Abstract
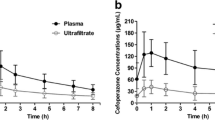
In patients with acute renal failure, who were treated with continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration (CAVH) or continuous arteriovenous hemodiafiltration (CAVHD), we measured clearance rates of imipenem and cilastatin (Tiënam-500®). Literature data on volume of distribution and on the endogenous clearance in normals and in anuric patients and the observed clearance rates by CAVH/CAVHD were used to develop guidelines for dose adaptations. Based on the desired peak levels of imipenem, normal subjects should receive the fixed imipenem/cilastatin dose combination (500 mg/500 mg) q.i.d. and patients with acute renal failure should receive the same dose b.i.d. After starting treatment with either CAVH, CAVHD or continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVH), no further dose adjustment is necessary. The non-renal clearance rate of cilastatin is very low compared to that of imipenem. If a patient develops anuria, the clearance rate of imipenem decreases from the normal value of 245 ml/min to 116 ml/min. Clearance rate of cilastatin, however, decreases from 230 ml/min to 3 ml/min. Therefore, in patients with renal failure accumulation of cilastatin will occur. On the other hand, if the patient is treated by CAVHD, the relative contribution of the dialyser clearance to the total drug clearance is much greater for cilastatin than for imipenem. As a result, the accumulation of cilastatin is reversed. During treatment by CAVHD, the clearance rate of imipenem raises 15%–25% and that of cilastatin 335%–600%. For this reason, we conclude that the use of the fixed dose combination (500 mg/500 mg) b.i.d. in patients with acute renal failure treated by CAVHD may be justified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birnbaum J, Kahan FM, Kropp H, Mcdonald JS (1985) Carbapenems, a new class of beta lactam antibiotics. Am J Med 78 [Suppl] 6a:3–21
Berman SJ, Sugihari JG, Nakamura JM, Wong EGC, Musgrave JE, Wong LMF, Siemsen AM (1985) Multiple dose study of imipenem/cilastatin in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing long term hemodialysis. Am J Med 78 [Suppl] 6a: 113–116
Vincent HH, Akçahuseyin E, Vos MC, van Ittersum FJ, van Duyl WA, Schalekamp MADH (1990) Determinants of blood flow and ultrafiltration in continuous arteriovenous haemodiafiltration: predictions and laboratory and clinical observations. Nephrol Dial Transplant 5:1031–1037
Burton RG, Gorewit RC (1984) Ultrasonic flowmeter. Uses widebeam transit-time technique. Med Electronics 15:68–73
Gravallese DA, Musson DG, Pauliukonis LT, Bayne WF (1984) Determinations of imipenem in human plasma and urine by highperformance liquid chromatography. Comparison with microbiological methodology and stability. J Chromatogr 310:71–84
Myers CM, Blumer JL (1984) Determination of imipenem and cilastatin in serum by high pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 26:78–81
Calandra GB, Brown KR, Grad LC, Akonkhai VI, Wang C, Aziz M (1985) Review of experiences and tolerability in the first 2516 patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin. Am J Med 78 [Suppl] 6a:65–70
Kroh U, Hofmann W, Dehne M, El Abed K, Lennartz H (1989) Dosisanpassung von Pharmaka während kontinuierlicher Hämofiltration. Anaesthesist 38:225–232
Wise R, Donovan MR, Lockley J, Drumm J, Andrews JM (1986) The pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of imipenem. J Antimicrob Chemother 18 [Suppl] E:93–101
Verpooten GA, Verbist L, Buntinx AP, Entwistle LA, Jones KH, de Broe ME (1984) The pharmacokinetics of imipenem (thienamycinformamidine) and the renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor cilastatin sodium in normal subjects and patients with renal failure. Br J Pharmacol 18:183–193
Drusano GL, Weir M, Forrest A, Plaisance K, Emm T, Standiford HC (1987) Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin in patients with various degrees of renal function. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:860–864
Keller E, Fecht H, Bohler J, Schollmeyer P (1989) Single-dose kinetics of imipenem/cilastatin during continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration in intensive care patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 4:640–645
Rogers JD, Meisinger MAP, Ferber F, Calandra GB, Demetriades JL, Bland JA (1985) Pharmacokinetics of imipenem and cilastatin in volunteers. Rev Infect Dis 7 [Suppl] 3:435–446
Gibson TP, Demetriades JL, Bland JA (1985) Imipenem/cilastatin: pharmacokinetic profile in renal insufficiency. Am J Med 78 [Suppl] 6a:54–61
Yourassowsky E, van de Linden MP, Lismont MJ, Crokaert F, Glupczynski Y (1986) Effect on growth curves and killing curves of brief exposure of Escherichia Coli to imipenem and piperacillin. J Antimicrob Chemother 18 [Suppl] E:61–65
Gundmundsson S, Vogelman B, Craig WA (1986) The in vivo postantibiotic effect of imipenem and other new antimicrobials. J. Antimicrob Chemother 18 [Suppl] E:67–73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vos, M.C., Vincent, H.H. & Yzerman, E.P.F. Clearance of imipenem/cilastatin in acute renal failure patients treated by continuous hemodiafiltration (CAVHD). Intensive Care Med 18, 282–285 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01706474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01706474