Abstract
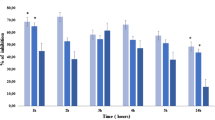
Ebselen (2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one), a seleno-organic compound with glutathione peroxidase-like activityin vitro, was compared with indometacin, BW 755C, and levamisole as an inhibitor of carrageenan- and CVF (cobra venom factor)-induced paw oedema in the rat. The antiinflammatory potency of ebselen against CVF-induced oedema (ED50=56 mg/kg p.o.) was similar to that of BW 755C, while indometacin was weakly active in this model, and levamisole exerted stronger activity. In the carrageenan model, ebselen exhibited weak inhibitory potency, like BW 755C, while indometacin markedly inhibited this inflammatory response, and levamisole was inactive. Unlike cyclooxygenase inhibitors, ebselen produced almost no gastric irritation in rats up to 316 mg/kg p.o. Moreover, ebselen inhibited significantly diclofenac-induced gastric intolerance at 31.6 and 316 mg/kg p.o. Thus, ebselen represents a new tool for antiinflammatory therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. V. Wedmore and T. J. Williams,Control of vascular permeability by polymorphonuclear leucocytes in inflammation. Nature289, 646–650 (1981).
J. C. Fantone and P. A. Ward,Role of oxygen-derived free radicals and metabolites in leukocyte-dependent inflammatory reactions. Am. J. Pathol.107, 397–418 (1982).
K. Ley and K.-E. Arfors,Changes in macromolecular permeability by intravascular generation of oxygen-derived free radicals. Microvasc. Res.24, 25–33 (1982).
R. M. McMilland and S. J. Foster,Leukotriene B 4 and inflammatory disease. Agents and Actions24, 114–119 (1988).
A. Müller, E. Cadenas, P. Graf and H. Sies,A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound — I. Glutathione peroxidase-like activity in vitro and antioxidant capacity of PZ 51 (ebselen). Biochem. Pharmac.33, 3235–3239 (1984).
A. Wendel, M. Fausel, H. Safayhi, G. Tiegs and R. Otter,A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound. — II. Activity of PZ 51 in relation to glutathione peroxidase. Biochem. Pharmac.33, 3241–3245 (1984).
M. J. Parnham and S. Kindt,A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound — III. Effects of PZ 51 (ebselen) on glutathione peroxidase and secretory activities of mouse macrophages. Biochem. Pharmac.33, 3247–3250 (1984).
P. Kuhl, H. O. Borbe, H. Fischer, A. Römer and H. Safayhi.Ebselen reduces the formation of LTB 4 in human and porcine leucocytes by isomerisation to its 5S,12R-6-trans-isomer, Prostaglandins31, 1029–1048 (1986).
S. Ichikawa, K. Omura, T. Katayama, N. Okamura, T. Ohtsuka, S. Ishibashi and H. Masayasu,Inhibition of superoxide anion production in guinea pig polymorphonuclear leucocytes by a seleno-organic compound, ebselen. J. Pharmacobio-Dyn.10, 595–597 (1987).
I. Cotgreave, S. K. Duddy, G. E. N. Kass, D. Thompson and P. Moldéus,Studies on the anti-inflammatory activity of ebselen. Ebeselen interferes with granulocyte oxidative burst by dual inhibition of NADH oxidase and protein kinase C? Biochem. Pharmac.38, 649–656 (1989).
M. J. Parnham, S. Leyck, N. Dereu, J. Winkelmann and E. Graft,Ebselen (PZ 51): A GSH-peroxidase-like organoselenium compound with anti-inflammatory activity. Adv. Inflamm. Res.10, 398–400 (1986).
A. Wendel and G. Tiegs,A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound — VI. Protection by ebselen (PZ 51) against galactosamine/endotoxin-induced hepatitis in mice. Biochem. Pharmac.35, 2115–2118 (1986).
M. J. Parnham, S. Leyck, P. Kuhl, J. Schalkwijk and W. B. van den Berg,Ebselen: A new approach to the inhibition of peroxidase-dependent inflammation. Int. J. Tiss. React.9, 45–50 (1987).
H. P. Hartung, B. Schäfer, K. Heininger and K. V. Toyka,Interference with arachidonic acid metabolism suppresses experimental allergic neuritis. Ann. Neurol.20, 168 (1986).
