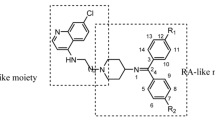
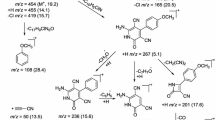
Abstract
Chloroquine (CQ) is generally considered to be one of the most fascinating, useful and versatile drugs developed during the modern era of synthetic organic chemistry (Knox and Owens 1966; Sams 1967). It was first prepared in 1934 by H. Andersag in the Elberfeld-Leverkusen laboratories of the I. G. Farbenindustrie, as part of a programme which included the synthesis of such important compounds as mepacrine, pentaquine, isopentaquine, pamaquine, primaquine, and sontoquine (Coatney 1963). The objective of this programme was to develop substitutes for quinine which, except for its prompt effect in alleviating the symptoms of an acute attack, is the poorest of antimalarial drugs (Walker 1949; 1950). The hope in preparing CQ was that it would prove to be less toxic than mepacrine. When this hope appeared not to be realised (Coatney 1963; see also Table 1), CQ was given only a very limited clinical trial, and it was then abandoned (in favour of sontoquine) as being “too toxic for human use.” The magnitude of this error of judgement became apparent when, in the course of the American wartime antimalarial survey (Wiselogle 1946), CQ proved to be the best of the many compounds which were tested for prophylactic-suppressive activity. Others of this group seemed worthy of further intensive study (see Table 1) including those assigned Survey Nos. (SN) 8137, 9584, 10751, and 13425. Trials in man (Berliner et al. 1948), involving initially the administration of 200 mg/week, and building up to 600 mg/week by the 5th week, revealed the incidence of side effects to be greatest for SN 9584 and least for SN 8137.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham R, Hendy RJ (1970) Irreversible lyosomal damage induced by chloroquine in the retinae of pigmented and albino rats. Exp Mol Pathol 12:185–200
Aikawa M (1972) High-resolution autoradiography of malaria parasites treated with 3Hchloroquine. Am J Pathol 67:277–280
Allison AC, Young MR (1964) Uptake of dyes and drugs by living cells in culture. Life Sci 3:1407–1414
Allison JL, O’Brien RL, Hahn FE (1965) DNA:Reaction with chloroquine. Science 149:1111–1113
Alving AS, Eichelberger L, Craige B Jr, Jones R Jr, Whorton CM, Pullman TN (1948) Stud-ies in the chronic toxicity of chloroquine (SN-7618) J Clin Invest 27 (Suppl):60–65
Appleton B, Wolfe MS, Mishtout GI (1973) Chloroquine as a malarial suppressive; absence of visual effects, Milit Med 138:225–226
Bagnall AW (1957) The value of chloroquine in rheumatic disease; a 4-year study of continuous therapy. Can Med Assoc J 77:182–194
Banyal HS, Fitch CD (1982) Ferriprotoporphyrin IX binding substances and the mode of action of chloroquine against malaria. Life Sci 31:1141–1144
Barlow OW, Auerbach ME, Rivenburg H (1945) Studies on the pharmacology of atabrine in mice, rats, ducks and dogs. J Lab Clin Med 30:20–31
Barrett-Conner E (1978) Chemoprophylaxis of malaria. Ann Intern Med 89:417–419
Barrow A (1974) The disposition and metabolism of amodiaquine in small mammals. Xenobiotica 11:669–680
Berliner RW, Earle DP Jr, Taggart JV, Zubrod CG, Welch WJ, Conan NJ, Bauman E, Scudder ST, Shannon JA (1948) Studies on the chemotherapy of the human malarias. VI. The physiological disposition, antimalarial acitivity and toxicity of several derivatives of 4-aminoquinolines. J Clin Invest 27 (Suppl):98–107
Bernstein H, Zvaifler N, Rubin M, Mansour AM (1963) The ocular deposition of chloroquine. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2:384–392
Berti T, Cima L (1955) Distribuzione degli aminoderivati fenotiazinici nell’ organismo animali; ricerche in diversi specie animali con la cloropromazina. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 100:373–379
Bigger JT, Hoffman BF (1980) Antiarrhythmic drugs. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th edn. Macmillan, New York, pp 761–792
Bock E (1939) Über morphologische Veränderungen menschlicher Malariaparasiten durch Atebrineinwirkung. Arch für Schiffs-and Tropen-Hygiene 43:209–214
Bowman RL, Caulfield PA, Udenfriend S (1955) Spectrophotofluorometric assay in the visible and ultraviolet. Science 122:32–33
Bratton AC Jr (1945) A short-term chronic toxicity test employing mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 85:111–118
Brodie BB, Udenfriend S, Dill W (1947a) The estimation of basic organic compounds in biological material. V. Estimation by salt formation with methyl orange. J Biol Chem 168:335–339
Brodie BB, Udenfriend S, Dill W, Chenkin T ( 1947b) The estimation of basic organic compounds in biological material. III. Estimation by conversion to fluorescent compounds. J Biol Chem 168:319–325
Bruce-Chwatt LJ (1977) Prolonged antimalarial prophylaxis. Br Med J 2:1287
Burckhalter JH, Tendick FH, Jones EM, Jones PA, Holcombe WF, Rawlins AL (1948) Aminoalkyl phenols as antimalarials. II. (Heterocyclic-amino)-2-amino-o-cresols. J Am Chem Soc 70:1363–1373
Cambiaggi A (1957) Unusual ocular lesions in a case of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Ophthalmol 57:451–453
