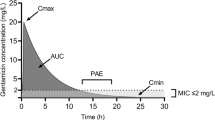
Summary
The concept of accelerating bacterial eradication and accomplishing a more rapid clinical cure by optimising dosing of antimicrobial agents is coming to fruition after many years of research. By integrating the pharmacokinetic parameters of an antibiotic with measures of microorganism susceptibility such as the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), it is possible to optimise both clinical and bacteriological cure. Recently, area under the inhibitory curve (AUIC) has been introduced as the 24-hour area under the curve (AUC) divided by the MIC. The AUIC has been shown to be an effective parameter to predict infectious outcome and it has the advantage that it can be easily calculated by estimating the patient’s creatinine clearance and using population clearance of drugs vs creatinine clearance equations. In this review, total clearance vs creatinine clearance equations were derived for 53 antimicrobials, using pharmacokinetic data extracted from the literature. These equations were then validated by calculating half-life and AUC (for specific doses) and comparing the results to published values and ranges. In the validation phases the percentage error for each antibiotic equation was variable, ranging from 0.5 to 61% when estimating half-life, and 0.35 to 51% when estimating AUC. When a subset of antimicrobials was validated against values derived from studies of AUC vs decreasing creatinine clearance, the majority of percentage errors were within 0.35 to 56%, with only a minimal number of outliers over the studied ranges of renal function (0–129 ml/min/70kg). Possible explanations for these outliers include multiple routes of elimination and research based on populations different to those used to derive the original equation. Percentage errors were within acceptable ranges, when considering that most antimicrobials have a large therapeutic/toxic ratio. By targeting an AUIC value of 350, well above the theoretical threshold therapeutic value of 125, doses associated with an accelerated bacterial eradication rate are possible without substantially overdosing the patient. This remains true even if the calculated values from these equations are greater than a 50% overestimation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarons L, Vozeh S, Wenk M, Weiss PH, Follath F. Population pharmacokinetics of tobramycin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 28: 305–314, 1989
Adam D, De Visser I, Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid administered alone and in combination. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 22: 353–357, 1982
Anti-Infective Agents. In McEvoy et al. (Eds) AHES Drug Information 91, pp. 31–488. American Society of Hospital Pharmacists, Bethesda, 1991
Benet LZ, Williams RL. Design and optimization of dosage regimens; pharmacokinetic data. In Gilman et al. (Eds) Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, pp. 1655–1735, Pergamon Press, New York, 1990
Blum RA, Kohli RK, Harrison NJ, Schentag JJ. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin (2.0 grams) and sulbactam (1.0 gram) coadministered to subjects with normal and abnormal renal function and with endstage renal disease on hemodialysis. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 33: 1470–1476, 1989
Blum RA, Schultz RW, Schentag JJ. Pharmacokinetics of lome-floxacin in really compromised patients. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 34: 2364–2368, 1990
Boeckh M, Lode H, Borner K, Hoffken G, Wagner J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activity of vancomycin alone and in combination with ceftazidime in healthy volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 92–95, 1988
Bolton WK, Scheld WM, Spyker DA, Sande MA. Pharmacokinetics of cefoperazone in normal volunteers and subjects with renal insufficiency. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 19: 821–825, 1981
Colaizzi PA, Polk RE, Poynor WJ, Raffalovich AC, Cefali EA, et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of azlocillin and piperacillin in normal adults. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 29: 938–940, 1986
Dettli LC. Drug dosage in patients with renal disease. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 16: 274–280, 1974
Drusano GL. Role of pharmacokinetics in the outcome of infections. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 289–297, 1988
Drusano GL, Townsend RJ, Walsh TJ, Forrest A, Antal EJ, et al. Steady-state serum pharmacokinetics of novobiocin and rifampin alone and in combination. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 30: 42–45, 1986
Farinotti R, Trouvin JH, Bocquet V, Vermerie N, Carbon C. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin after single and multiple intravenous infusions in healthy subjects. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1590–1592, 1988
Fillastre JP, Fourtillan JB, Leroy A, Ramis N, Lefevre MA, et al. Pharmacokinetics of cefonicid in uraemic patients. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 18: 203–211, 1986
Flor S. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin. American Journal of Medicine 87 (Suppl. 6C): 24S–30S, 1989
Foord RD. Cefuroxime: human pharmacokinetics. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 9: 741–747, 1976
Forrest A, Ballow CH, Nix DE, Birmingham MC, Goss TF, et al. Population pharmacodynamics of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, in press, 1993
Frimodt-Moller N, Maigaard S, Toothaker RD, Bundtzen RW, Brodey MV, et al. Mezlocillin pharmacokinetics after single intravenous doses to patients with varying degrees of renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 17: 599–607, 1980
Gilman et al. Goodman and Gilman’s pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Pergamon Press, New York, 1990
Guay DRP, Meatherall RC, Harding GK, Brown GR. Pharmacokinetics of cefixime (CL 284,635; FK 027) in healthy subjects and patients with renal insufficiency. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 30: 485–490, 1986
Guglielmo BJ, Rodondi LC. Comparison of antibiotic activities by using serum bactericidal activity over time. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 32: 1511–1514, 1988
Hampel B, Lode H, Wagner J, Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of cefadroxil and cefaclor during an eight-day dosage period. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 22: 1061–1063, 1982
Horber FF, Frey FJ, Descoeudres C, Murray AT, Reubi EC. Differential effect of impaired renal function on the kinetics of clavulanic acid and amoxicillin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 29: 614–619, 1986