I. A. Cotgreave, U. Johansson, G. Westergren, P. W. Moldéus and R. Brattsand,The anti-inflammatory activity of ebselen but not thiols in experimental alveolitis and bronchiolitis. Agents and Actions24, 313–319 (1988).
K. Stockhaus and H. Wick,Die Sekretion von Saft- und Säuremengen bei Ratten mit unterbundenem Pylorus (Shay-Ratten). Arzneim.-Forsch.20, 856–858 (1970).
S. Leyck, E. Etschenberg, U. Hadding and J. Winkelmann,A new model of acute inflammation: Cobra venom factor induced paw oedema. Agents and Actions13, 437–438 (1983).
C. A. Winter, E. A. Risley and G. W. Nuss,Carrageenin-induced edema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for anti-inflammatory drugs. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.111, 544–547 (1962).
S. Leyck, N. Dereu, E. Etschenberg, M. Ghyczy, E. Graf, J. Winkelmann and M. J. Parnham,Improvement of the gastric tolerance of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs by polyene phosphatidylcholine (Phospholipon® 100). Eur. J. Pharmacol.117, 35–42 (1985).
R. Vinegar, J. F. Truax, J. L. Selph, A. Lea and P. R. Johnston,Quantitative in vivo studies of the acute actions of anti-inflammatory drugs in the rat. Eur. J. Rheumatol. Inflammation1, 204–211 (1978).
S. T. Hoffstein, R. M. Manzi, K. A. Razgaitis, P. E. Bender and J. Gleason,Structural requirements for chemotactic activity of leukotriene B 4 (LTB 4). Prostaglandins31, 205–215 (1986).
H. Safayhi, G. Tiegs and A. Wendel,A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound — V. Inhibition by ebselen (PZ 51) of rat peritoneal neutrophil lipoxygenase. Biochem. Pharmac.34, 2691–2694 (1985).
D. K. Imagawa, N. E. Osifchin, W. A. Paznekes, M. L. Shin and M. M. Mayer,Consequences of cell membrane attack by complement: Release of arachidonate and formation of inflammatory derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.80, 6647–6651 (1983).
T. Sacks, C. F. Moldow, P. R. Craddock, T. K. Bowers and B. S. Jacob,Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes: An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J. Clin. Invest.61, 1161–1167 (1978).
G. A. Higgs, J. A. Salmon, B. Henderson and J. R. Vane,Pharmacokinetics of aspirin and salicylate in relation to inhibition of arachidonate cyclooxygenase and anti-inflammatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA84, 1417–1420 (1987).
S. Abramson, H. M. Korchak, R. Ludewig, H. Edelson, K. Haines, R. Levin, R. Herman, L. Rider, S. Kimmel and G. Weissmann,Modes of action of aspirin-like drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA82, 7227–7231 (1985).
A Lorico, P. Masturzo, S. Villa, M. Salmona, N. Semeraro and G. de Gaetano,Gentisic acid: An aspirin metabolite with multiple effects on human blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol.35, 2443–2445 (1986).
B. M. Peskar,On the synthesis of prostaglandins by human gastric mucosa and its modification by drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta487, 307–314 (1977).
U. Aehringhaus, H. Weiler, B. A. Peskar and B. M. Peskar,Molecular mechanism of the gastric toxicity of antirheumatic drugs. Arch. Toxicol.Suppl. 7, 323–327 (1984).
K. D. Rainsford,Mechanisms of gastrointestinal ulceration by nonsteroidal antiinflammatory/analgesic drugs. Adv. Inflam. Res.6, 51–64 (1984).
Y. Kurebayashi, Y. Tabuchi and M. Akasaki,Gastric cytoprotection by ebselen against the injury induced by necrotizing agents in rats. Arzneim.-Forsch./Drug Res.39, 250–253 (1989).
G. Pihan, C. Regillo and S. Szabo,Free radicals and lipid proxidation in ethanol- or aspirin-induced gastric mucosal injury. Digest. Disease Sc.32, 1395–1401 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leyck, S., Parnham, M.J. Acute antiinflammatory and gastric effects of the seleno-organic compound ebselen. Agents and Actions 30, 426–431 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966308
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01966308