Abstract
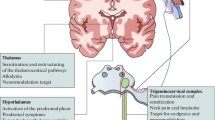
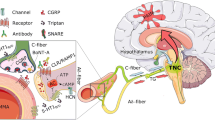
Migraine is a neurovascular disorder which affects one fifth of the general population. Disability due to migraine is severe and involves patients from infancy through senescence and it is aggravated by the fact there is no complete cure. However, various drugs for the symptomatic or prophylactic treatment of the disease are available. Recently, better knowledge of the neurobiological and pharmacological aspects of a subset of trigeminal primary sensory neurons has provided key information for the development of effective molecules that specifically target the activation of the trigeminovascular system and may represent a significant advancement in the treatment of the disease. These novel antagonists block the receptor for the sensory neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), which upon release from peripheral terminals of trigeminal perivascular neurons dilates cranial arterial vessels. Whether neurogenic vasodilatation is the major contributing factor to generate the pain and the associated symptoms of the migraine attack or whether other sites of action of CGRP receptor antagonists are responsible for the antimigraine effect of these compounds is the subject of current and intense research.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiyar N, Daines RA, Disa J et al (2001) Pharmacology of SB-273779, a nonpeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide 1 receptor antagonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:768–775
Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE et al (2003) Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron 39:497–511
Amara SG, Arriza JL, Leff SE et al (1985) Expression in brain of a messenger RNA encoding a novel neuropeptide homologous to calcitonin gene-related peptide. Science 229:1094–1097
Baluk P, Bertrand C, Geppetti P et al (1995) NK1 receptors mediate leukocyte adhesion in neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. Am J Physiol 268:L263–L269
Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW et al (2004) Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron 41:849–857
Bautista DM, Jordt SE, Nikai T et al (2006) TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell 124:1269–1282
Bautista DM, Siemens J, Glazer JM et al (2007) The menthol receptor TRPM8 is the principal detector of environmental cold. Nature 448:204–208
Bevan S, Geppetti P (1994) Protons: small stimulants of capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. Trends Neurosci 17:509–512
Boeglin D, Hamdan FF, Melendez RE et al (2007) Calcitonin gene-related peptide analogues with aza and indolizidinone amino acid residues reveal conformational requirements for antagonist activity at the human calcitonin gene-related peptide 1 receptor. J Med Chem 50:1401–1408
Brain SD, Williams TJ (1989) Interactions between the tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide lead to the modulation of oedema formation and blood flow in rat skin. Br J Pharmacol 97:77–82
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR et al (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313:54–56
Brazil P, Friedman A (1957) Further observations in craniovascular studies. Neurology 7:52–55
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M et al (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389:816–824
Caterina MJ, Rosen TA, Tominaga M et al (1999) A capsaicin-receptor homologue with a high threshold for noxious heat. Nature 398:436–441
Chiba T, Yamaguchi A, Yamatani T et al (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist human CGRP-(8–37). Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 256:E331–E335
Chuang HH, Prescott ED, Kong H et al (2001) Bradykinin and nerve growth factor release the capsaicin receptor from PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated inhibition. Nature 411:957–962
Connor H, Bertin L, Gillies S et al (1998) The GR205171 clinical study group. Clinical evaluation of a novel, potent, CNS penetrating NK1 receptor antagonist in the acute treatment of migraine. Cephalalgia 18:392
Cooper GJS, Willis AC, Clark A et al (1987) Purification and characterization of a peptide from amyloid-rich pancreases of type 2 diabetic patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8628–8632
Diener HC (2003) RPR100893, a substance-P antagonist, is not effective in the treatment of migraine attacks. Cephalalgia 23:183–185
Doods H (2001) Development of CGRP antagonists for the treatment of migraine. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2:1261–1268