Carr RE, Henkind P, Rothfield N, Siegel IM (1968) Ocular toxicity of antimalarial drugs:long-term follow-up. Am J Ophthalmol 66:738–744
Chambon P, Vo Phi H, Remenant J-M (1968) Enquète expérimentale sur le métabolisme de quelques médicaments antimalariques:chloroquine et amodiaquine. Bordeaux Meélical 8:1471–1477
Chlumsky A, Chlumsky J, Malina L (1980) Liver changes in porphyria cutanea tarda patients treated with chloroquine. Br J Dermatol 102:261–266
Chou AC (1980) Oxidant drugs release ferriprotoporphyrin IX (FP) from hemoglobin. Fed Proc 39:2092
Chou AC, Fitch CD (1980) Hemolysis of mouse erythrocytes by ferriprotoporphyrin IX and chloroquine:Chemotherapeutic implications. J Clin Invest 66:856–858
Chou AC, Fitch CD (1981) Mechanism of hemolysis induced by ferriprotoporphyrin IX. J Clin Invest 68:672–677
Chou AC, Chevli R, Fitch CD (1980) Ferriprotoporphyrin IX fulfills the criteria for identification as the chloroquine receptor of malaria parasites. Biochemistry 19:1543–1549
Ciak J, Hahn FE (1966) Chloroquine:Mode of action. Science 151:347–349
Coatney GR (1963) Pitfalls in a discovery:the chronicle of chloroquine. Am J Trop Med Hyg 12:121–128
Coatney GR, Cooper WC, Eddy NB, Greenberg J (1953) Survey of antimalarial agents. US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Cohen SN, Yielding KL (1965a) Spectrophotometric studies of the interaction of chloroquine with deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 240:3123–3131
Cohen SN, Yielding KL (1965b) Inhibition of DNA and RNA polymerase reactions by chloroquine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54:521–527
Cohen SN, Phifer KO, Yielding KL (1964) Complex formation between chloroquine and ferrihemic acid in vitro and its effect on the antimalarial action of chloroquine. Nature 202:805–806
Cohen Y, Lacapère J, Vial M-C (1963) Distribution de la (14C)-chloroquine chez le rat normal et arthritique. Biochem Pharmacol 12 (Suppl):174–175
Council on Drugs (1961) New drugs and developments in therapeutics:hydroxychloroquine sulfate. JAMA 178:576
Crabb DW, Jersild RA Jr, McCune SA, Swartzentruber MS, Harris RA (1980) Inhibition of hepatocyte proteolysis and lactate gluconeogenesis by chloroquine. Arch Biochem Biophys 203:49–57
Culwell WB, Cooper WC, White WC, Lints HA, Coatney GR (1948) Studies in human malaria. XX. The intramuscular administration of chloroquine. J Natl Malaria Soc 7:311–315
Dale AJD, Parkhill EM, Layton DD (1965) Studies on chloroquine retinopathy in rabbits. JAMA 193:241–243
deDuve C, deBarsy T, Poole B, Trouet A, Tulkens P, Van Hoof J (1974) Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol 23:2495–2531
Dencker L, Lindquist NG (1975) Distribution of chloroquine in the inner ear. Arch Otolaryngol 101:185–188
Dencker L, Lindquist NG, Tjälve H (1976) Uptake of 14C-labeled chloroquine and an 125I-labeled chloroquine analogue in some polypeptide hormone producing cell systems. Med Biol 54:62–68
Dingle JT, Barrett AJ (1969) Uptake of biologically active substances by lysosomes. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 173:85–93
Drenckhahn D, Lüllman-Rauch R (1978) Drug-induced retinal lipoidosis:differential susceptibilities of pigment epithelium and neuroretina toward several amphiphilic cationic drugs. Exp Mol Pathol 28:360–371
Dubois EL (1978) Antimalarials in the management of discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum 8:33–51
Duggan DE, Bowman RL, Brodie BB, Udenfriend S (1957) A spectrophotometric study of compounds of biological interest. Arch Biochem Biophys 68:1–14
Dunn MJ (1969) Alterations of red blood cell sodium transport during malarial infection. J Clin Invest 48:674–684
Eckman JR, Modler S, Eaton JW, Berger E, Engel RR (1977) Host heure catabolism in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant malaria. J Lab Clin Med 90:767–770
Edington GM, Gilles HM (1969) Pathology in the tropics. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore Editorial (1976) Chemoprophylaxis of malaria. Br Med J 2:1215–1216
Essien EE (1978) Metabolism of chloroquine:N-oxidation, an important metabolic route in man and its significance in chloroquine metabolism. Nigerian J Pharm 9:63–69
Fedorko ME, Hirsch JG, Cohn ZA (1968) Autophagic vacuoles produced in vitro. II. Studies on the mechanism of formation of autophagic vacuoles produced by chloroquine. J Cell Biol 38:392–402
Fink E, Minet G, Nickel P (1979) Chloroquin-enantiomere Wirkung gegen Nagetieremalaria (P. vinckei) und Bindung an DNS. Arzneimittelforsch 29:163–164
Finkle BS, Cherry EJ, Taylor DM (1971) Gas-liquid chromatographic system for the detection of poisons, drugs, and human metabolites encountered in forensic toxicology. J Chromatogr Sci 9:393–419
Fischer VW (1976) Evolution of a chloroquine induced cardiomyopathy in the chicken. Exp Mol Pathol 25:242–252
Fischer VW, Fitch CD (1975) Affinity of chloroquine for bone. J Pharm Pharmacol 27:527–529
Fischer VW, Nelson JS (1974) Chloroquine-enhanced cerebellovascular changes in nutritionally imbalanced chicks. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 29:65–77
