Summary
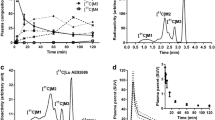
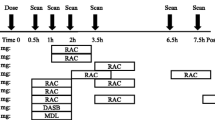
Eight normal subjects (3 females and 5 males) were studied using intravenous L-11C] deprenyl and positron emission tomography. In a single blind study one subject received tracer alone, one subject received an oral pre-dose of 20 mg of L-deprenyl and 6 subjects received oral pre-doses of 10 to 50 mg of a novel reversible MAO-B inhibitor (Ro 19-6327). Dynamic PET scans beginning 12 h after the oral dose were collected over 90 min and arterial blood was continuously sampled. Data analysis was modelled for two tissue compartments and using an iterative curve fitting technique the value of the rate constant for irreversible binding of L-[11C] deprenyl to MAO-B (k3) in whole brain was obtained for each subject.
The dose response curves obtained indicated that a dose of at least 0.48 mg·kg−1 of Ro 19-6327 was necessary for >90% decrease in whole brain k3. Inhibition of MAO-B in platelets isolated from blood samples taken at the time of scanning correlated strongly with decrease in whole brain k3 (r=0.949).
The results indicate that PET can be used to determine the dose of Ro 19-6327 necessary to inhibit >90% of brain MAO-B. This technique is an attractive alternative to traditional large scale patient-based dose-finding studies. Moreover it is shown that inhibition of platelet MAO-B can be used as a marker for central MAO-B inhibition with Ro 19-6327.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine. Science 219: 979–80
Birkmayer W, Riederer P (1983) Parkinson's disease. Springer, Vienna
Tetrud JW, Langston JW (1989) The effect of deprenyl (selegiline) on the natural history of Parkinson's Disease. Science 245: 519–522
The Parkinson Study Group (1989) Effect of deprenyl on the progression of disability in early Parkinson's Disease. N Engl J Med 321: 1364–1371
Da Prada M, Kettler R, Keller HH, Burkard WP (1988) Ro 19-6327, a reversible, highly selective inhibitor of the type B monoamine oxidase, completely devoid of tyramine-potentiating effects: comparison with selegiline. In: Dahlstrom A (ed) Progress in catecholamine research part B: central aspects, Liss, pp 359–363
Cesura AM, Galva MD, Imhof R, Picotti GB, Da Prada M (1989) [3H] Ro 19-6327: a reversible ligand and affinity labelling probe for monoamine oxidase B. Eur J Pharmacol 162: 457–465
Da Prada M, Kettler R, Keller HH, Bonetti EP, Imhof R (1986) Ro 16-6491: a new reversible and highly selective MAO-B inhibitor protects mice from the dopaminergic toxicity of MPTP. In: Yahr MD, Bermann KJ (eds) A dvances in neurology, vol 45: Parkinson's disease. Raven Press, New York, p 175
Kettler R, DaPrada M (1989) Platelet MAO-B activity in humans and stumptail monkeys; in vivo effects of the reversible MAO-B inhibitor Ro 19-6327. In: Przuntek H, Riederer P (eds) Early diagnosis and preventive therapy in Parkinson's Disease. Springer, New York, pp 213–219
Spinks TJ, Jones T, Gilardi MC, Heather JD (1988) Physical performance of the latest generation of commercial positron scanner. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 35: 721–725
Lammertsma AA, Frackowiak RSJ, Hoffman JM, Huang S-C, Weinberg IN, Dahlbom M, MacDonald NS, Hoffman EJ, Mazziotta JC, Heather JD, Forse GR, Phelps ME, Jones T (1989) The C15O2 build-up technique to measure regional cerebral blood flow and volume of distribution of water. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9: 461–470
Frost JJ, Douglass KH, Mayberg HS, Dannals RF, Links JM, Wilson HT, Ravert HT, Crozier WC, Wagner HN Jr (1989) Multicompartmental Analysis of [11C]-Carfentanil Binding to Opiate Receptors in Humans Measured by Positron Emission Tomography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9: 398–409
Maycock AL, Abeles RH, Salach JI, Singer TP (1976) The structure of the covalent adduct formed by the interaction of 3-dimethylamino-1-propyne and the flavine of mitochondrial amine oxidase. Biochemistry 15: 114–125
Fowler JS, Macgregor RR, Wolf AP, Arnett CD, Dewey SL, Schlyer D, Christman D, Logan J, Smith M, Sachs H, Aquilonius SM, Bjurling P, Halldin C, Hartvig P, Leenders KL, Lundqvist H, Oreland L, Stalnacke C-G, Langstrom B (1987) Mapping human brain monoamine oxidase A and B with 11C-labelled suicide inactivators and PET. Science 235: 481–485
Arnett CD, Fowler JS, Macgregor RR, Schlyer DJ, Wolf AP, Langstrom B, Halldin C (1987) Turnover of brain monoamine oxidase measured in vivo by positron emission tomography using L-[11C] Deprenyl. J Neurochem 49: 522–527
Schulz R, Antonin K-H, Hoffman E, Jedrychowski M, Nilsson E, Schick C, Bieck PR (1989) Tyramine kinetics and pressor sensitivity during monoamine oxidase inhibition by selegiline. Clin Pharmacol Ther 46: 528–536
Winblad B, Gottfries C-G, Oreland L, Wiberg A (1979) Monoamine oxidase in platelets and brains of non-psychiatric and non-neurological geriatric patients. Med Biol 57: 129–132
Young WF, Laws ER, Sharbrough FW, Weinshilboum RM (1986) Human monoamine oxidase. Lack of brain and platelet correlation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43: 604–609
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bench, C.J., Price, G.W., Lammertsma, A.A. et al. Measurement of human cerebral monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) activity with positron emission tomography (PET): a dose ranging study with the reversible inhibitor Ro 19-6327. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 40, 169–173 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280072
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280072