PA, Beck L, Markovich D (2003) Hyposulfatemia, growth retardation, reduced fertility and seizures in mice lacking a functional NaSi-1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13704–13709
Dawson PA, Steane SE, Markovich D (2004) Behavioural abnormalities of the hyposulphataemic Nas1 knock-out mouse. Behav Brain Res 154:457–463
Dawson PA, Steane SE, Markovich D (2005) Impaired memory and olfactory performance in NaSi-1 sulphate transporter deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 159:15–20
Dawson PA, Gardiner B, Grimmond S et al (2006) Transcriptional profile reveals altered hepatic lipid and cholesterol metabolism in hyposulfatemic NaS1 null mice. Physiol Genomics 26:116–124
Dawson PA, Gardiner B, Lee S et al (2008) Kidney transcriptome reveals altered steroid homeostasis in NaS1 sulfate transporter null mice. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 112:55–62
Dawson PA, Huxley S, Gardiner B et al (2009) Reduced mucin sulfonation and impaired intestinal barrier function in the hyposulfataemic NaS1 null mouse. Gut 58:910–919
Dawson PA, Choyce A, Chuang C et al (2010a) Enhanced tumor growth in the NaS1 sulfate transporter null mouse. Cancer Sci 101:369–373
Dawson PA, Russell CS, Lee S et al (2010b) Urolithiasis and hepatotoxicity are linked to the anion transporter Sat1 in mice. J Clin Invest 120:706–712
Fernandes I, Hampson G, Cahours X et al (1997) Abnormal sulfate metabolism in vitamin D-deficient rats. J Clin Invest 100:196–203
Fernandes I, Laouari D, Tutt P et al (2001) Sulfate homeostasis, NaSi-1 cotransporter, and SAT-1 exchanger expression in chronic renal failure in rats. Kidney Int 59:210–221
Goudsmit A Jr, Power MH, Bollman JL (1939) The excretion of sulfates by the dog. Am J Physiol 125:506
Hagenbuch B, Stange G, Murer H (1985) Transport of sulphate in rat jejunal and proximal tubular basolateral membrane vesicles. Pflugers Arch 405:202–208
Hierholzer K, Cade R, Gurd R et al (1960) Stop flow analysis of renal reabsorption and excretion of sulfate in the dog. Am J Physiol 198:833–837
Karniski LP, Lotscher M, Fucentese M et al (1998) Immunolocalization of sat-1 sulfate/oxalate/bicarbonate anion exchanger in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol 275:F79–F87
Kuo SM, Aronson PS (1988) Oxalate transport via the sulfate/HCO3 exchanger in rabbit renal basolateral membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem 263:9710–9717
Lee A, Markovich D (2004) Characterization of the human renal Na(+)–sulphate cotransporter gene (NAS1) promoter. Pflugers Arch 448:490–499
Lee A, Beck L, Markovich D (2000a) The human renal sodium sulfate cotransporter (SLC13A1; hNaSi-1) cDNA and gene: organization, chromosomal localization, and functional characterization. Genomics 70:354–363
Lee HJ, Sagawa K, Shi W et al (2000b) Hormonal regulation of sodium/sulfate co-transport in renal epithelial cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 225:49–57
Lee A, Beck L, Markovich D (2003) The mouse sulfate anion transporter gene Sat1 (Slc26a1): cloning, tissue distribution, gene structure, functional characterization, and transcriptional regulation thyroid hormone. DNA Cell Biol 22:19–31
Lee A, Dawson PA, Markovich D (2005) NaSi-1 and Sat-1: structure, function and transcriptional regulation of two genes encoding renal proximal tubular sulfate transporters. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1350–1356
Lee S, Dawson PA, Hewavitharana AK et al (2006) Disruption of NaS1 sulfate transport function in mice leads to enhanced acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 43:1241–1247
Lee S, Kesby JP, Muslim MD et al (2007) Hyperserotonaemia and reduced brain serotonin levels in NaS1 sulphate transporter null mice. Neuroreport 18:1981–1985
Lotscher M, Custer M, Quabius ES et al (1996) Immunolocalization of Na/SO4-cotransport (NaSi-1) in rat kidney. Pflugers Arch 432:373–378
Low I, Friedrich T, Burckhardt G (1984) Properties of an anion exchanger in rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 246:F334–F342
Lucke H, Stange G, Murer H (1979) Sulphate-ion/sodium-ion cotransport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat kidney cortex. Biochem J 182:223–229
Lucke H, Stange G, Murer H (1981) Sulfate–sodium cotransport by brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat ileum. Gastroenterology 80:22–30