Fitch CD (1969) Chloroquine resistance in malaria:a deficiency of chloroquine binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 64:1181–1187
Fitch CD (1970) Plasmodium falciparum in owl monkeys:drug resistance and chloroquine binding capacity. Science 169:289–290
Fitch CD (1972) Chloroquine resistance in malaria:drug binding and cross resistance patterns. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 39 (Suppl):265–271
Fitch CD (1977) Chloroquine susceptibility in malaria:dependence on exposure of parasites to the drug. Life Sci 21:1511–1514
Fitch CD, Chevli R (1981) Sequestration of the chloroquine receptor in cell-free preparations of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium berghei. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 19:589–592
Fitch CD, Chevli R, Banyal HS, Phillips G, Pfaller MA, Krogstad DJ (1982) Lysis of Plasmodium falciparum by ferriprotoporphyrin IX and a chloroquine-ferriprotoporphyrin IX complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 21:819–822
Fitch CD, Ng RCK, Chevli R (1978) Erythrocyte surface:novel determinant of drug susceptibility in rodent malaria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 14:185–193
Fitch CD, Yunis NG, Chevli R, Gonzalez Y (1974) High-affinity accumulation of chloro-quine by mouse erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium berghei. J Clin Invest 54:24–33
Fitzhugh OG, Nelson AA, Holland OL (1948) The chronic oral toxicity of chloroquine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 93:147–152
Fletcher KA, Baty JD, Price-Evans DA, Gilles HM (1975) Studies on the metabolism of chloroquine in rhesus monkeys and human subjects. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 69:6
Fogel BJ, Shields CE, Von Doenhoff AE Jr (1966) The osmotic fragility of erythrocytes in experimental malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 15:269–275
François T, Maudgal MC (1964) Experimental chloroquine retinopathy. Opthalmologica (Basel) 148:442–452
François J, Maudgal MC (1965) Experimental chloroquine keratotherapy. Am J Ophthalmol 60:459–464
François J, Maudgal MC (1967) Experimentally-induced chloroquine retinopathy in rabbits. Am J Ophthalmol 64:886–902
Friedman L, Rothkoff L, Zaks U (1980) Clinical observations on quinine toxicity. Ann Ophthalmol 12:640–642
Friedman MJ (1978) Erythrocytic mechanism of sickle cell resistance to malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:1994–1997
Friedman MJ (1979) Oxidant damage mediates variant red cell resistance to malaria. Nature 280:245–247
Friedman MJ, Roth EF, Nagel RL, Trager W (1979) Plasmodium falciparum:physiological interactions with the human sickle cell. Exp Parasitol 47:73–80
Frisk-Holmberg M, Bergkvist Y, Domeij-Nyberg B, Hellstrom L, Jansson F (1979) Chloroquine serum concentrations and side-effects:evidence for dose-dependent kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25:345–350
Fuhrmann G, Koenig K (1955) Untersuchungen über die Resorption und Ausscheidung der oral anwendbaren Resochin ( Chloroquin)-Salze. Zeits Tropenmed Parasitol 6:431–437
Fulton JD, Rimington C (1953) The pigment of the malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. J Gen Microbiol 8:157–159
Gambardella A, Diglio V, Tedeschi G (1955) Intossicazione acuta e cronica da chlorochina. Acta Med Ital Inf Parass 10:12–20
Gebel M, Doss M, Schmidt FW (1978) Chloroquine treatment of porphyria cutanea tarda. Diagn ther porphyrias lead intox intern symp. In: Doss M (ed) Clin Biochem. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 133–135
Giles CL, Henderson JW (1965) The ocular toxicity of chloroquine therapy. Am J Med Sci 249:132–137
Gleiser CA, Dukes TW, Lawwill T, Read WK, Bay WW, Brown RS (1969) Ocular changes in swine associated with chloroquine toxicity. Am J Ophthalmol 67:399–405
Goldman L, Cole DP, Preston RH (1953) Chloroquine disphosphate in the treatment of dis-coid lupus erythematosus. JAMA 152:1428–1429
Gonzalez-Noriega A, Grubb JH, Talkad V, Sly WS (1980) Chloroquine inhibits lysosomal enzyme pinocytosis and enhances lysosomal enzyme secretion. J Cell Biol 85:839–852
Graham JDP (1960) An overdose of Plaquenil. Br Med J I:1256
Graniewski-Wijnands HS, van Lith GHM, Vijfvinkel-Bruin-Enga S (1979) Ophthalmological examination of patients taking chloroquine. Doc Ophthalmol 48:231–234
Grundmann M, Bayer A, Vrublovsk P, Mikulíkovâ I (1973) Effect of chloroquine on adrenocortical function. I. Concentration of chloroquine and morphological changes in the suprarenal gland of rats on long-term administration of chloroquine. Z Rheumaforsch 32:306–312
Grundmann M, Mikulikovâ I, Vrublovsk P (1971) Tissue distribution of subcutaneously administered chloroquine in the rat. Arzneimittelforsch 21:573–574
Grundmann M, Mikulíkovâ I, Vrublovsk P (1972 a) Tissue distribution of chloroquine in rats in the course of long-term application. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 197:45–52
Grundmann M, Vrublovsk P, Mikulíkovâ I (1970) Tissue distribution of chloroquine in the rabbit. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 184:366–373