Doods H, Hallermayer G, Wu D et al (2000) Pharmacological profile of BIBN4096BS, the first selective small molecule CGRP antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 129:420–423
Doods H, Arndt K, Rudolf K et al (2007) CGRP antagonists: unravelling the role of CGRP in migraine. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:580–587
Durham PL (2004) CGRP-receptor antagonists – a fresh approach to migraine therapy? New Engl J Med 350:1073–1075
Edvinsson L (2004) Blockade of CGRP receptors in the intracranial vasculature: a new target in the treatment of headache. Cephalalgia 24:611–622
Edvinsson L, Sams A, Jansen-Olesen I et al (2001) Characterisation of the effects of a non-peptide CGRP receptor antagonist in SK-N-MC cells and isolated human cerebral arteries. Eur J Pharmacol 415:39–44
Ennis MD, Ghazal NB, Hoffman RL et al (1998) Isochroman-6-carboxamides as highly selective 5-HT1D agonists: potential new treatment for migraine without cardiovascular side effects. J Med Chem 41:2180–2183
Fanciullacci M, Tramontana M, Bianco ED et al (1991) Low pH medium induces calcium dependent release of CGRP from sensory nerves of guinea-pig dural venous sinuses. Life Sci 49:PL27–PL30
Fanciullacci M, Alessandri M, Figini M et al (1995) Increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide from the extracerebral circulation during nitroglycerin-induced cluster headache attack. Pain 60:119–123
Fay T (1935) The mechanism of headache. Trans Am Neurol Assoc 62:74–77
Feindel W, Penfield W, Mc NF (1960) The tentorial nerves and localization of intracranial pain in man. Neurology 10:555–563
Fernandez-Patron C, Stewart KG, Zhang Y et al (2000) Vascular matrix metalloproteinase-2-dependent cleavage of calcitonin gene-related peptide promotes vasoconstriction. Circ Res 87:670–676
Ferrari MD, Saxena PR (1993) On serotonin and migraine: a clinical and pharmacological review. Cephalalgia 13:151–165
Ferrari MD, Roon KI, Lipton RB et al (2001) Oral triptans (serotonin 5-HT(1B/1D) agonists) in acute migraine treatment: a meta-analysis of 53 trials. Lancet 358:1668–1675
Fluhmann B, Muff R, Hunziker W et al (1995) A human orphan calcitonin receptor-like structure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 206:341–347
Franco-Cereceda A (1991) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and human epicardial coronary arteries: presence, release and vasodilator effects. Br J Pharmacol 102:506–510
Gazzieri D, Trevisani M, Springer J et al (2007) Substance P released by TRPV1-expressing neurons produces reactive oxygen species that mediate ethanol-induced gastric injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 43:581–589
Geppetti P, Holzer P (1996) Neurogenic inflammation. CRC, Boca Raton
Geppetti P, Del Bianco E, Cecconi R et al (1992) Capsaicin releases calcitonin gene-related peptide from the human iris and ciliary body in vitro. Regul Pept 41:83–92
Giffin NJ, Kowacs F, Libri V et al (2003) Effect of the adenosine A1 receptor agonist GR79236 on trigeminal nociception with blink reflex recordings in healthy human subjects. Cephalalgia 23:287–292
Goadsby PJ, Edvinsson L, Ekman R (1990) Vasoactive peptide release in the extracerebral circulation of humans during migraine headache. Ann Neurol 28:183–187
Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD (2002a) Migraine – current understanding and treatment. New Engl J Med 346:257–270
Goadsby PJ, Hoskin KL, Storer RJ et al (2002b) Adenosine A1 receptor agonists inhibit trigeminovascular nociceptive transmission. Brain 125:1392–1401
Goldstein DJ, Wang O, Saper JR et al (1997) Ineffectiveness of neurokinin-1 antagonist in acute migraine: a crossover study. Cephalalgia 17:785–790
Goldstein J, Roon I, Offen W et al (1999) Migraine treatment with selective with 5-ht1F receptor agonist (SSOFRA) LY334370. Cephalalgia 19:318
Gomez-Mancilla B, Cutler N, Leibowitz M et al (2001) Safety and efficacy of PNU-142633, a selective 5-HT1D agonist, in patients with acute migraine. Cephalalgia 21:727–732
Graham J, Wolff H (1938) Mechanism of migraine headache and action of ergotamine tartrate. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 39:737–763
Gray DW, Marshall I (1992) Human alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates adenylate cyclase and guanylate cyclase and relaxes rat thoracic aorta by releasing nitric oxide. Br J Pharmacol 107:691–696
Ho TW, Mannix LK, Fan X et al (2007) Randomized controlled trial of an oral CGRP antagonist, MK-0974, in acute treatment of migraine. Neurology 70:1304–1312
Huang SM, Bisogno T, Trevisani M et al (2002) An endogenous capsaicin-like substance with high potency at recombinant and native vanilloid VR1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8400–8405