Markovich D (2001) Physiological roles and regulation of mammalian sulfate transporters. Physiol Rev 81:1499–1533
Markovich D (2006) Sulfate transport by SLC26 transporters. Novartis Found Symp 273:42–51; discussion 51–58, 261–264
Markovich D (2008) Expression cloning and radiotracer uptakes in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nat Protoc 3:1975–1980
Markovich D, Aronson PS (2007) Specificity and regulation of renal sulfate transporters. Annu Rev Physiol 69:361–375
Markovich D, Murer H (2004) The SLC13 gene family of sodium sulphate/carboxylate cotransporters. Pflugers Arch 447:594–602
Markovich D, Forgo J, Stange G et al (1993) Expression cloning of rat renal Na+/SO4(2−) cotransport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8073–8077
Markovich D, Bissig M, Sorribas V et al (1994) Expression of rat renal sulfate transport systems in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Functional characterization and molecular identification. J Biol Chem 269:3022–3026
Markovich D, Murer H, Biber J et al (1998) Dietary sulfate regulates the expression of the renal brush border Na/Si cotransporter NaSi-1. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1568–1573
Markovich D, Wang H, Puttaparthi K et al (1999a) Chronic K depletion inhibits renal brush border membrane Na/sulfate cotransport. Kidney Int 55:244–251
Markovich D, Werner A, Murer H (1999b) Expression cloning with Xenopus oocytes. In: Hildebrandt F, Igarashi P (eds) Techniques in molecular medicine. Springer, Heidelberg
Murer H, Markovich D, Biber J (1994) Renal and small intestinal sodium-dependent symporters of phosphate and sulphate. J Exp Biol 196:167–181
Pritchard JB, Renfro JL (1983) Renal sulfate transport at the basolateral membrane is mediated by anion exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2603–2607
Puttaparthi K, Markovich D, Halaihel N et al (1999) Metabolic acidosis regulates rat renal Na–Si cotransport activity. Am J Physiol 276:C1398–C1404
Regeer RR, Markovich D (2004) A dileucine motif targets the sulfate anion transporter sat-1 to the basolateral membrane in renal cell lines. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C365–C372
Regeer RR, Lee A, Markovich D (2003) Characterization of the human sulfate anion transporter (hsat-1) protein and gene (SAT1; SLC26A1). DNA Cell Biol 22:107–117
Regeer RR, Nicke A, Markovich D (2007) Quaternary structure and apical membrane sorting of the mammalian NaSi-1 sulfate transporter in renal cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:2240–2251
Sagawa K, Benincosa LJ, Murer H et al (1998a) Ibuprofen-induced changes in sulfate renal transport. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:1092–1097
Sagawa K, DuBois DC, Almon RR et al (1998b) Cellular mechanisms of renal adaptation of sodium dependent sulfate cotransport to altered dietary sulfate in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:1056–1062
Sagawa K, Han B, DuBois DC et al (1999a) Age- and growth hormone-induced alterations in renal sulfate transport. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:1182–1187
Sagawa K, Murer H, Morris ME (1999b) Effect of experimentally induced hypothyroidism on sulfate renal transport in rats. Am J Physiol 276:F164–F171
Schneider EG, Durham JC, Sacktor B (1984) Sodium-dependent transport of inorganic sulfate by rabbit renal brush- border membrane vesicles. Effects of other ions. J Biol Chem 259:14591–14599
Turner RJ (1984) Sodium-dependent sulfate transport in renal outer cortical brush border membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 247:F793–F798
Ullrich KJ, Rumrich G, Kloss S (1980) Bidirectional active transport of thiosulfate in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch 387:127–132
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Australian Research Council, the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Cancer Council Queensland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Markovich, D. Physiological Roles of Mammalian Sulfate Transporters NaS1 and Sat1. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 59, 113–116 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-011-0114-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-011-0114-5