Grundmann M, Vrublovskÿ P, Demkovâ V, Mikulíkovâ I, Pégfimova E (1972 b) Tissue dis- tribution and urinary excretion of chloroquine in rats. Arzneimittelforsch 22:82–88
Grundmann M, Vrublovsk P (1977) Tissue distribution of chloroquine in guinea pigs. Acta Univ Palacki Olomouc Fac Med 81:273–279
Haberkorn A, Kraft HP, Blaschke G (1979) Antimalarial activity of the optical isomers of chloroquine. Zeits Tropenmed Parasitol 30:308–312
Hahn FE (1974) Chloroquine (resochin). In: Corcoran JW, Hahn FE (eds) Antibiotics III. Mechanism of action of antimicrobial and antitumor agents. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 58–78
Hara S (1979) Lysosomal arysulfatases in the bovine eye. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 83:619–628
Harder A, Kovatchev S, Debuch H (1980) Interactions of chloroquine with different glycerophospholipids. Hoppe-Seylers Z Physiol Chem 361:1847–1850
Henkind P, Rothfield N (1963) Ocular abnormalities in patients treated with synthetic antimalarial drugs. N Engl J Med 269:433–439
Hobbs HE, Calnan CD (1958) The ocular complications of chloroquine therapy. Lancet 1:1207–1209
Hobbs HE, Sorsby A, Freedman A (1959) Retinopathy following chloroquine therapy. Lancet 2:478
Hoekenga MT (1957) Propoquin in the treatment of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 6:987–989
Hollander JL (1965) The calculated risk of arthritis treatment. Ann Intern Med 62:1062–1064
Holt PJL (1979) Chloroquine in rheumatic disease. Lancet 1:502
Holtzmann JL (1965) Detection of nanogram quantities of chloroquine by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 13:66–70
Homewood CA, Warhurst DC, Peters W, Baggaley VC (1972) Lysosomes, pH and the antimalarial actions of chloroquine. Nature 235:50–52
Jacobs RL (1965) Selection of strains of Plasmodium berghei resistant to quinine, chloroquine, and pyrimethamine. J Parasitol 51:481–482
Jailer JW, Rosenfeld M, Shannon JA (1947) The influence of orally administered alkali and acid on the renal excretion of quinacrine, chloroquine, and sontoquine. J Clin Invest 26:1168–1172
Jearnpipatkul A, Govitrapong P, Yuthavong Y, Wilairat P, Panijpan B (1980) Binding of antimalarial drugs to hemozoin from Plasmodium berghei. Experientia 36:1063–1064
Josephson ES, Udenfriend S, Brodie BB (1947) The estimation of basic organic compounds in biological material. VI. Estimation by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. J Biol Chem 168:341–344
Kersley GD (1964) The value and dangers of antimalarial therapy in arthritis, with special relation to ophthalmic complications. Proc R Soc Med 57:669–671
Kiel FW (1964) Chloroquine suicide. JAMA 190:398–400
Klinefelter HF (1979) Antimalarials in rheumatoid arthritis. Hosp Pract 14:24
Klinghardt GW (1974) Experimentelle Schädigungen von Nervensystem und Muskulatur durch Chlorochin:Modelle verschiedenartiger Speicherdystrophien. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 28:117–141
Knox JM, Owens DW (1966) The chloroquine mystery, including antimalarial agents in general. Arch Dermatol 94:205–214
Kobayashi M, Iwasaki M, Shigeta Y (1980) Receptor mediated insulin degradation de-creased by chloroquine in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biochem (Tokyo) 88:39–44
Kurnick NB, Radcliffe IE (1962) Reaction between DNA and quinacrine and other antimalarials. J Lab Clin Med 60:669–688
Kuroda K (1962) Detection and distribution of chloroquine metabolites in human tissues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 137:156–161
Kurtz SM, Kaump DH, Schardein JL, Roll DE, Reutner TF, Fisken RA (1967) The effect of long-term administration of amopyroquin, a 4-aminoquinoline compound, on the retina of pigmented and nonpigmented animals. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 6:420–425
Laboratory Data (1946) SN-7618, Department of Medical Research, Winthrop Chemical, New York
Lacapère J, Delaville G, Bonhomme F (1962) Use and mode of action of antimalarials:distribution of aminoquinolines in various tissues. Rev Rhumat 29:252–257
Ladda R, Sprinz H (1969) Chloroquine sensitivity and pigment formation in rodent malaria. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 130:524–527
Lantz CH, Van Dyke K (1971) Studies concerning the mechanism of action of antimalarial drugs. II Inhibition of the incorporation of adenosine-5’-monophosphate-3H into nucleic acids of erythrocyte-free malarial parasites. Biochem Pharmacol 20:1157–1166
Larribaud J, Colonna P, Chevrel M, Romani B, Roux J, Pidoux A, Renouf P, Lefebure RY (1961) Intoxication aiguë par la chloroquine absorbée par voie orale; à propos de deux observations. Press Méd 69:2193–2196
Larsson B, Tjälve H (1979) Studies on the mechanism of drug binding to melanin. Biochem Pharmacol 28:1181–1187
Lawwill T, Appleton B, Alstatt L (1968) Chloroquine accumulation in human eyes. Am J Ophthalmol 65:530–532
Legros J, Rosner I (1971) Modifications électrorétinographiques après administration chronique de fortes doses d’hydroxychloroquine et de déséthylhydroxychloroquine chez le rat albinos. Arch Ophthalmol (Paris) 31:165–180