Jelliffe RW. Creatinine clearance: bedside estimate. Annals of Internal Medicine 79: 604, 1973
Jungbluth GL, Cooper DL, Doyle GD, Chudzik GM, Jusko WJ. Pharmacokinetics of ticarcillin and clavulanic acid (Timentin) in relation to renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 30: 896–900, 1986
Kowalsky SF, Echols RM, Venezia AR, Andrews EA. Pharmacokinetics of ceftizoxime in subjects with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 24: 151–155, 1983
Kroboth PD, Brown A, Lyon JA, Kroboth FJ, Juhl RP. Pharmacokinetics of single-dose erythromycin in normal and alcoholic liver disease subjects. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 21: 135–140, 1982
Lode H, Stahlmann R, Koeppe P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of cephalexin, cefaclor, cefadroxil, and CGP 9000. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 16: 1–6, 1979
Matzke GR, Abraham PA, Halstenson CE, Keane WF. Cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime kinetics in renal impairment. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 38: 31–36, 1985
Matzke GR, McGory RW, Halstenson CE, Keane WF. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in patients with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 25: 433–437, 1984
Matzke GR, Millikin SP, Kovarik JM. Variability in pharmacokinetic values for gentamicin, tobramycin, and netilmicin in patients with renal insufficiency. Clinical Pharmacy 8: 800–806, 1989
Meyers BR, Srulevitch ES, Jacobson J, Hirschman SZ. Crossover study of the pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone administered intravenously or intramuscularly to healthy volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 24: 812–814, 1983
Meyers BR, Wilkinson P, Mendelson MH, Walsh S, Bournazos C, et al. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin-sulbactam in healthy elderly and young volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 35: 2098–2101, 1991
Mihindu JCL, Scheid WM, Bolton ND, Spyker DA, Swabb EA, et al. Pharmacokinetics of aztreonam in patients with various degrees of renal dysfunction. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 24: 252–261, 1983
Nakagawa K, Koyama M, Tachibana A, Komiya M, Kikuchi Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics of cefotetan (YM09330) in humans. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 22: 935–941, 1982
Nilsen OG, Saltvedt E, Walstad RA, Marstein S. Single-dose pharmacokinetics of lomefloxacin in patients with normal and impaired renal function. American Journal of Medicine 92 (Suppl. 4A): 38S–40S, 1992
Pharmacokinetic Data Table A-II-1. In Gilman et al. (Eds) Goodman and Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics 8th ed., pp. 1655–1735, Pergamon Press, New York, 1990
Plantier J, Forrey AW, O’Neill MA, Blair AD, Christopher TG, et al. Pharmacokinetics of amikacin in patients with normal or impaired renal function: radioenzymatic acetylation assay. Journal of Infectious Diseases 134: 5323–5330, 1976
Scheid WM, Spyker DA, Donowitz GR, Bolton WK, Sande MA. Moxalactam and cefazolin: comparative pharmacokinetics in normal subjects. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 19: 613–619, 1981
Schentag JJ, Nix DE, Adelman MH. Mathematical examination of dual individualization principles (I): relationships between AUC above MIC and area under the inhibitory curve for cefmenoxime, ciprofloxacin, and tobramycin. DICP, Annals of Pharmacotherapy 25: 1050–1057, 1991
Schentag JJ, Smith IL, Swanson DJ, De Angelis C, Fracasso JE, et al. Role for dual individualization with cefmenoxime. American Journal of Medicine 77 (Suppl. 6A): 43–50, 1984
Smith BR, LeFrock JL, Thyrum PT, Doret BA, Yeh C, et al. Cefotetan pharmacokinetics in volunteers with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 29: 887–893, 1986
Srinivasan S, Francke EL, Neu HC. Comparative pharmacokinetics of cefoperazone and cefamandole. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 19: 298–301, 1981
Standiford HC, Drusano GL, Bustamante CI, Rivera G, Forrest A, et al. Imipenem coadministered with cilastatin compared with moxalactam: integration of serum pharmacokinetics and microbiologic activity following single-dose administration to normal volunteers. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 29: 412–417, 1986
Stratton CW, Weinstein MP, Relier LB. Correlation of serum bactericidal activity with antimicrobial agent level and minimal bactericidal concentration. Journal of Infectious Diseases 145: 160–168, 1982
Tjandramaga TB, Van Hecken A, Mullie A, Verbesselt R, De Schepper PJ, et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime and moxalactam. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 22: 237–241, 1982
Vallee F, LeBel M. Comparative study of pharmacokinetics and serum bactericidal activity of ceftizoxime and cefotaxime. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 35: 2057–2064, 1991
Verpooten GA, Verbist L, Buntinx AP, Entwistle LA, Jones KH, et al. The pharmacokinetics of imipenem (thienamycin formamidine) and the renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor cilastatin sodium in normal subjects and patients with renal failure. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 183–193, 1984
Welage LS, Schultz RW, Schentag JJ. Pharmacokinetics of ceftazidime in patients with renal insufficiency. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 25: 201–204, 1984
Welling PG, Craig WA, Bundtzen RW, Kwok FW, Gerber AU, et al. Pharmacokinetics of piperacillin in subjects with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 23: 881–887, 1983
Wise R, Dyas A, Hegarty A, Andrews JM. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of azthreonam. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 22: 969–971, 1982
Wolfson JS, Hooper DC. Comparative pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin. American Journal of Medicine 87 (Suppl. 6C): 31S–36S, 1989
Wolfson JS, Swartz MN. Serum bactericidal activity as a monitor of antibiotic therapy. New England Journal of Medicine 312: 968–975, 1985
Yuen GJ, Drusano GL, Plaisance K, Forrest A, Caplan ES. Ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics in critically ill trauma patients. American Journal of Medicine 87 (Suppl. 5A): 70S–75S, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amsden, G.W., Ballow, C.H. & Schentag, J.J. Population Pharmacokinetic Methods to Optimise Antibiotic Effects. Drug Invest. 5, 256–268 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259590
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259590