Abstract
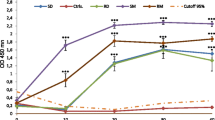
The effect of 5–2,500 infectiveToxocara canis and 5–1,000T. cati eggs on the humoral immune response and on the distribution of larvae in the organism was studied in paratenic hosts — inbred C57BL6/J mice. With each dose ofT. canis eggs the maximal antibody level was recorded on day 56 post infection and was followed by a moderate decline that lasted until day 154 of the experiment. A correlation between the antibody level and the egg count was observed only with the infective dose of 5–50 eggs. A more rapid occurrence of antibodies was recorded in mice infected with a high dose of eggs. In those given 5 and 7T. cati eggs the antibody level exceeded the extinction threshold value only from day 21 to day 84. Low doses ofT. canis (n=5) andT. cati (n=7) eggs caused a comparable distribution of larvae in mice, and the larval recoveries on day 70 post infection ranged between 10.00% and 25.74%. Following a dose of 500T. cati eggs, 22.28% of the larvae were recovered, although only 1.08% were localized in the brain. A dose of 1,000T. canis eggs yielded, 36.37% of the larvae, with as much as 28.13% being found in the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Shehada MN, Herbert IV (1984/85) The migration of larvalToxocara canis in mice. II. Post-intestinal migration in primary infections. Vet Parasitol 17:75–83
Abo-Shehada MN, Al-Zubaidy BA, Herbert IV (1991) Acquired immunity toToxocara canis infection in mice. Vet Parasitol 38:289–298
Aljeboori TI, Ivey MH (1970)Toxocara canis infections in baboons. I. Antibody, white-cell and serum-protein responses following infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 19:249–254
Barriga OO (1988) A critical look at the importance, prevalence and control of toxocariasis and the possibilities of immunological control. Vet Parasitol 29:195–234
Bowman DD, Mika-Grieve M, Grieve RB (1987) Circulating excretory-secretory antigen levels and specific antibody responses in mice infected withToxocara canis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 36:75–82
De Savigny DH (1975) In vitro maintenance ofToxocara canis larvae and a simple method for the production ofToxocara ES antigen for use in serodiagnostic tests for visceral larva migrans. J Parasitol 61:781–782
De Savigny DH, Voller A, Woodruff AW (1979) Toxocariasis: serological diagnosis by enzyme-immunoassay. J Clin Pathol 32:284–288
Dubinský P, Hovorka J, Juriš P (1991) Toxocarosis of carnivores in the urban area from the aspect of environmental protection. Proceedings, 1st symposium on diseases of carnivores, 9–11 September, Košice, Slovak Republic, pp 59–60
Dunsmore JD, Thompson RC, Bates IA (1983) The accumulation ofToxocara canis larvae in the brains of mice. Int J Parasitol 13:517–521
Gillespie SH (1988) The epidemiology ofToxocara canis. Parasitol Today 4:180–182
Havasiová K (1989) Selected serological methods in the immunodiagnosis of human larval toxocarosis. Dissertation Thesis, Helminthological Institute SAS, Košice, Slovak Republic
Havasiová K, Dubinský P, Štefancíková A (1993) A seroepidemiological study ofToxocara infection in humans in the Slovak Republic. J Helminthol 67:291–296
Kayes SG, Omholt PE, Grieve RB (1985) Immune responses of CBA/J mice to graded infections withToxocara canis. Infect Immun 48:697–703
Lohmann K, Schnieder T, Stoye M (1989) Verhalten und Pathogenität der Larven vonToxocara canis Werner 1782 (Anisakidae) in der Maus. Zentralbl Veterinarmed [B] 36:609–618
Mancal P (1987) Methods of enzyme immunoanalysis. USOL, Prague
Parsons JC, Grieve RB (1990) Effect of egg dosage and host genotype on liver trapping in murine larval toxocariasis. J Parasitol 76:53–58
Prociv P (1986)Toxocara pteropodis, T. canis andT. cati infections in guinea pigs. Trop Biomed 3:97–106
Prokopic J, Figallová V (1982) Migration of some roudworm species in experimentally infected white mice. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 29:309–313
Tomašovicová O, Havasiová-Reiterová K, Dubinský P, Hovorka I (1993) Intrauterine and lectogenic transfer ofToxocara canis larvae in paratenic hosts. Helminthologia 30:111–113
Sugane K, Oshima T (1983) Trapping of large numbers of larvae in the livers ofToxocara canis-reinfected mice. J Helminthol 57:95–99
Uhlíková M, Hübner J (1983) Larval toxocarosis. Avicenum, Prague
Unbehauen I (1991) Untersuchunger über das Vorkommen von Darmparasiten bei Katzen im Raum Lübeck. Inaugural Dissertation, Tierärztlichen Hochschule, Hannover, Germany
Van Knapen F, Leusden J van, Polderman AM, Framchimont JH (1983) Visceral larva migrans: examination by means of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of human sera for antibodies to the excretory-secretory antigens of the second-stage larvae ofToxocara canis. Z Parasitenkd 69:113–118
Worley G, Green JA, Frothingham TE, Sturner RA, Walls KW, Pakalnis VA, Ellis GS (1984)Toxocara canis infection: clinical and epidemiological association with seropositivity in kindergarten children. J Infect Dis 149:591–597
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Havasiová-Reiterová, K., Tomašovicová, O. & Dubinský, P. Effect of various doses of infectiveToxocara canis andToxocara cati eggs on the humoral response and distribution of larvae in mice. Parasitol Res 81, 13–17 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932411
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00932411