Lewis HM, Frumess GM (1956) Plaquenil in the treatment of discoid lupus erythematosus:preliminary report. Arch Dermatol 73:576–581
Lie SO, Schofield B (1973) Inactivation of lysosomal function in normal cultured fibroblasts by chloroquine. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3109–3114
Life Sciences Division (1969) A study of the pharmacology and toxicology of vision in the soldier. I. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine. Life Sciences Research Office, Bethesda Maryland, Contract No DA–HC, 19–68–00001
Lindquist N, Ullberg S (1972) Melanin affinity of chloroquine and chlorpromazine studied by whole body autoradiography. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 31:1–32
Loeb RF, Clark WM, Coatney GR et al. (1946) Activity of a new antimalarial agent, chloro-quine, SN-7618. JAMA 130:1069–1070
Lukasiewicz RJ, Fitzgerald JM (1974) Comparison of three photochemicalfluorometric methods for the determination of chloroquine. Appl Spectroscopy 28:151–155
Lüllmann H, Lüllmann-Rauch R, Wassermann O (1978) Lipidosis produced by amphiphilic drugs. Biochem Pharmacol 27:1103–1108
Lüllmann H, Plösch H, Ziegler A (1980) Ca replacement by cationic amphiphilic drugs from lipid monolayers. Biochem Pharmacol 29:2969–2974
Ma K, Sourkes TL (1980) Inhibition of diamine oxidase by antimalarial drugs. Agents Actions 10:395–397
MacKenzie AH (1970) An appraisal of chloroquine. Arthritis Rheum 13:280–291
Mackerras MJ, Ercole QN (1949) Observations on the action of quinine, atebrin, and plas-moquine on the gametocytes of P. falciparum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 42:455–463
Macomber PB, O’Brien RL, Hahn FE (1966) Chloroquine:physiological basis of drug re-sistance in Plasmodium berghei. Science 152:1374–1375
Macomber PB, Sprinz H, Tousimis AJ (1967) Morphological effects of chloroquine on Plasmodium berghei in mice. Nature 214:937–939
Mandel EH (1963) The side-effects of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine:results of a comparative study in vivo. NY State J Med 63:3111–3113
Manku MS, Horrobin DF (1976) Chloroquine, quinine, procaine, quinidine, and clomipra-mine are prostaglandin agonists and antagonists. Prostaglandins 12:789–801
Marchiafava E, Bignami A (1894) On summer-autumn malarial fevers. The New Sydenham Society, London (translated by Thompson JH )
Marks JS, Power BJ (1979) Is chloroquine obsolete in the treatment of rheumatic disease? Lancet 1:371–373
Marx P, Brech P, Meisner T (1960) Visual disturbances and eye changes accompanying quinoline therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Klin Wochenschr 38:443–447
Matsuzawa Y, Hostetler KY (1980) Effects of chloroquine and 4,4’bis-(diethylaminoethoxy)-a,ß-diethyldiphenylethane on the incorporation of [3H]glycerol into the phospholipids of rat liver lysosomes and other subcellular fractions, in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta 620:592–602
McChesney EW, Wyzan HS, McAuliff JP (1956) The determination of 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials:revaluation of the induced fluorescence method, with specific application to hydroxychloroquine analysis. J Pharm Sci 45:640–645
McChesney EW, Nachod FC, Tainter ML (1957) Rationale for the treatment of lupus erythematosus with antimalarials. J Invest Dermatol 29:97–104
McChesney EW, Banks WF Jr (1960) The metabolic fate of a new cardiac regulator com-pound (amotriphene) in rats, dogs, and monkeys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2:206–219
McChesney EW, McAuliff JP (1961) Laboratory studies of the 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials. I. Some biochemical characteristics of chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and SN-7718. Antibiot Chemother 11:800–810
McChesney EW, Banks WF Jr, McAuliff JP (1962) Laboratory studies of the 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials. II. Plasma levels of chloroquinoline and hydroxychloroquine in man after various oral dosage regimens. Antibiot Chemother 12:583–594
McChesney EW, Banks WF Jr, Sullivan DJ (1965a) Metabolism of chloroquine and hy- droxychloroquine in albino and pigmented rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 7:627–636
McChesney EW, Banks WF Jr, Wiland J (1965b) Effect of ascorbic acid on tissue deposition of chloroquine in the guinea pig. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 119:740–742
McChesney EW, Conway WD, Banks WF Jr, Rogers JE, Shekosky JM (1966) Studies of the metabolism of some compounds of the 4-amino-7-chloroquinoline series. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 151:482–493
McChesney EW, Banks WF Jr, Fabian RJ (1967 a) Tissue distribution of chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, and desethylchloroquine in the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 10:50 1513
McChesney EW, Fasco MJ, Banks WF Jr (1967b) The metabolism of chloroquine in man during and after repeated oral dosage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 158:323–331
McChesney EW, Shekosky JM, Hernandez PH (1967c) Metabolism of chloroquine-14C in the rhesus monkey. Biochem Pharmacol 16:2444–2447
