Abstract
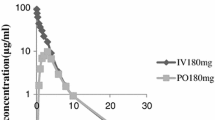
Five healthy fasting male subjects were each given single doses of intravenous ampicillin (471 mg), oral ampicillin tablets (495 mg), oral bacampicillin hydrochloride tablets (562 mg ampicillin equivalent), and oral pivampicillin hydrochloride capsules (491 mg ampicillin equivalent) in a crossover experiment. The resulting concentrations of ampicillin were determined in plasma and urine. The pharmacokinetic analysis was made according to a two-compartment open model. The total distribution volume of unbound ampicillin during the disposition phase was 0.247 ± 0.045 (sd) liter/kg, which is only slightly more than the extracellular fluid, suggesting that tissue binding and intracellular distribution of ampicillin are limited. The bioavailability of the esters bacampicillin (86 ± 11%) and pivampicillin (92± 18%) was significantly greater than that of ampicillin (62 ± 17%); however, the difference between the esters was not statistically significant. The absorption for all drugs given orally proceeded at a constant rate, suggesting zero-order release rates from the products. The absorption rate was highest for bacampicillin (0.89 ± 0.39% of dose absorbed per minute), followed by pivampicillin (0.64 ± 0.19) and ampicillin (0.58 ± 0.16). Bacampicillin also had the shortest lag time for the start of absorption (7.0 ± 0.9 min) under the present conditions. Thus, in comparison with ampicillin, the esters have a higher bioavailability, which, in fact, is close to the theoretically highest possible value by clearance concepts. The higher bioavailability in connection with higher absorption rates may be clinically important in ampicillin treatment by the oral route.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Jalling, A. S. Malmborg, A. Lindman, and L. O. Boréus. Evaluation of a micromethod for determination of antibiotic concentration in plasma.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 4:150–157 (1972).
D. C. Grove and W. A. Randall.Assay Methods of Antibiotics: A Laboratory Manual, Medical Encyclopedia, New York, 1955.
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, Dekker, New York (1975).
M. Ehrnebo. Pharmacokinetics, and distribution properties of pentobarbital in humans following oral and intravenous administration.J. Pharm. Sci. 63:1114–1118 (1974).
K. Diem and C. Leutner.Documenta Geigy—Scientific Tables, 7th ed., Ciba-Geigy, Basel, 1975, pp. 518, 555.
J. Ekstrand, M. Ehrnebo, and L. O. Boréus. Determination of fluoride bioavailability in man following intravenous and oral administration: The importance of renal clearance and urinary flow.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 23:329–337 (1978).
J. C. K. Loo and S. Riegelman. New method for calculating the intrinsic absorption rate of drugs.J. Pharm. Sci. 57:918–928 (1968).
L. Z. Benet. General treatment of linear mammillary models with elimination from any compartment as used in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:536–541 (1972).
C. M. Metzler, G. L. Elfring, and A. J. McEwen. A package of computer programs for pharmacokinetic modeling.Biometrics 30: No. 3 (1974).
Z. Modr and K. Dvoracek. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin and hetacillin.Rev. Czech. Med. 16:84–95 (1970).
T. Bergan and B. Øydvin. Cross over study of pencillin pharmacokinetics after intravenous infusions.Chemotherapy 20:263–279 (1974).
P. Bolme, B. Dahlström, N. Å. Diding, O. Flink, and L. Paalzow. Ampicillin: Comparison of bioavailability and pharmacokinetics after oral and intravenous administration of three brands.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 10:237–243 (1976).
A. Philipson. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin during pregnancy.J. Infect. Dis. 136:370–376 (1977).
T. Bergan. Pharmacokinetic comparison of oral bacampicillin and parenteral ampicillin.Antimicob. Agents Chemother. 13:971–974 (1978).
C. Simon, V. Malerczyk, G. Zieroff, K. Lehmann, and V. Thiesen. Blut-, Harn- und Gallespiegel von Ampicillin bei intravenöser Dauerinfusion.Arzneim. Forsch. 25:654–657 (1975).
W. J. Jusko and G. P. Lewis. Comparison of ampicillin and hetacillin pharmacokinetics in man.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:69–76 (1973).
