Abstract
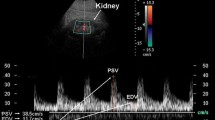
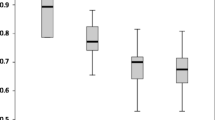
Acute rejection episodes are the most common cause leading to loss of renal grafts in the early postoperative phase. Doppler sonography presents a noninvasive tool to detect increased arterial blood flow resistance as a result of rejection. This can be measured by the increase in the resistive index (RI) and the pulsatility index (PI). In a prospective study including 65 consecutive patients we investigated whether the detection of rejection episodes is improved by determining RI or PI serially twice a week instead of performing a single examination in cases of transplant dysfunction. In 330 examinations with a color-coded Doppler device (Philips QAD 1, Philips Medical Systems Hamburg, Germany) flow profiles were obtained by means of pulse-wave Doppler over at least three interlobar arteries of the renal transplant and RI and PI were calculated. In 41 cases primary rejections were better recognized by an increase in PI compared to the preceding value than by the absolute PI value (with a sensitivity of 90%; specificity was 76% and 42% respectively). The RI was less specific (with a sensitivity of 90%; specificity was 47% for the relative RI increase and 30% for the absolute RI value). The continuous PI increase started an average of 3.3 days (95% CI −15.25 to + 1.55) before rejection was diagnosed. Vascular rejection episodes showed higher PI values than interstitial rejections (3.86 ± 2.14 vs. 2.19 ± 0.87; P < 0.01). The serial investigation technique of PI allows better recognition of rejection episodes than the single measurement of RI or PI performed so far. Doppler sonography recognizes rejection at an early stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RI:
-
resistive index
- PI:
-
pulsatility index
- ARF:
-
acute renal failure
- ROC:
-
receiver operating characteristic
References
Allen KS, Jorkasky DK, Arger PH, Velchik MG, Grumbach K, Coleman BG, Mintz MC, Betsch SE, Perloff LJ (1988) Renal allografts: prospective analysis of Doppler sonography. Radiology 169:371–376
Arima M, Ishibashi M, Usami M, Sagawa S, Mizutani S, Sonoda T, Ichikawa S, Ihara H, Nagano S (1979) Analysis of the arterial blood flow patterns of normal and allografted kidneys by the directional ultrasonic Doppler technique. J Urol 122:587–591
Arima M, Takahara S, Ihara H, Ichikawa Y, Ischibshi M, Sagawa S, Nagano S, Takaha M, Sonoda T (1982) Predictability of renal allograft prognosis during rejection crisis by ultrasonic Doppler flow technique. Urology 19:389–394
Arima M, Ogino T, Hosokawa S, Ihara H, Ikoma F (1989) Functional image diagnosis of kidney transplants using ultrasonic Doppler flowmetry and magnetic resonance imaging. Transplant Proc 21:1907–1911
Crockcroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31–41
Deane C (1992) Doppler and color Doppler ultrasonography in renal transplants: chronic rejection. J Clin Ultrasound 20:539–544
de Gaetano AM, Boldrini G, Nanni G, Serino F, Giovannini I, Castagneto M (1989) Noninvasive surveillance of allografted kidneys by ultrasonic duplex scanning. Angiology 40:705–715
Don S, Kopecky KK, Filo RS, Leapman SB, Thomalla JV, Jones JA, Klatte EC (1989) Duplex Doppler US of renal allografts: causes of elevated resistive index. Radiology 171:709–712
Drake DG, Day DL, Letourneau JG, Alford BA, Sibley RK, Mauer SM, Bunchman TE (1990) Doppler evaluation of renal transplants in children: a prospective analysis with histopathologic correlation. Am J Roentgenol 154:785–787
García R, Rodríguez-Iturbe B, Henríquez-La Roche C, Marín C, Mosquera J (1989) Intrarenal manometry in the diagnosis of acute rejection superimposed on acute tubular necrosis in renal transplantation. Clin Nephrol 32:21–26
Genkins SM, Sanfilippo FP, Carroll BA (1989) Duplex Doppler sonography of renal transplants: lack of sensitivity and specificity in establishing pathologic diagnosis. Am J Roentgenol 152:535–539
Granato DB, Salimi Z, George EA, Salinas Madrigal L, Garvin PJ (1988) Recurrent hemolytic uremic syndrome in a renal transplant recipient. Clin Nucl Med 13:171–174
Griffin JF, Short CD, Lawler W, Mallick NP, Johnson RW (1986) Diagnosis of disease in renal allografts: correlation between ultrasound and histology. Clin Radiol 37:59–62
Guckel C, Krestin GP, Wienand P (1989) Duplexsonographie und Kernspintomographie bei der Abklärung nephrologischer Komplikationen nach Nierentransplantation. Rofo Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Neuen Bildgeb Verfahr 151:547–552
