Abstract
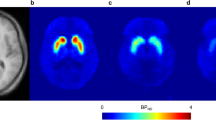
Raclopride, a highly selective D2-dopamine receptor antagonist, was administered in doses up to 4 mg b.i.d. to ten schizophrenic patients in an open label non-comparative study lasting 4 weeks. Safety, tolerability, potential antipsychotic effect, prolactin response and drug effect on plasma homovanillic acid were evaluated. Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy was determined by positron emission tomography (PET). No major deviations were found in biochemical and physiological safety parameters. Raclopride was well tolerated. The mean BPRS score was reduced by 55% at endpoint. In the global evaluation seven patients were “very much” or “much” improved. Extrapyramidal side effects were recorded in four patients and disappeared after dose reduction or single doses of biperiden. An increase in plasma prolactin of short duration was observed in both sexes. A significant decrease of plasma HVA was obtained after 4 weeks of treatment. In two of the patients the central D2-dopamine receptors occupancy was measured using PET. The receptor occupancy was 68 and 72% which is the same as that found in patients treated with conventional neuroleptics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergström M, Boethius J, Eriksson L, Greitz T, Ribbe T, Widen L (1981) Head fixation device for reproducible positron alignment in transmission CT and positron emission tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 8:74–87
Braude WM, Barnes TRE, Gore SM (1983) Clinical characteristics of akathisia. A systematic investigation of acute psychiatric inpatient admissions. Br J Psychiatry 43:139–150
Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH (1976) Dopamine receptor binding clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science 192:481–483
Dahl SG (1986) Plasma level monitoring of antipsychotic drugs: Clinical utility. Clin Pharmacokinet 11:36–61
ECDEU Manual — Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology (1976) US Department of Health, Education and Welfare
Edlund PO (1986) Automated analysis of homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid in biological fluids by coupledcolumn liquid chromatography and dual coulometric-amperometric detection J Pharm Biomed Anal 4:641–652
Farde L, Ehrin E, Eriksson L, Greitz T, Hall H, Hedström C-G, Litton J-E, Sedvall G (1985) Substituted benzamides as ligands for visualization of dopamine receptor binding in the human brain by positron emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3863–3867
Farde L, Hall H, Ehrin E, Sedvall G (1986) Quantitative analysis of D2 dopamine receptor binding in the living human brain by PET. Science 231:258–261
Farde L, Halldin C, Stone-Elander S, Sedvall G (1987a) PET analysis of human dopamine receptor subtypes using11C-SCH 23390 and11C-raclopride. Psychopharmacology 92:278–284
Farde L, Wiesel F-A, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1987b) Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Arch Gen Psychiatry (in press)
Farde L, Wiesel F, Hall H, Halldin C, Stone-Elander S, Sedvall G (1987c) PET-determination of striatal D2-dopamine receptors in drug-naive schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44:671–672
Fuxe K, Ögren S-O, Fredholm B, Agnati L, Hökfelt T, Perez de la Mora M (1976) Possibilities of a differential blockade of central monoamine receptors. In: de Ajuriaguerra J, Tissot R (eds) Rhinencephale neurotransmetteurs et psychoses. Symposium Bel-Air V, Georg & Cie, Geneve, pp 253–289
Härnryd C, Bjerkenstedt L, Björk K, Gullberg B, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A, Wik G, Åberg-Wistedt A (1984a) Clinical evaluation of sulpiride in schizophrenic patients — a double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Acta Psychiatr Scand [Suppl] No 311, 69:7–30
Härnryd C, Bjerkenstedt L, Gullberg B, Oxenstierna G, Sedvall G, Wiesel F-A (1984b) Time course for effects of sulpiride and chlorpromazine on monoamine metabolite and prolactin levels in cerebrospinal fluid from schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand [Suppl] 311, 69:75–92
Jenner P, Testa B, van de Waterbeemd, Marsden (1982) Interaction of substituted benzamide drugs with cerebral dopamine receptors. In: Ackenheil M, Matussek N (eds) Special aspects of psychopharmacology
Köhler C, Hall H, Ögren S-O, Gawell L (1985) Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of3H-raclopride. A potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2251–2259
Mann BS, Moslehuddin KS, Owen RT, Clayton AR, Rohatgi KK, Sud P, Vaddadi KS (1985) A clinical assessment of zuclopenthixol dihydrochloride (clopixol tablets) in the treatment of psychotic illness. Pharmatherapeutica 4:387–392
Montgomery SA, Taylor P, Montgomery D (1978) Development of a schizophrenia scale sensitive to change. Neuropharmacology 17:1061–1063
Ögren S-O, Hall H, Köhler C, Magnusson O, Sjöstrand S-E (1986) The selective dopamine D2 receptor antagonist raclopride discriminates between dopamine-mediated motor functions. Psychopharmacoloty 90:287–294
Overall JE, Gorman DR (1962) The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychological reports, Southern Universities Press 10:799–812
Pickar D, Labarca R, Linnoila M, Roy A, Hommer D, Everett D, Paul S (1984) Neuroleptic-induced decrease in plasma homovanillic acid: Correlation with antipsychotic activity in schizophrenic patients. Science 225:954
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1980) Relationship of neuroleptic drug effects at brain dopamine, serotonin, adrenergic and histamine receptors to clinical potency. Am J Psychiatry 137:1518–1522
Sedvall G, Farde L, Persson A, Wiesel FA (1986) Imaging of neurotransmitter receptors in the living human brain. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:995–1005
Seeman P, Lee T, Chau-Wong M, Wong K (1976) Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine receptors. Nature 261:717–719
Silverstone T, Levine S, Freeman HL, Dubini A (1984) Zetidoline, a new antipsychotic — first controlled trial in acute schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 145:294–299
Toru M, Schimazonon Y, Miyasaka M, Kokubo T, Mori Y, Nasu T (1972) A double-blind comparison of sulpiride with chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. J Clin Pharmacol 12:221–229
Wagner HN, Burns HD, Dannals RF, Wong DF, L»ngström B, Duelfer T, Frost JJ, Raert HT, Links JM, Rosenblom SB, Lukas SE, Kramer AV, Kuhar MJ (1983) Imaging dopamine receptors in the human brain by positron tomography. Science 221:1264–1266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farde, L., Wiesel, F.A., Jansson, P. et al. An open label trial of raclopride in acute schizophrenia. Confirmation of D2-dopamine receptor occupancy by PET. Psychopharmacology 94, 1–7 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735871
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00735871