Summary
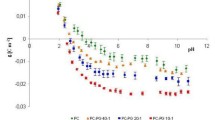
A comparative study of the charge transport kinetics of oppositely charged lipophilic probe ions in lipid bilayer membranes of varying composition was carried out by using the charge pulse technique. The ions investigated were the chemical analogs tetraphenylborate, tetraphenylarsonium and tetraphenylphosphonium. Membrane structural aspects investigated were the type of solvent used in membrane formation, sterol content, and the nature of the principal lipid. The overall results indicate that the character of the transport process involving positive lipophilic probes is, in contrast to positively charged carrier complexes, very similar to that deduced in previous studies of negative lipophilic ions. The major effect on transport of lipophilic ions of both signs using differentn-alkane solvents appears to be due to changes in the thickness of the membrane hydrocarbon region. Positive ion transport is relatively sensitive to the inclusion of sterols of several types in both monoolein and lecithin membranes, as compared with negative ion transport, suggesting that a combination of sterol-induced dipolar field and fluidity changes are involved. Results involving several variations in lipid structure, with the possible exception of hydrocarbon tail saturation, when interpreted in terms of dipolar field changes deduced under the assumption of charge independent fluidity effects, are consistent with monolayer surface potential measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, N.K.1968. The Physics and Chemistry of Surfaces. Dover, New York
Andersen, O.S., Feldberg, S., Nakadomari, H., Levy, S., McLaughlin, S. 1978. Electrostatic interactions among hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes.Biophys. J. 21:35
Andersen, O.S., Fuchs, M. 1975. Potential energy barriers to ion transport within lipid bilayers. Studies with tetraphenylborate.Biophys. J. 15:795
Benz, R., Cros, D. 1978. Influence of sterols on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 506:265
Benz, R., Fröhlich, O., Läuger, P. 1976. Influence of membrane structure on the kinetics of carrier-mediated ion transport through lipid bilayers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 464:465
Benz, R., Fröhlich, O., Läuger, P., Montal, M. 1975. Electrical capacity of black lipid films and of lipid bilayers made from monolayers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 394:323
Benz, R., Gisin, B.F.1978. Influence of membrane structure on ion transport through lipid bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 40:293
Benz, R., Janko, K. 1976. Voltage-induced capacitance relaxation of lipid bilayer membrane. Effect of membrane composition.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:721
Benz, R., Läuger, P. 1976. Kinetic analysis of carrier-mediated ion transport by the charge-pulse technique.J. Membrane Biol. 27:171
Benz, R., Läuger, P. 1977. Transport kinetics of dipicrylamine through lipid bilayer membranes. Effects of membrane structure.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 468:245
Benz, R., Läuger, P., Janko, K. 1976. Transport kinetics of hydrophobic ions in lipid bilayer membranes. Charge pulse relaxation studies.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:701
Benz, R., Stark, G., Janko, K., Läuger, P.1973. Valinomycin-mediated ion transport through neutral lipid membranes: Influence of hydrocarbon chain length and temperature.J. Membrane Biol. 14:339
Bruner, L.J. 1975. The interaction of hydrophobic ions with lipid bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 22:125
Demel, R.A., Bruckdorfer, K.R., Van Deenen, L.L.M. 1972. The effect of sterol structure on the permeability of liposomes to glucose, glycerol and Rb+.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 255:321
Fettiplace, R., Andrews, D.M., Haydon, D.A. 1971. The thickness, composition and structure of some lipid bilayers and natural membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 5:277
Haydon, D.A. 1975. Functions of the lipid in bilayer ion permeability.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 264:2
Haydon, D.A., Hladky, S.B. 1972. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: A critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems.Q. Rev. Biophys. 5:187
Janko, K., Benz, R. 1977. Properties of lipid bilayer membranes made from lipids containing phytanic acid.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 470:8
Ketterer, B., Neumcke, B., Läuger, P. 1971. Transport mechanism of hydrophobic ions through lipid bilayer membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 5:225
LeBlanc, O.H., Jr. 1970. Single ion conductances in lipid bilayers.Biophys. J. (Abstr.) 10:94a
Liberman, Ye.A., Topaly, V.P. 1969. Permeability of biomolecular phospholipid membranes for fat soluble ions.Biophysics 14:477
McLaughlin, S. 1977. Electrostatic potentials at membrane-solution interfaces.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. F. Bronner and A. Kleinzeller, editors. p. 71. Academic Press, New York
Montal, M., Mueller, P. 1972. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 69:3561
Neumcke, B., Läuger, P. 1969. Nonlinear electrical effects in lipid bilayer membranes.Biophys. J. 9:1160
Pagano, R.E., Ruysschaert, J.M. Miller, I.R. 1972. The molecular composition of some lipid bilayer membranes in aqueous solution.J. Membrane Biol. 10:11
Paltauf, F., Hauser, H., Phillips, M. C. 1971. Monolayer characteristics of some 1,2-diacyl, 1-alkyl-2-acyl and 1,2-dialkyl phospholipids at the airwater interfaces.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 249:539
Parsegian, A. 1969. Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: Solutions of four relevant electrostatic problems.Nature (London) 221:844
Racker, E., Hinkle, P.C. 1974. Effect of temperature on the function of a proton pumpJ. Membrane Biol. 17:181
Szabo, G. 1974. Dual mechanism for the action of cholesterol on membrane permeability.Nature (London) 257:47
Szabo, G. 1976. The influence of dipole potentials on the magnitude and the kinetics of ion transport in lipid bilayer membranes.In: Extreme Environment: Mechanisms of Microbial Adaptation. M.R. Heinrich, editor. p. 321. Academic Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pickar, A.D., Benz, R. Transport of oppositely charged lipophilic probe ions in lipid bilayer membranes having various structures. J. Membrain Biol. 44, 353–376 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01944229
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01944229