P. R. Byron and R. E. Notari. Critical analysis of “flip-flop” phenomenon in two-compartment pharmacokinetic model.J. Pharm. Sci. 65:1140–1144 (1976).
J. C. K. Loo, E. L. Foltz, H. Wallick, and K. C. Kwan. Pharmacokinetics of pivampicillin and ampicillin in man.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:35–43 (1974).
M. Ehrnebo. Distribution of ampicillin in human whole blood.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 30:730–731 (1978).
T. C. Eickhoff, J. W. Kislak, and M. Finland. Sodium ampicillin: Absorption and excretion of intramuscular and intravenous doses in normal young men.Am. J. Med. Sci. 70:163–171 (1965).
P. Naumann. Experimentelle und klinische Untersuchungen zur parenteralen Anwendung von Ampicillin.Deutsch. Med. Wochenschr. 90:1085–1092 (1965).
B. Lund, J. P. Kampmann, F. Lindahl, and J. Mølholm Hansen. Pivampicillin and ampicillin in bile, portal and peripheral blood.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:587–591 (1976).
N. O. Bodin. B. Ekström, U. Forsgren, L.-P. Jalar, L. Magni, C.-H. Ramsay, and B. Sjöberg. Bacampicillin: A new orally well-absorbed derivative of ampicillin.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 8:518–525 (1975).
Å. Swan. Gastroinestinal absorption and metabolism of two35S-labelled ampicillin esters.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 9:299–306 (1976).
M. W. Kunst and H. Matie. Absorption of pivampicillin in postoperative patients,Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 8:11–14 (1975).
M. Rozencweig, M. Staquet, and J. Klastersky. Antibacterial activity and pharmaco-kinetics of bacampicillin and ampicillin.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 19:592–597 (1976).
J. Sjövall, L. Magni, and T. Bergan. Pharmacokinetics of bacampicillin compared with those of ampicillin, pivampicillin and amoxicillin.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 13:90–96 (1978).
M. Rowland. Influence of route of administration on drug availability.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:70–74 (1972).
M. Cole, M. D. Kenig, and V. A. Hewitt. Metabolism of pencillins to penicilloic acids and 6-aminopenicillanic acid in man in its significance in assessing pencillin absorption.Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 3:463–468 (1973).
P. J. McNamara, W. A. Colburn, and M. Gibaldi. Absorption kinetics of hydroflumethiazide.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 18:190–193 (1978).
W. A. Colburn, A. R. DiSanto, and M. Gibaldi. Pharmacokinetics of erythromycin on repetitive dosing.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 17:592–600 (1977).
H. Ehrsson, S.-O., Nilsson, M. Ehrnebo, I. Wallin, and G. Wennersten. Effect of food on kinetics of 8-metoxsalen.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 25:167–171 (1979).
E. R. Garrett, H. Roseboom, J. R. Green, and W. Schuermann. Pharmacokinetics of papaverine hydrochloride and the biopharmaceutics of its oral dosage form.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Biopharm. 16:193–208 (1978).
S. C. Penzotti and J. W. Poole. Transport mechanisms ofβ-lactam antibiotics across everted rat gut.J. Pharm. Sci. 63:1803–1806 (1974).
A. Tsuji, E. Nakashima, I. Kagami, N. Honjo, and T. Yamana. Effect of dose-concentration on the absorption of amoxiciliin and ampicillin from the rat intestine.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 29:707–708 (1977).
K. Miyazaki, O. Ogino, M. Nakano, and T. Arita. Intestinal absorption mechanisms of ampicillin derivatives in rats. I. Intestinal absorption of ampicillin derivatives.Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 25:246–252 (1977).
L. Magni, B. Sjöberg, J. Sjövall, and J. Wessman. Clinical pharmacological studies with bacampicillin. In J. D. Williams and A. M. Geddes (eds.),Chemotherapy, Vol. 5: Penicillins and Cephalosporins, Plenum Press, New York, 1976, pp. 109–114.
F. Nordbring. Review of side-effects of aminopenicillins. Infection.7 (suppl. 5):503–506 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council, Project No. 522 (L. O. B.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehrnebo, M., Nilsson, SO. & Boréus, L.O. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin and its prodrugs bacampicillin and pivampicillin in man. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 7, 429–451 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062386
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062386