Summary
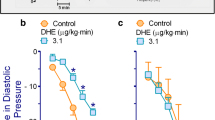
Contractions of the cat nictitating membrane have been used to explore the effects of calcium channel blockers on neurotransmission in vivo, by comparing the effects of verapamil and nifedipine on contractions of nictitating membrane following either electrical stimulation of the superior cervical ganglion or intravenous injection of the α-adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine. Verapamil (0.3, 0.6 and 1.2 mg/kg, iv) produced a dose related and reversible inhibition of stimulation induced contractions but did not affect phenylephrine responses of nictitating membrane. Intravenous nifedipine (10, 20 and 40 μg/kg) produced inconsistent effects on both stimulation- and phenylephrine-induced contractions of the nictitating membrane. Thus only verapamil appears to selectively affect noradrenergic neurotransmission in this model, possibly by altering the neurotransmitter release from the terminals innervating the nictitating membrane in the cat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clasbrummel B, Osswald H, Illes P (1989) Inhibition of noradrenaline release by omega conotoxin GVIA inthe rat tail artery. Br J Pharmacol 96:101–110
Dooley DJ, Lupp A, Hertting G (1987) Inhibition of central neurotransmitter release by omega-conotoxin GVIA, a peptide modulator of n-type voltage sensitive calcium channel. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:467–470
Fleckenstein A (1971) Specific inhibitors and promotors of calcium action in excitation contraction coupling of heart muscle and their role in the production or prevention of myocardial lesion. In: Harris P, Opai L (eds) Calcium and the heart. Academic Press, London, pp 135–189
Godfraind T, Miller RC (1983) Pharmacology of coronary arteries. In: DeBakey ME, Gotti AM Jr (eds) Factors influencing the course of myocardial ischaemia. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 101–119
Godfraind T, Miller R, Wibo M (1986) Calcium channel antagonism and calcium entry blockade. Pharmacol Rev 38:321–416
Grebb JA (1986) Nifedipine and flunarizine block amphetamine induced behavioral stimulation in mice. Life Sci 38:2375–2381
Haeusler G (1972) Differential effect of verapamil on excitation-contraction coupling in adrenergic nerve terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 180:672–682
Heesch CM, Miller BM, Thames MD, Abboud FM (1983) Effects of calcium channel blockers on isolated baroreceptors and baroreflex. Am J Physiol 245:H653-H661
Koss MC, Gherezghiher T (1988) Pharmacological characterization of alpha adrenoceptors involved in nictitating membrane and pupillary responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in cats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:18–23
Koss MC, Logan LG, Gherezghiher T (1988) Alpha-adrenoceptor activation of nictitating membrane and iris in cats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:519–524
Larsson B, Hogestatt ED, Mattiasson A, Andersson K-E (1984) Differential effects of nifedipine, verapamil and diltiazem on noradrenaline induced contraction, adrenergic transmitter release and alpha-adrenocreptor binding in the female rabbit urethra. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 326:14–21
Merocutti C, Pierelli F, Sanarelli L, Stefano E, Mattioli GL (1986) Antiepileptic effects of calcium antagonists (nimodipine) on cefazoline induced epileptogenic foci in rabbits. Epilepsia 27:498–503
Middlemiss DM, Spedding M (1985) A functional correlate for dihydropyridine binding sites in rat brain. Nature 314:94–96
Millard RW, Lathrop DA, Grupp G, Ashraf M, Grupp IL, Schwartz A (1982) Differential cardiovascular effects of calcium channel blocking agents: Potential mechanisms. Am J Cardiol 49:499–506
Miller RJ (1988) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal functions. Science 235:46–52
Nakaya H, Schwartz A, Millard RW (1983) Reflex chronotropic and inotropic effects of calcium channel blocking agents in conscious dogs: Diltiazem verapamil and nifedipine compared. Circ Res 52:302–311
Nishi K, Akaike N, Oyama Y, Ito M (1983) Action of calcium antagonists on calcium currents in helix neurons: specificity and potency. Circ Res [Suppl] 52:53–59
Peroutka SJ (1983) The pharmacology of calcium channel antagonists: a novel class of anti-migraine agents? Headache 23:278–283
Robinson BF, Dobbs RJ, Kelsey CR (1980) Effects of nifedipine on resistance vessels, arteries and veins in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10:433–438
Roychoudhary AK, Gurtu S, Dhawan KN, Sinha JN, Gupta GP (1991) Evidence for a central component in the cardiovascular effects of calcium channel blockers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 17:1015–1018
Singh BN, Roche AHG (1977) Effects of intravenous verapamil on haemodynamics in patients with heart disease. Am Heart J 94:593–599
Starke K, Späth L, Wichmann T (1984) Effect of verapamil, diltiazem and ryosidine on the release of dopamine and acetylcholine in rabbit caudate nucleus slices. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 325:124–130
Szabo B, Hedler L, Schurr C, Starke K (1988) Peripheral sympathoinhibitory cardiovascular effects of opioid peptides in anaesthetized rabbits. Br J Pharmacol 941:781–788
Wessler I, Dooley DJ, Werhand J, Schlemmer F (1990) Differential effects of calcium antagonists (ω-conotoxin, nifedipine, verapamil) on the electrically evoked release of 3H ACh from myenteric plexus, phrenic nerve and neocortex of rats. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs' Arch Pharmacol 341:288–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to S. Gurtu at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurtu, S., Seth, S. & Roychoudhary, A.K. Evidence for verapamil-induced functional inhibition of noradrenergic neurotransmission in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345, 172–175 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165732
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165732