Summary
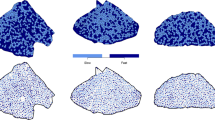
Methods that objectively assess the muscle fibre-type arrangement may improve the detection of fibre-type grouping, a diagnostic sign of a denervation and reinnervation process. To distinguish between a diseased and a normal muscle, there is a need for quantitative data on the fibre-type arrangement in healthy human muscles at different ages. In this study, cross-sections were prepared of whole autopsied vastus lateralis muscle from 24 previously physically healthy men, aged 15 to 83 years. The arrangements of type 1 and type 2 fibres were assessed in terms of the number of enclosed fibres in individual fascicles throughout each muscle. Recent improvements to the enclosed fibre method were used to define measures of randomness which facilitated the combination of several sample areas and the quantification of the fibre-type arrangements. Segregation was typical for young muscles, randomness was most common between 30 and 50 years of age, while some fibre-type grouping was considered “normal” in old muscles. The arrangements of type 1 and type 2 fibres were quantitatively similar, irrespective of the age of the individual. The results imply that the fibre population changes considerably during a lifetime, and that it undergoes a continuous denervation and reinnervation process with normal ageing. Because of its importance, age should be accommodated in the analysis of a muscle sample, irrespective of the statistical model and method used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown WF, Strong MJ, Snow R (1988) Methods for estimating numbers of motor units in biceps-brachialis muscles and losses of motor units with aging. Muscle Nerve 11: 423–432
Downham DY, Wilson BC, Lexell J, Sjöström M (1987) Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscle: a method for the detection of neurogenic muscle disorders. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol 4: 81–91
Dubowitz V (1985) Muscle biopsy: a practical approach 2nd edn. Baillière Tindall, London, p 96
Froes MMQ, Kristmundsdottir F, Mahon M, Cumming WJK (1987) Muscle morphometry in motor neuron disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 13: 405–419
Jennekens FGI, Tomlinson BE, Walton J (1971) Data on the distribution of fibre types in five human limb muscles: an autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 14: 245–257
Jennekens FGI, Tomlinson BE, Walton J (1971) Histochemical aspects of five limb muscles in old age: an autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 14: 259–276
Johnson MA, Polgar J, Weightman D, Appleton D (1973) Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles: an autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 18: 111–129
Lexell J, Downham D, Sjöström M (1983) Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscle. A statistical and computational model for the study of fibre-type grouping and early diagnosis of skeletal muscle fibre denervation and reinnervation. J Neurol Sci 61: 301–314
Lexell J, Downham D, Sjöström M (1984) Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscle. A statistical and computational study of the fibre-type arrangement in m. vastus lateralis of young, healthy males. J Neurol Sci 65: 353–365
Lexell J, Downham D, Sjöström M (1986) Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscle. Fibre-type arrangement in m. vastus lateralis from three groups of healthy men between 15 and 83 years. J Neurol Sci 72: 211–222
Lexell J, Downham D, Sjöström M (1987) Morphological detection of neurogenic muscle disorders: how can statistical methods aid diagnosis? (review). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 75: 109–115
Lexell J, Taylor CC, Sjöström M (1988) What is the cause of the ageing atrophy? Total number, size and proportion of different fiber types studied in whole vastus lateralis muscle from 15-to 83-year-old men. J Neurol Sci 84: 275–294
Slater CR, Harris JB (1988) Motor unit anatomy and physiology. In: Walton J (ed) Disorders of voluntary muscle, 4th edn. Churchill Livingstone, London, p 22
Stålberg E, Borges O, Ericsson M, Essén-Gustavsson B, Fawcett PR, Nordesjö LO, Nordgren B, Uhlin R (1989) The quadriceps femoris muscle in 20–70-year-old subjects: relationship between knee extension torque, electrophysiological parameters, and muscle fiber characteristics. Muscle Nerve 12: 382–389
Tomlinson BE, Irving D (1977) The numbers of limb motor neurons in the human lumbosacral cord throughout life. J Neurol Sci 34: 213–219
Tomonaga M (1977) Histochemical and ultrastructural changes in senile human skeletal muscle. J Am Geriatr Soc 25: 125–131
Wilson BC, Downham DY, Lexell J, Sjöström M (1988) Some probability models for diagnosing neurogenic disorders. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol 5: 167–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants and scholarships from the Swedish Work Environment Fund, the Swedish Institute, the Tore Nilsson Foundation, the Swedish Society of Medicine and the Research Concil of the Swedish Sports Federation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lexell, J., Downham, D.Y. The occurrence of fibre-type grouping in healthy human muscle: a quantitative study of cross-sections of whole vastus lateralis from men between 15 and 83 years. Acta Neuropathol 81, 377–381 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293457
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293457