Abstract
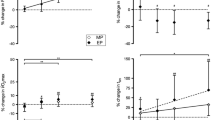
We evaluated the impact of (s.c.) recombinant human erythropoietin (r-HuEPO) therapy on the hematological status, exercise capacity, and dietary intake of nine pediatric patients (mean age 12.4±3.2 years) receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Five children without medical illness served as controls for the exercise testing portion of the study. Following 7.9±2.8 weeks of twice weekly r-HuEPO (50 units/kg per dose), the hematocrit increased from 21.9±3.5% to 31.3±2.5% (P<0.001). A further increase to 33.2±3.0% occurred after 2 months of once weekly therapy. The blood transfusion requirement decreased from 0.5 transfusions per patient-month to 0.05 transfusions per patient-month (P<0.01). Graded exercise testing demonstrated an increase in peak oxygen consumption from 17.8±5.2 to 24.0±7.6 ml/kg per min (P<0.01). The oxygen consumption at anaerobic threshold increased from 13.1±3.9 to 17.1±3.5 ml/kg per min (P<0.02). Treadmill time increased from 5.3±1.2 to 7.5±1.3 min (P<0.001). In each case, the percentage improvement was significantly greater than the improvement seen in the control population. Dietary evaluation revealed no significant change in caloric or protein intake, despite a subjectively improved appetite. r-HuEPO, given by the s.c. route, corrects the anemia and improves the exercise capacity of pediatric patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ulmer HE, Greiner H, Schuler HW, Scharer K (1987) Cardiovascular impairment and physical working capacity in children with chronic renal failure. Acta Paediatr Scand 67:43–49
Holliday MA (1978) Growth retardation in children with renal disease. In: Edelman CM (ed) Pediatric kindney disease. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 331–341
Eschbach JW, Kelly MR, Haley NR, Abels RI, Adamson JW (1989) Treatment of the anemia of progressive renal failure with recombinant human erythropoietin. N Engl J Med 321:158–163
Mayer G, Thum J, Cada M, Stummvoll HK, Graf H (1988) Working capacity is increased following recombinant human erythtropoietin treatment. Kidney Int 34:525–528
Montini G, Zacchello G, Baraldi E, Zanconato S, Suppiej A, Fabris F, Andreetta B, pavanello L, Zacchello F (1990) Benefits and risks of anemia correction with recombinant human erythropoietin in children maintained by hemodialysis. J Pediatr 117:556–560
Macdougall IC, Roberts DE, Neubert P, Dharmasena AD, Coles GA, Williams JD (1989) Pharmacokinetics of intravenous, intraperitoneal, and subcutaneous recombinant erythropoietin in patients on CAPD. In: Baldamus CA, Scigalla P, Wieczoerek L, Koch KM (eds) Erythropoietin: from molecular structure to clinical application. Karger, Basel, pp 112–121
Reybrouck TM, Weymans M, Stijns H, Knops J, Hauwaert L van der (1986) Ventilatory anaerobic threshold for evaluating exercise performance in children with congenital left-to-right intercardiac shunt. Pediatr Cardiol 7:19–24
Froelicher VF, Marcondes GD (1989) Manual of exercise testing. Year Book Medical, Chicago
Sinek N, Sabath R, Sotiropoulos G (1990) A comparison of directly measured oxygen uptake to a predicted value and field performance in prepubescent boys. Ped Exer Sci 2:179
Pate R, Lonnett M (1988) In: Blair S, Panter P, Pate R, Smith L, Taylor C (eds) Resource Manual for Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Lea et Febiger, p 38
Logan Computrition System. Computrition, Chatsworth
Science and Education Administration, United States Department of Agriculture (1976–1984) Composition of foods. Agriculture Handbook. Government Printing Office, Washington, D. C.
Chandra M, Clemons GK, McVicar MI (1988) Relation of serum erythropoietin levels to renal excretory functin: evidence for lowered set point for erythropoietin production in chronic renal failure. J Pediatr 113:1015–1021
Chandra M, Clemons GK, McVicar M, Wilkes B, Bluestone PA, Mailloux LU, Mossey RT (1988) Serum eryhtropoietin levels and hematocrit in end-stage renal disease: influence of the mode of dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 12:208–213
Offner G, Hoyer PF, Latta K, Winkler L, Brodehl J, Scigalla P (1990) One year's experience with recombinant erythropoietin in children undergoing continuous ambulatory or cycling peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 4:498–500
Kitagawa T, Ito K, Komatsu Y, Ito H, Sakai T, Sakai K, Takada T, Takahashi S, Tzusuki K, Seino Y, Wada H (1990) The clinical studies of recombinant human erythropoietin (Epoetin) in children with renal anemia. Contemp Dial Nephrol 11:40–46
Sinai-Trieman L, Salusky IB, Fine RN (1989) Use of subcutaneous recombinant human erythropoietin in children undergoing continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis. J Pediatr 114:550–554
Eschbach JW, Adamson JW (1989) Guidelines for recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 14:2–8
Scigalla P, Bonzel KE, Bulla M, Burghard R, Dippel J, Geisert J, Leumann E, Lilien T, Muller-Wiefel DE, Offner G, Pistor K, Zoellner K (1989) In: Baldamus CA, Scigalla P, Wieczorek L, Koch KM (eds) Erythropoietin: from molecular structure to clinical application. Karger, Basel, pp 227–241
Van Wyck DB (1989) Iron management during recombinant human eryhtropoietin therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 14:9–13
Cook JD, Skikne BS (1987) Intestinal regulation of body iron. Blood Rev 1:267–272
Hamstra RD, Block MH, Schocket AL (1980) Intravenous iron dextran in clinical medicine. JAMA 243:1726–1731
Washington RL, VanGundy JC, Cohen C, Sondheimer H, Wolfe R (1988) Normal aerobic and anaerobic exercise data for North American school-aged children. J Pediatr 112:223–233
Robertson HT, Haley NR, Guthrie M, Cardenas D, Eschbach JW, Adamson JW (1990) Recombinant erythropoietin improves exercise capacity in anemic hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 15: 325–332
Ellis P, Paganini E (1990) Epoetin alfa therapy: dietary considerations. In: Alan J Watson (ed) New directions in anemia, a profile of the anemic dialysis patient (report) vol 8, no. 1. Amgen, Calif.
Warady BA, Kriley M, Lovell H, Farrell SE (1988) Growth and development of infants with end-stage renal disease receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. J Pediatr 112:714–719
Grimm G, Stockenhuber F, Schneeweiss B, Madl C, Zeitlhofer J, Schneider B (1990) Improvement of brain function in hemodialysis patients treated with erythropoietin. Kidney Int 38:480–486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Warady, B.A., Sabath, R.J., Smith, C.A. et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in pediatric patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Pediatr Nephrol 5, 718–723 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00857883
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00857883