Abstract
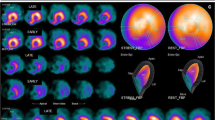
To assess chemotherapeutically induced myocardial damage, myosin-specific antibody scans and ejection fraction measurements were performed in 32 patients with breast cancer and in 9 patients with other tumours. All patients had received chemotherapy including anthracyclines. The ejection fraction decreased by ≥ 10% in 14 of 41 (34%) patients after chemotherapy. Antimyosin uptake in the myocardium was observed in 38 of 41 (92%) patients after chemotherapy. Antimyosin uptake was quantified by means of a heart-to-lung ratio, revealing a correlation between the degree of antimyosin uptake in the myocardium and the cumulative dose of anthracycline. Patients with a decreased ejection fraction showed more intense antimyosin uptake, indicating more severe myocardial damage. A higher degree of antimyosin uptake was found in 17 breast cancer patients treated with doxorubicin compared with 15 patients treated with mitoxantrone. We conclude that antimyosin studies provide a sensitive, non-invasive method to monitor myocardial damage in patients treated with anthracyclines. Antimyosin uptake in the myocardium precedes ejection fraction deterioration. This technique may be helpful in the early identification of patients at risk of congestive heart failure during chemotherapy including anthracyclines.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander J, Dainiak N, Berger HJ, et al. (1979) Serial assessment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity with quantitative radionuclide angiocardiography. N Engl J Med 300:278–283
Ballester M, Carrió I, Abadal L, et al. (1988) Patterns of evolution of myocyte damage after human heart transplantation detected by indium-111 monoclonal antimyosin. Am J Cardiol 62:623–627
Billingham ME, Bristow MR (1984) Evaluation of anthracycline cardiotoxicity: predictive ability and functional correlation of endomyocardial biopsy. Cancer Treat Symp 3:71–76
Bristow MR, Lopez MB, Mason JW et al. (1982) Efficacy and cost of cardiac monitoring in patients receiving doxorubicin. Cancer 50:32–41
Carrió I, Berná L, Ballester M, et al. (1988) Indium-111 antimyosin scintigraphy to assess myocardial damage in patients with suspected myocarditis and cardiac rejection. J Nucl Med 29:1893–1900
Choi BW, Berger HJ, Schwartz PE, et al. (1983) Serial radionuclide assessment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity in cancer patients with abnormal baseline resting left ventricular performance. Am Heart J 106:638–643
Dardir MH, Ferrans VJ, Mikhael SY, et al. (1989) Cardiac morphologic and functional changes induced by epirubicin chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 7:947–958
Druck MM, Gulenchyn KY, Evans WK, et al. (1984) Radionuclide angiography and endomyocardial biopsy in the assessment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Cancer 53:1667–1674
Estorch M, Carrió I, Bernd L, et al. (1990) 111-In-antimyosin scintigraphy after doxorubicin therapy in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Nucl Med 12:1965–1970
Hortobagyi GN, Frye D, Budzar U, et al. (1989) Decreased cardiac toxicity of doxorubicin administered by continuous intravenous infusion in combination chemotherapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 63:37–45
Khaw BA, Gold HK, Yasuda T, et al. (1986) Scintigraphic quantification of myocardial necrosis in patients after intravenous injection of myosin-specific antibody. Circulation 74:501–508
McKillop JH, Bristow MR, Goris ML, et al. (1983) Sensitivity and specificity of radionuclide ejection fractions in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. Am Heart J 106:1048–1056
Neidhart JA, Gochnour D, Roach R, et al. (1986) A comparison of mitoxantrone and doxorubicin in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 4:672–677
Obrador D, Ballester M, Carrió I, et al. (1989) High prevalence of myocardial monoclonal antimyosin antibody uptake in patients with chronic idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 13:1289–1293
Piver MS, Marchetti DL, Parthasarathy KL, et al. (1985) Doxorubicin hydrochloride (Adriamycin) cardiotoxicity evaluated by sequential radionuclide angiocardiography. Cancer 56:76–80
Schwartz RG, McKenzie MB, Alexander J, et al. (1987) Congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction complicating doxorubicin therapy. Am J Med 82:1109–1118
Shpall EJ, Jones RB, Holland JF, et al. (1988) Intensive single-agent mitoxantrone for metastatic breast cancer. JNCI 80:204–208
Singer JW, Narahara KA, Ritchie JL, et al. (1978) Time and dose-dependent changes in ejection fraction determined by radionuclide angiography after anthracycline therapy. Cancer Treat Rep 62:945–948
Vorobiof DA, Iturralde M, Falkson G (1985) Assessment of ventricular function by radionuclide angiography in patients receiving 4′-epidoxorubicin and mitoxantrone. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 15:253–257
Yasuda T, Palacios IF, Dec GW, et al. (1987) Indium-111 monoclonal antimyosin antibody imaging in the diagnosis of acute myocarditis. Circulation 76:306–311
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work has been supported by grant DGICYT PM89-0125 and by a research grant from Amersham Ibérica
Offprint requests to: I. Carrió
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrió, I., Estorch, M., Berná, L. et al. Assessment of anthracycline-induced myocardial damage by quantitative indium 111 myosin-specific monoclonal antibody studies. Eur J Nucl Med 18, 806–812 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175059
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175059