Abstract
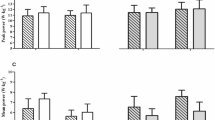
Physical activity has been suggested to be one of the determinants of bone turnover and to prevent age-related bone loss. To examine this we measured the serum levels of osteocalcin (bone Gla-protein, BGP), C-terminal procollagen peptide (PICP), serum alkaline phosphatase, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase, and S-calcium as indices of bone formation in 19 actively performing and 15 ex-lifters. All were nationally or internationally ranked male athletes. Their values were compared with those from 38 age- and gendermatched controls. Actively performing weight lifters had 35% higher (P<0.05) serum concentration of osteocalcin than the controls. The ex-lifters did not differ from the agematched controls. Also serum calcium was elevated in active lifters (6%) (P<0.01) but not in ex-lifters. No difference was found for serum-ALP, B-ALP, or PICP in either of the groups. Our study indicates that in addition to an already documented and well-known higher bone mineral density in heavily exercising athletes, they have an indication of higher bone formation as measured by biochemical markers. In athletes who have retired from competitional training, however, the bone formation does not differ from that of more sedentary controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karlsson MK, Johnell O, Obrant K (1993) Bone mineral density in weight lifters. Calcif Tissue Int 52:212–215
Nilsson BE, Westlin NE (1971) Bone density in athletes. Clin Orthop Rel Res 77:179–182
Gutin B, Casp MJ (1992) Can vigorous exercise play a roll in osteoporosis prevention? A Review. Osteoporosis Int 2:55–69
Colletti LA, Edwards J, Gordon L, Shary J, Bell NH (1989) The effect of muscle building exercise on bone mineral density of radius, spine and hip in young men. Calcif Tissue Int 45:12–14
Bewier W, Pyka G, Kozak K, Newhall K, Wisswell R, Marcus R (1989) Aerobic capacity, muscle strength and bone density in elderly men and women. J Bone Miner Res 4:421–432
Donaldson CL, Huller SE, Vogel JM, Huttner S, Bayers JH, McMillan D (1970) Effect of prolonged bedrest on bone mineral. Metabolism 19:1071–1084
Rambaut PC, Johnston RS (1979) Prolonged weightlessness and calcium loss in men. Acta Astronaut 6:1113–1116
Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bisec JP, Hanson J (1990) Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone mineral and soft tissue composition. Am J Clin Nutr 51:1106–1112
Price PA, Otsuka AS, Poster JW, Kristaponis J, Roman N (1976) Primary structure of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein from bovine bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:1447
Hauschka PV, Lian BJ, Gallop PM (1975) Direct identification of the calcium-binding amino acid, gamma-carboxyglutamate, in mineralized tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72(10):3925–3929
Lian JB, Grundberg CM (1988) Osteocalcin. Biochemical consideration and clinical applications. Clin Orthop 226:267–291
Delmas PD (1988) Biochemical markers of bone turnover in osteoporosis. In: Riggs LB, Riggs MJL (eds) Osteoporosis: etiology, diagnosis and management. Raven Press, New York, pp 297–316
Delmas PD (1990) Biochemical markers of bone turnover for the clinical assessment of metabolic bone disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 19(1):1–18
Price PA, Parthemore JG, Deftos LE (1980) New biochemical marker for bone metabolism. J Clin Invest 66:878
Slovic DM, Grundberg CM, Neer RM, Lian JB (1984) Clinical evaluation of bone turnover by serum osteocalcin measurements in hospital settings. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 59:228
Kraenzlin M, Taylor A, Baylink D (1989) Biochemical markers for bone formation and bone resorption. In: Clinical impact of bone and connective tissue markers. Academic Press, London, pp 289–303
Duda RJ, O'Brien JF, Katzmann JA, Peterson JM, Mann KG, Riggs BL (1988) Concurrent assays of circulating bone Gla-protein and bone alkaline phosphatase: effect of sex, age and metabolic bone disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 66(5):951–957
Åkesson K, Ljunghall S, Gärdsell P, Sernbo I, Obrant KJ (1993) Serum osteocalcin and fracture susceptibility in elderly women. Calcif Tissue Int 53:86–90
Garnero P, Delmas PD (1993) Assessment of the serum levels of bone alkaline phosphatase with a new immunoradiometric assay in patients with metabolic bone disease. JCEM 77(4):1046–1053
Bowers G, Comb RB (1975) Measurement of total alkaline phosphatase activity in human serum. Clin Chem 21(13):1988–1995
Bell NH, Godsen RN, Henry DP, Shary J, Stein S (1988) The effect of muscle building exercise on Vitamin D and mineral metabolism. J Bone Miner Res 3:369–373
Karlsson M, Johnell O, Obrant KJ (1994) High bone mineral density returns to normal after cessation of training career. Orthopedic Research Society, New Orleans, USA, vol 19(1):35–36
Hassager C, Riis BJ, Podenphant J, Christiansen C (1989) Nandrolone decanoate. Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis for two years and effects of withdrawal. Maturitas 11:305–317
Fiore C, Cottini E, Fargetta C, Di Salvo G, Foti R, Raspagliesi M (1991) The effects of muscle-building exercise on forearm bone mineral content and osteoblast activity in drug-free and anabolic steroids self-administering young men. Bone Miner 13(1):77–83
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, M.K., Vergnaud, P., Delmas, P.D. et al. Indicators of bone formation in weight lifters. Calcif Tissue Int 56, 177–180 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298605
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298605