Summary
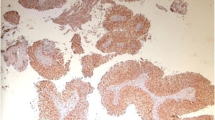
Acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF) is a regulatory peptide which, on account of its structural homologies with the products of oncogenes, is involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and motility. We previously reported the presence of aFGF in the urine of patients with transitional cell carcinoma (TCC). aFGF can also induce the motility of a rat-derived bladder carcinoma cell line (NBTII). This immunohistochemical study used polyclonal rabbit antibodies against acidic and basic FGF and peroxidase detection. Native NBTII nude mice xenografts and aFGF transfected NBTII (NFS14) nude mice xenografts were used as tissue controls for antibody specificity. The samples included 4 normal urothelia and 12 TCC. In addition, cytospins of 4 different tumoral cell lines of human bladder and normal bladder cells were stained. The results showed strong immunostaining in all tumoral urothelium samples using anti-aFGF and a very low amount of staining or none at all in healthy tissues. A primary analysis suggested that the strongest reaction was obtained in high-grade tumors (3 + vs + for lower-grade tumors). Using bFGF antibody, strong immunohistochemical staining was detected on basal membranes and stromal vessels and none in urothelium. These data confirm aFGF expression in the epithelial cell compartment of bladder cancer and the likely involvement of this regulatory peptide in the biology of TCC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyer B, Tucker GC, Valles AM, Franke WW, Thiery JP (1989) Rearrangements of desmosomal and cytoskeletal proteins during the transition from epithelial to fibroblastoid organization in cultured rat bladder carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 109:1495
Bubenik J, Baresova M, Viklicky V, Jukuobkova J, Sainerova H, Donner J (1973) Established cell line of urinary bladder carcinoma (T-24) containing tumour specific antigen. Int J Cancer 11:765
Caruelle D, Grassi J, Courty J, Groux-Muscatelli B, Pradelles P, Barritault D, Caruelle JP (1988) Development and testing of radio and enzyme immunoassay for acidic fibroblast growth factor. Anal Biochem 173:328
Chodak GW, Schneiner CJ, Zetter BR (1981) Urine from patients with TCC stimulates migration of capillary endothelial cells. N Engl J Med 305:869
Chodak GW, Hospelhorn V, Judge SM, Mayforth R, Koeppen H, Sasse J (1988) Increased levels of fibroblast growth factor-like activity in urine from patients with bladder or kidney cancer. Cancer Res 48:2083
Coughlin SR, Barr PJ, Cousens LS, Freto LJ, Williams LT (1988) Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors stimulate tyrosine kinase activity in vivo. J Biol Chem 263:988
Elliott AY, Bronson DL, Stein N, Fraley EE (1976) In vitro cultivation of epithelial cells derived from tumors of the human urinary tract. Cancer Res 36:365
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M, Sasse J, Wadzinski M, Ingber D, Vlodavsky I (1988) Heparin-binding angiogenic protein-basic fibrovlast growth factor is stored within basement membrane. Am J Pathol 130:393
Gavrilovic J, Moens G, Thiery JP, Jouanneau J (1990) Expression of transfected transforming growth factor α induces a motile fibroblast-like phenotype with extracellular matrix-degrading potential in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell Reg 1:1003
Goustin AS, Leof EB, Shipley GD, Moses HL (1986) Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res 46:1015
Klagsbrun M (1989) The fibroblast growth factor family: structural and biological properties. Prog Growth Factor Res 1:207
Klagsbrun M, Longer R, Levenson R, Smith S, Lille Hei C (1977) The stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in chondiocytes and 3T3 cells by a growth factor isolated from cartilage. Exp Cell Res 105:99
Moscatelli D (1988) Metabolism of receptor-bound and matrix bound basic fibroblast growth factor by bovine capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 107:753
Olwin B, Burnus L, Kudha A, Weddecke B, Shaw D, Zuber M (1990) Characterization of a putative fibroblast growth factor receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. J Cell Biochem 14F:91
Rettenmier CW, Chen JH, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ (1985) The product of the c.fms proto-oncogene: a glycoprotein with associated tyrosine kinase activity. Science 228:320
Rigby CC, Franks LM (1970) A human tissue culture cell line from a transitional cell tumor of a urinary bladder: growth, chromosome pattern and ultrastructure. Br J Cancer 24:746
Schweigerer L, Neufeld G, Friedman J, Abraham JA, Fiddes JC, Gospodarowicz D (1987) Capillary endothelial cells express basic fibroblast growth factor: a mitogen that promotes their own growth. Nature 325:257
Shahabuddin S, Arnold F, Costello CG, Kumar S (1984) Tumour angiogenesis factor in urological cancers. Br J Urol 56:490
Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1985) Autocrine growth factors and cancer. Nature 313:745
Sporn MB, Todaro GJ (1980) Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med 303:878
Thomas KA (1988) Transforming potential of fibroblast growth factor genes. TIBS 13:327
Valles AM, Boyer B, Badet J, Tucker GC, Barritault D, Thiery JP (1990) Acidic fibroblast growth factor is a modulator of epithelial pasticity in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1124
Valles AM, Tucker GC, Thiery JP, Boyer B (1990) Alternative patterns of mitogenesis and cell scattering induced by acidic FGF as a function of cell density in a rat bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell Reg 1:975
Vigny M, Ollier-Hartmann MP, Lavigne M, Fayen N, Jeanny JC, Laurent M, Courtois Y (1988) Specific binding of basic fibroblast growth factor to basement membrane like structures and to purified heparan sulfate proteoglycan of EHS tumor. J Cell Physiol 137:321
Vlodavsky I, Folkman J, Sullivan R, Freidman R, Ishai-Michaeli R, Sasse J, Klagsbrun M (1987) Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2292
Williams RD (1980) Human urologic cancer cell lines. Invest Urol 17:359
Yayon A, Klagsbrun M (1990) Autocrine regulation of cell growth and transformation by basic fibroblast growth factor. Cancer Metastasis Rev 9:191
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by Commission de Recherche Clinique de Association Claude Bernard and Université Paris XII
This paper was selected for publication in Urological Research from the program of the 1991 meeting of the European Society of Urological Oncology and Endocrinology (ESUOE)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ravery, V., Jouanneau, J., Gil Diez, S. et al. Immunohistochemical detection of acidic fibroblast growth factor in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Urol. Res. 20, 211–214 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00299719
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00299719