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Harris DC, Antico V, Allen R, Gruenewald S, Lawrence S, Stewart JH, Chapman JR (1989) Doppler assessment in renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 21:1895–1896
Hollenbeck M, Stuhrmann M, Trapp R, Grabensee B (1991) Farbkodierte Dopplersonographie zur Früherkennung von Abstossungsreaktionen nach allogener Nierentransplantation Dtsch Med Wochenschr 116:921–927
Kelcz F, Pozniak MA, Pirsch JD, Oberly TD (1990) Pyramidal appearance and resistive index: insensitive and nonspecific sonography indicators of renal transplant rejection. Am J Roentgenol 155:531–535
Leimenstoll G, Engemann R, Grigat KP, Bartholdy A, Niedermayer W (1990) Duplex ultrasound: monitoring of rejection episodes of renal allografts. Transplant Proc 22:1392–1394
Mostbeck GH, Gossinger HD, Mallek R, Siostrzonek P, Schneider B, Tscholakoff D (1990) Effect of heart rate on Doppler measurements of resistive index in renal arteries. Radiology 175:511–513
Nicolet V, Carignan L, Dubuc G, Hebert G, Bourdon F, Paquin F (1988) Thickening of the renal collecting system: a nonspecific finding at US. Radiology 168:411–413
Perchik JE, Baumgartner BR, Bernardino ME (1991) Renal transplant rejection. Limited value of duplex Doppler sonography. Invest Radiol 26:422–426
Perrella RR, Duerinckx AJ, Tessler FN, Danovitch GM, Wilkinson A, Gonzalez S, Cohen AH, Grant EG (1990) Evaluation of renal transplant dysfunction by duplex Doppler sonography: a prospective study and review of the literature. Am J Kidney Dis 15:544–550
Platt JF, Ellis JH, Rubin JM, DiPictro MA, Sedman AB (1990) Intrarenal arterial Doppler sonography in patients with nonobstructive renal disease: correlation of resistive index with biopsy findings. Am J Roentgenol 154:1223–1227
Platt JF, Ellis JH, Rubin JM (1991) Renal transplant pyelocaliectasis: role of duplex Doppler US in evaluation. Radiology 179:425–428
Pozniak MA, Kelcz F, Stratta RJ, Oberley TD (1988) Extraneous factors affecting resistive index. Invest Radiol 23:899–904
Pozniak MA, Kelcz F, D'Alessandro A, Oberley T, Stratta R (1992) Sonography of renal transplants in dogs: the effect of acute tubular necrosis, cyclosporine nephrotoxicity, and acute rejection on resistive index and renal length. Am J Roentgenol 158:791–797
Rasmussen K, Pedersen E (1990) Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of renal allograft rejection and in monitoring the effect of treatment. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 50:57–61
Rifkin MD, Needleman L, Pasto ME, Kurtz AB, Foy PM, McGlynn E, Canino C, Baltarowich OH, Pennell RG, Goldberg BB (1987) Evaluation of renal transplant rejection by duplex Doppler examination: value of the resistive index. Am J Roentgenol 148:759–762
Rigsby CM, Taylor KJ, Weltin G, Burns PN, Bia M, Princenthal RA, Kashgarian M, Flye MW (1986) Renal allografts in acute rejection: evaluation using duplex sonography. Radiology 158:375–378
Rigsby CM, Burns PN, Weltin GG, Chen B, Bia M, Taylor KJ (1987) Doppler signal quantitation in renal allografts: comparison in normal and rejecting transplants, with pathologic correlation. Radiology 162:39–42
Salaman JR, Griffin PJA (1983) Fine-needle intrarenal manometry: a new test for rejection in cyclosporin-treated recipients of kidney transplants. Lancet II:709–711
Schwerk WB, Restrepo IK, Prinz H (1993) Semiquantitative Analysen intrarenaler arterieller Dopplerspektren bei gesunden Erwachsenen. Ultraschall Med 14:117–122
Stevens PE, Gwyther SJ, Hanson ME, Woodrow DF, Phillips ME, Boultbee JE (1993) Interpretation of duplex Doppler ultrasound in renal transplants in the early postoperative period. Nephrol Dial Transplant 8:255–258
Townsend RR, Tomlanovich SJ, Goldstein RB, Filly RA (1990) Combined Doppler and morphologic sonographic evaluation of renal transplant rejection. J Ultrasound Med 9:199–206
Warshauer DM, Taylor KJ, Bia MJ, Marks WH, Weltin GG, Rigsby CM, True LD, Lorber MI (1988) Unusual causes of increased vascular impedance in renal transplants: duplex Doppler evaluation. Radiology 169:367–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hollenbeck, M., Hilbert, N., Meusel, F. et al. Increasing sensitivity and specificity of Doppler sonographic detection of renal transplant rejection with serial investigation technique. Clin Investig 72, 609–615 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227454
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227454