Humphrey PP, Bland-Ward PA, Carruthers AM et al (2001) Inhibition of trigemnial nociceptive afferents by adenosine A1 receptor activation: a novel approach towards the design of new anti-migraine compounds. Cephalalgia 21:268–269
Hwang SW, Cho H, Kwak J et al (2000) Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6155–6156
Jordt SE, Bautista DM, Chuang HH et al (2004) Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature 427:260–265
Juhasz G, Zsombok T, Modos EA et al (2003) NO-induced migraine attack: strong increase in plasma calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) concentration and negative correlation with platelet serotonin release. Pain 106:461–470
Kapoor K, Arulmani U, Heiligers JPC et al (2003) Effects of the CGRP receptor antagonist BIBN4096BS on capsaicin-induced carotid haemodynamic changes in anaesthetised pigs. Br J Pharmacol 140:329–338
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M et al (1993) Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 192:553–560
Knotkova H, Pappagallo M, Szallasi A (2008) Capsaicin (TRPV1 Agonist) therapy for pain relief: farewell or revival? Clin J Pain 24:142–154
Lance J (1969) Mechanism and management of headache. Butterworths, New York
Lassen LH, Haderslev PA, Jacobsen VB et al (2002) CGRP may play a causative role in migraine. Cephalalgia 22:54–61
Lennerz JK, Ruhle V, Ceppa EP et al (2008) Calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR), receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1), and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) immunoreactivity in the rat trigeminovascular system: differences between peripheral and central CGRP receptor distribution. J Comp Neurol 507:1277–1299
Lewis T (1937) The nocifensor system of nerves and its reactions. Br Med J 194:431–435
Liedtke W, Choe Y, Marti-Renom MA et al (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103:525–535
Macpherson LJ, Geierstanger BH, Viswanath V et al (2005) The pungency of garlic: activation of TRPA1 and TRPV1 in response to allicin. Curr Biol 15:929–934
Markowitz S, Saito K, Moskowitz MA (1987) Neurogenically mediated leakage of plasma protein occurs from blood vessels in dura mater but not brain. J Neurosci 7:4129–4136
McKemy DD, Neuhausser WM, Julius D (2002) Identification of a cold receptor reveals a general role for TRP channels in thermosensation. Nature 416:52–58
McLatchie LM, Fraser NJ, Main MJ et al (1998) RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature 393:333–339
Morris HR, Panico M, Etienne T et al (1984) Isolation and characterization of human calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature 308:746–748
Moskowitz MA, Buzzi MG (1991) Neuroeffector functions of sensory fibres: implications for headache mechanisms and drug actions. J Neurol 238:S18–S22
Mudderry PK, Ghatei MA, Spokes RA et al (1988) Differential expression of [alpha]-CGRP and [beta]-CGRP by primary sensory neurons and enteric autonomic neurons of the rat. Neuroscience 25:195–205
Nagata K, Duggan A, Kumar G et al (2005) Nociceptor and hair cell transducer properties of TRPA1, a channel for pain and hearing. J Neurosci 25:4052–4061
Nicoletti P, Trevisani M, Manconi M et al (2008) Ethanol causes neurogenic vasodilation by TRPV1 activation and CGRP release in the trigeminovascular system of the guinea pig. Cephalalgia 28:9–17
Nilius B, Owsianik G, Voets T et al (2007) Transient receptor potential cation channels in disease. Physiol Rev 87:165–217
Njuki F, Nicholl CG, Howard A et al (1993) A new calcitonin-receptor-like sequence in rat pulmonary blood vessels. Clin Sci (Lond) 85:385–388
Olesen J, Diener HC, Husstedt IW et al (2004) Calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist BIBN 4096 BS for the acute treatment of migraine. N Engl J Med 350:1104–1110
Paone DV, Shaw AW, Nguyen DN et al (2007) Potent, orally bioavailable calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonists for the treatment of migraine: discovery of N-[(3R,6S)-6-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)azepan-3-yl]-4-(2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carboxamide (MK-0974). J Med Chem 50:5564–5567
Peier AM, Moqrich A, Hergarden AC et al (2002) A TRP channel that senses cold stimuli and menthol. Cell 108:705–715
Penfield W, McNaughton M (1940) Dural headache and the innervation of the dura mater. Arch Neurol Psychiatr 44:43–75
Petermann J, Born W, Chang J et al (1987) Identification in the human central nervous system, pituitary, and thyroid of a novel calcitonin gene-related peptide, and partial amino acid sequence in the spinal cord. J Biol Chem 262:542–545
Petersen K, Birk S, Lassen L et al (2005) The CGRP-antagonist, BIBN4096BS does not affect cerebral or systemic haemodynamics in healthy volunteers. Cephalalgia 25:139–147