McChesney EW (1983) Animal toxicity and pharmacokinetics of hydroxychloroquine sulfate. Am J Med 75 (Suppl):11–18
McConnell DG, Wachtel J, Havener WH (1964) Observations on experimental chloroquine retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 71:552–553
Meier-Ruge W (1965) Experimental investigation of the morphogenesis of chloroquine retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 73:540–544
Merwin CF, Winkelmann RK (1962) Antimalarial drugs in the therapy of lupus erythematosus. Mayo Clin Proc 37:253–268
Meshnick SR, Chang K-P, Cerami A (1977) Heme lysis of the bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem Pharmacol 26:1923–1928
Meyer W, Weyerbrock W (1979) Probleme der Basis-Therapie rheumatischer Erkrankun-gen mit Chloroquin, Gold und d-Penicillamin. Internist (Berlin) 20:426–432
Minker E, Matejka Z (1981) Pharmacological basis of dosage form of two antimalarials:chloroquine and mepacrine. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 57:197–200
Monnet R, Boiteau H, Moussion C (1964) Identification et dosage de la chloroquine dans les milieux biologiques par spectrophotometrie dans l’ultraviolet. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 22:429–434
Most H, London IM, Kane CA, Lavietes PH, Schroeder EF, Hayman JM Jr (1946) Chloro-quine for treatment of acute attacks of vivax malaria. JAMA 131:963–967
Murayama K, Nakajima A (1977) Determination of chloroquine in urine by gas chromatog-raphy. Yakagaku Zasshi 97:445–449
Murayama K, Kobayashi K, Futemma M, Nakajima A (1977) Effect of ammonium chloride on the excretion of chloroquine in rabbit urine. Yakugaku Zasshi 97:949–954
Nguyen-Dinh P, Trager W (1978) Chloroquine resistance produced in vitro in an African strain of human malaria. Science 200:1397–1398
O’Brien RL, Allison JL, Hahn FE (1966a) Evidence for intercalation of chloroquine into DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 129:622–624
O’Brien RL, Olenick JG, Hahn FE (1966b) Reactions of quinine, chloroquine and quinacrine with DNA and their effects on the DNA and RNA polymerase reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 55:1511–1517
Ogino N, Ohki S, Yamamoto S, Hayaishi O (1978) Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthetase from bovine vesicular gland microsomes. J Biol Chem 253:5061–5068
Okuma O, Poole B (1978) Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3327–3331
Olatunde IA (1971) Chloroquine concentrations in the skin of rabbits and man. Br J Pharmacol 43:335–340
Orjih AU, Banyal HS, Chevli R, Fitch CD (1981) Hemin lyses malaria parasites. Science 214:667–669
Osifo NG (1979a) The regional uptake of chloroquine in the brain. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 50:109–114
Osifo NG (1979b) Drug-related transient dyskinesia. Clin Pharmacol Ther 25:767–771
Osifo NG (1979c) The effect of pyrogen on the in vivo metabolism and initial kinetics of chloroquine in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 31:747–751
Osifo NG, di Stefano V (1978) Enhanced lethality and tissue levels of chloroquine in rats pretreated with pyrogens. Res Commun Chem Pharm Pharmacol 22:513–521
Parker FS, Irvin JL (1952) The interaction of chloroquine with nucleic acid and nucleoproteins. J Biol Chem 199:897–909
Pau H, Baümer A (1959) Resochineinlagerungen in der Kornea. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 135:362–377
Paulini E, Pereira JP (1963) Estudos de sal antimalârico. II. Observaçóes sôbre excreçâo de três derivados de cloroquina. Rev Bras Malariol Doenças Trop 15:47–54
Percival SPB, Meanock I (1968) Chloroquine:ophthalmological safety and clinical assessment in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 111:579–584
Perez R, Mansour AM, Rubin M, Zvaifler NJ (1964) Chloroquine binding to melanin:characteristics and significance. Arthritis Rheum 7:337
Peters W (1965) Drug resistance in Plasmodium berghei, Vincke and Lips, 1948. I. Chloroquine resistance. Exp Parasitol 17:80–89
Peters W (1968) The chemotherapy of rodent malaria. V. Dynamics of drug resistance, part I:methods of studying the acquisition and loss of resistance to chloroquine by Plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 62:277–287
Peters W (1970) Chemotherapy and drug resistance in malaria. Academic Press, London
Peters W (1980) Chemotherapy of malaria. In: Kreier JP (ed) Malaria vol I. Academic Press, New York, pp 145–283
Phifer KO, Yielding KL, Cohen SN (1966) Investigations of the possible relation of ferrihernic acid to drug resistance in Plasmodium berghei. Exp Parasitol 19:102–109
Polet H (1970) Influence of sucrose on chloroquine-3-H3 content of mammalian cells in vitro:the possible role of lysosomes in chloroquine resistance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 173:71–77
Polet H (1976) Chloroquine-3H:mechanism of uptake by Chang liver cells in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:687–694
Polet H, Barr CF (1968) Chloroquine and dihydroquinine. In vitro studies of their antimalarial effect upon Plasmodium knowlesi. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 164:380–386