Premkumar LS, Ahern GP (2000) Induction of vanilloid receptor channel activity by protein kinase C. Nature 408:985–990
Quirion R, D Van Rossum, Dumont Y et al (1992) Characterization of CGRP1 and CGRP2 receptor subtypes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 657:88–105
Raddino R, Pela G, Manca C et al (1997) Mechanism of action of human calcitonin gene-related peptide in rabbit heart and in human mammary arteries. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 29:463–470
Ramadan NM, Skljarevski V, Phebus LA et al (2003) 5-HT1F receptor agonists in acute migraine treatment: a hypothesis. Cephalalgia 23:776–785
Ray B, Wolff H (1940) Experimental studies on headache: pain-sensitive structures of the head and their significance in headache. Arch Surg 41:813–856
Salvatore CA, Hershey JC, Corcoran HA et al (2008) Pharmacological characterization of MK-0974 [N-[(3R,6S)-6-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-2-oxo-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)azepan-3-yl]-4-(2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carbox amide], a potent and orally active calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist for the treatment of migraine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 324:416–421
Schoonman GG, van der Grond J, Kortmann C et al (2008) Migraine headache is not associated with cerebral or meningeal vasodilatation – a 3T magnetic resonance angiography study. Brain 131:2192–2200
Simone DA, Ochoa J (1991) Early and late effects of prolonged topical capsaicin on cutaneous sensibility and neurogenic vasodilatation in humans. Pain 47:285–294
Smith D, Hill RG, Edvinsson L et al (2002) An immunocytochemical investigation of human trigeminal nucleus caudalis: CGRP, substance P and 5-HT1D-receptor immunoreactivities are expressed by trigeminal sensory fibres. Cephalalgia 22:424–431
Snider RM, Constantine JW, Lowe JA 3rd et al (1991) A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science 251:435–437
Story GM, Peier AM, Reeve AJ et al (2003) ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell 112:819–829
Struthers AD, Brown MJ, Macdonald DW et al (1986) Human calcitonin gene related peptide: a potent endogenous vasodilator in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 70:389–393
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1999) Vanilloid (capsaicin) receptors and mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev 51:159–212
Szolcsanyi J (1977) A pharmacological approach to elucidation of the role of different nerve fibres and receptor endings in mediation of pain. J Physiol 73:251–259
Taylor CK, Smith DD, Hulce M et al (2006) Pharmacological characterization of novel alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor peptide antagonists that are selective for human CGRP receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:749–757
Tfelt-Hansen P, De Vries P, Saxena PR (2000) Triptans in migraine: a comparative review of pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. Drugs 60:1259–1287
Thomsen LL, Iversen HK, Brinck TA et al (1993) Arterial supersensitivity to nitric oxide (nitroglycerin) in migraine sufferers. Cephalalgia 13:395–399
Tominaga M, Caterina MJ, Malmberg AB et al (1998) The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron 21:531–543
Trevisani M, Smart D, Gunthorpe MJ et al (2002) Ethanol elicits and potentiates nociceptor responses via the vanilloid receptor-1. Nat Neurosci 5:546–551
Welch KMA (2003) Concepts of migraine headache pathogenesis: insights into mechanisms of chronicity and new drug targets. Neurol Sci 24:S149–S153
Williamson DJ, Hill RG, Shepheard SL et al (2001) The anti-migraine 5-HT(1B/1D) agonist rizatriptan inhibits neurogenic dural vasodilation in anaesthetized guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol 133:1029–1034
Wolff H (1948) Headache and other head pain. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 59–97
Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA et al (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400:452–457
Acknowledgements
The paper was supported in part by grants from Consorzio Ferrara Ricerche, Ferrara, and by Fondazione DEI-Onlus, Florence, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Benemei, S., Nicoletti, P., Capone, J.G., Cesaris, F.D., Geppetti, P. (2009). Migraine. In: Canning, B., Spina, D. (eds) Sensory Nerves. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, vol 194. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-79090-7_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-79089-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-79090-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)