Polet H, Barr CF (1969) Uptake of chloroquine-3-H3 by Plasmodium knowlesi in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 168:187–192
Powers KG, Jacobs RL, Good WC, Koontz LC (1969) Plasmodium vinckei:production of chloroquine-resistant strain. Exp Parasitol 26:193–202
Prouty RW, Kuroda K (1958) Spectrophotometric determination and distribution of chloroquine in human tissue. J Lab Clin Med 52:477–480
Rachmilewitz EA (1974) Denaturation of the normal and abnormal hemoglobin molecule. Semin Hematol 11:441–462
Rees RB, Maibach HI (1963) Chloroquine:a review of reactions and dermatologic indications. Arch Dermatol 88:280–289
Ridout RM, Decker RS, Wildenthal K (1978) Chloroquine-induced lysosomal abnormalities in cultured foetal mouse hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 10:175–183
Ritschel WA, Hammer GV, Thomson GA (1978) Pharmacokinetics of antimalarials and proposals for dosage regimens. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxico 116:395–401
Robinson AE, Coffer AI, Camps FE (1970) The distribution of chloroquine in man after fatal poisoning. J Pharm Pharmacol 22:700–703
Rosenthal AR, Kolb H, Bergsma D, Huxsoll D, Hopkins JL (1978) Chloroquine retinopathy in the rhesus monkey. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 17:1158–1175
Rubin M, Bernstein HP, Zvaifler NJ (1963) Studies on the pharmacology of chloroquine:recommendations for the treatment of chloroquine retinopathy. Arch Ophthalmol 70:474–481
Rubin M, Slonicki A (1966) A proposed mechanism for the skin-eye syndrome. Proceedings of the 5th international congress of the collegium internationale neuropsychopharmacologicum Washington, March 1966, pp 661–679 (Excerpta Medica international congress series No 129 )
Rubin M, Zvaifler N, Bernstein H, Mansour A (1965) Chloroquine toxicity. In: Drugs and Enzymes (Proceedings of the 2nd International Pharmacological Meeting, Prague, 2023 August 1963 ) Pergamon Press, Oxford
Rudzinska MA, Trager W, Bray RS (1965) Pinocytotic uptake and digestion of hemoglobin in malaria parasites. J Protozool 12:563–576
Sams WM Jr (1967) Chloroquine:mechanism of action. Mayo Clin Proc 42:300–309
Sams WM Jr, Epstein JH (1965) The affinity of melanin for chloroquine. J Invest Dermatol 45:482–487
Sando GN, Titus-Dillon P, Hall CW, Neufeld EF (1979) Inhibition of receptor mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme into fibroblasts by chloroquine, procaine, and ammonia. Exp Cell Res 119:359–364
Schmidt LH, Hughes HB, Schmidt IH (1953) The pharmacological properties of 2,4-diamino-5-p-chlorophenyl-6-ethyl-pyrimidine (daraprim). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 107:921–30
Schneider J, Nenna A, Couture J (1963) Étude comparative de la circulation dans le sang et de l’élimination urinaire de la chloroquine base et du sulfate de chloroquine. Bull WHO 29:417–421
Scholnick PL, Epstein J, Marver HS (1973) The molecular basis of the action of chloroquine in porphyria cutanea tarda. J Invest Dermatol 61:226–232
Schueler FW, Cantrell WF (1964) Antagonism of the antimalarial action of chloroquine by ferrihemate and a hypothesis for the mechanism of chloroquine resistance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 143:278–281
Scruggs JH (1964) Ocular complications from chloroquine therapy. Tex Med 60:362–365
Shriver DA, White CB, Sandor A, Rosenthale ME (1975) A profile of the rat gastrointes-tinal toxicity of drugs used to treat inflammatory diseases. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 32:73–83
Sinton JA (1938) The action of atebrin upon the gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum. Rivista di Malariologia 17:305–330
Smith CC (1950) A short term chronic toxicity test. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 100:408–420
Spector WS (ed) (1956) Handbook of toxicology, vol I. Saunders, Philadelphia
Stauber WT, Hedge AM, Trout JJ, Schottelius BA (1981) Inhibition of lysosomal function in red and white skeletal muscle by chloroquine. Exp Neurol 71:295–306
Stollar D, Levine L (1963) Antibodies to denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in lupus erythematose serum. V. Mechanism of DNA-anti DNA inhibition by chloroquine. Arch Biochem Biophys 101:335–341
Surrey AR, Hammer HF (1950) Preparation of 7-chloro-4-[4-(N-ethyl, n-2-hydroxyethylamino)-1-methylbutylaminol]-quinoline and related compounds. J Am Chem Soc 72:1814–1815
Tanenbaum L, Tuffanelli DL (1980) Antimalarial agents:chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine and quinacrine. Arch Dermatol 116:587–591
Thompson PE, Olszewski B, Bayles A, Waitz JA (1967) Relations among antimalarial drugs:results of studies with cycloguanil-, sulfone-, or chloroquine-resistant Plasmodium berghei in mice. Am J Trop Med Hyg 16:133–145
Thompson PE, Weston K, Glazko AJ, Fisken RA, Reutner TF, Bayles A, Weston JK (1958) Laboratory studies on amopyroquin (propoquin). Antibiot Chemother 8:450–460
Tietze C, Schlesinger P, Stahl P (1980) Chloroquine and ammonium ion inhibit receptor-mediated endocytosis of mannose-glycoconjugates by macrophages:apparent inhibition of receptor recycling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 93:1–8
Titus EO, Craig LC, Golumbic C, Mighton HR, Wempen IM, Elderfield RC (1948) Identification by distribution. IX. Application to metabolic studies of 4-aminoquinoline antimalarials. J Org Chem 13:39–62
Trenholme GM, Williams RL, Patterson EC, Frischer H, Carson PE, Rieckmann KH (1974) A method for the determination of amodiaquin. Bull WHO 51:431–434
Tschudy D (1974) Porphyrin metabolism and the porphyrias. In: Bondy PK, Rosenberg LE (eds) Disease of metabolism:genetics and metabolism, 7th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 775–824
Udenfriend S, Duggan DE, Vasta BM, Brodie BB (1957) A spectrophotofluorometric study of compounds of pharmacological interest. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 120:26–32
Van Dyke K, Szustkiewicz C, Lantz CH, Saxe LH (1969) Studies concerning the mechanism of action of antimalarial drugs:inhibition of the incorporation of adenosine-8–3H into nucleic acids of Plasmodium berghei. Biochem Pharmacol 18:1417–1425
Varga F (1966) Intestinal absorption of chloroquine in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 163:38–46
Varga F (1968a) Tissue distribution of chloroquine in the rat. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 34:319–325
Varga F (1968b) Intracellular localization of chloroquine in the liver and kidney of the rat. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung 34:327–332
Varga F, Fischer E, Szily TS (1975) Effect of gastric emptying time on the intestinal absorption of chloroquine in rats. Pharmacology 13:401–408
Viala A, Durand A, Cano J-P, Jouglard J (1972) La chloroquine:sort dans l’organisme et toxicologie analytique. Eur J Toxicol 5:189–202
Viala A, Cano J-P, Durand A (1975) Determination of chloroquine in biological material by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr 111:299–303
Walker AJ (1949/1950) Malaria therapy, 1950. Bull Tulane Med Fac 9:48–51
Warhurst DC (1973) Chemotherapeutic agents and malaria research. Symp Br Soc Parasitol 11:1–28
Warhurst DC, Hockley DJ (1967) Mode of action of chloroquine on Plasmodium berghei and P. cynomolgi. Nature 214:935–936
Warhurst DC, Killick-Kendrick R (1967) Spontaneous resistance to chloroquine in a strain of rodent malaria (Plasmodium berghei yoelii). Nature 213:1048–1049
Warhurst DC, Thomas SC (1975) Localization of mepacrine in Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium falciparum by fluorescence microscopy. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 69:417–420
Wassermann HP (1965) The circulation of melanin — its chemical and physiological significance. S Afr Med J 39:711–716
Weissmann G (1964) Labilization and stabilization of lysosomes. Fed Proc 23:1038–1044 Weniger H (1979) Review of side-effects and toxicity of chloroquine. WHO, Geneva, WHO/ MAL 79:906
Whisnant JP, Espinosa RE, Kierland RR, Lambert EH (1963) Chloroquine neuromyopathy. Mayo Clin Proc 38:501–513
Whitehouse MW, Boström H (1965) Biochemical properties of anti-inflammatory drugs. VI. The effects of chloroquine (resochin), mepacrine (quinacrine), and some of their potential metabolites on cartilage metabolism and oxidative phosphorylation. Biochem Pharmacol 14:1173–1184
Wibo M, Poole B (1974) Protein degradation in cultured cells. II. Uptake of chloroquine by rat fibroblasts and the inhibition of cellular protein degradation and cathepsin B1. J Cell Biol 63:430–440
Wiesmann UN, Didonato S, Herschkowitz NN (1975) Effect of chloroquine on cultured fibroblasts:Release of lysosomal hydrolases and inhibition of their uptake. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 66:1338–1343
Williams RT (1959) Detoxication mechanisms, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 651–652
Wiselogle FY (1946) A survey of antimalarial drugs, 1941–1945, vol. I. JW Edwards, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Wollheim FA, Hanson A, Laurel] C-B (1978) Chloroquine treatment of rheumatoid arthritis:correlation of clinical response to plasma protein changes and chloroquine levels. Scand J Rheumatol 7:171–176
Yoshimura H (1964) Organ systems in adaptation; the skin. In: Handbook of Physiology, Sec. 4. American Physiological Society, Washington, DC, p 113
Zeller RW, Deering D (1958) Corneal complications of chloroquine ( Aralen) therapy. JAMA 168:2263–2264
Zvaifler NJ, Rubin M, Bernstein H (1963) Chloroquine metabolism:drug excretion and tissue distribution. Arthritis Rheum 6:799–800
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1984 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
McChesney, E.W., Fitch, C.D. (1984). 4-Aminoquinolines. In: Peters, W., Richards, W.H.G. (eds) Antimalarial Drug II. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 68 / 2. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69254-3_1
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69254-3_1
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-69256-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-69254-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive