Abstract
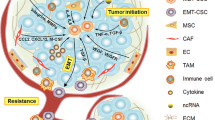
Since the “war on cancer” was waged more than 30 years ago, the fact remains that the metastatic breast cancer is still incurable and patients will ultimately die from this disease [1]. American Cancer Society has estimated that in the year 2012, there will be about 229,060 new cases of breast cancer and an estimated 39,920 new deaths caused by breast cancer in the United States alone [2]. Majority of breast cancer-related deaths are primarily due to metastatic disease which display poor prognosis with an estimated 5-year survival of ~20 %. Furthermore, therapeutic resistance and relapse are strongly associated with metastatic disease in breast cancer patients [1]. Despite the fact that the heterogeneity of tumor cells had been widely acknowledged, it has not been validated until the 1990s due to lack of markers and techniques. D. Bonnet and J. Dick were the first to describe the hierarchical organization of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and the existence of cancer stem cells (CSC). This was quickly followed by the identification of CSCs from number of malignancies enabling us to better characterize these cells in mouse models and preclinical settings. These ongoing functional studies suggested that CSCs may explain the failure to treat advance metastatic tumors. Thus the “seed and soil” hypothesis proposed by Stephen Paget more than 120 years ago may re-framed in a modern context explaining the ability of subset of tumor cells “seed” or “CSCs” to disseminate and metastasize to secondary organs where nutrient-rich microenvironment “soil” stimulates the secondary tumor growth by enhancing CSC self-renewal.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A (2012) Cancer statistics 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 62:10–29
O’Brien CA, Kreso A, Jamieson CH (2010) Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res 16:3113–3120
Shipitsin M, Polyak K (2008) The cancer stem cell hypothesis: in search of definitions markers and relevance Laboratory investigation. J Tech Meth Pathol 88:459–463
Kordon EC, Smith GH (1998) An entire functional mammary gland may comprise the progeny from a single cell. Development 125:1921–1930
Shackleton M, Vaillant F, Simpson KJ, Sting LJ, Smyth GK, Asselin-Labat ML, Wu L, Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE (2006) Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem cell. Nature 439:84–88
Wang X, Willenbring H, Akkari Y, Torimaru Y, Foster M, Al-Dhalimy M, Lagasse E, Finegold M, Olson S, Grompe M (2003) Cell fusion is the principal source of bone-marrow-derived hepatocytes. Nature 422:897–901
Wagers AJ, Sherwood RI, Christensen JL, Weissman IL (2002) Little evidence for developmental plasticity of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Science 297:2256–2259
Krause DS, Theise ND, Collector MI, Henegariu O, Hwang S, Gardner R, Neutzel S, Sharkis SJ (2001) Multi-organ multi-lineage engraftment by a single bone marrow-derived stem cell. Cell 105:369–377
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF (2003) Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:3983–3988
Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ, Wicha MS (2003) In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev 17:1253–1270
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE, Hawkins C, Squire J, Dirks PB (2003) Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res 63:5821–5828
Korkaya H, Paulson A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Brown M, Dutcher J, Clouthier SG, Wicha MS (2009) Regulation of mammary stem/progenitor cells by PTEN/Akt/beta-catenin signaling. PLoS Biol 7:e1000121
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA, Lander ES (2009) Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 138:645–659
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133:704–715
Goodell MA, Brose K, Paradis G, Conner AS, Mulligan RC (1996) Isolation and functional properties of murine hematopoietic stem cells that are replicating in vivo. J Exp Med 183:1797–1806
Zhou J, Wulfkuhle J, Zhang H, Gu P, Yang Y, Deng J, Margolick JB, Liotta LA, Petricoin E 3rd, Zhang Y (2007) Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:16158–16163
Kondo T, Setoguchi T, Taga T (2004) Persistence of a small subpopulation of cancer stem-like cells in the C6 glioma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:781–786
Hirschmann-Jax C, Foster AE, Wulf GG, Nuchtern JG, Jax TW, Gobel U, Goodell MA, Brenner MK (2004) A distinct “side population” of cells with high drug efflux capacity in human tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:14228–14233
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG, Liu S, Schott A, Hayes D, Birnbaum D, Wicha MS, Dontu G (2007) ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 1:555–567
Charafe-Jauffret E, Ginestier C, Iovino F, Wicinski J, Cervera N, Finetti P, Hur MH, Diebel ME, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Viens P, Xerri L, Bertucci F, Stassi G, Dontu G, Birnbaum D, Wicha MS (2009) Breast cancer cell lines contain functional cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity and a distinct molecular signature. Cancer Res 69:1302–1313
Ginestier C, Hur M, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG, Schott A, Hayes DF, Birnbaum D, Wicha MS, Dontu G (2007) ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant breast stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell 1:555–567
Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A, Koukourakis MI (2011) The CD44 +/CD24- phenotype relates to ‘triple-negative’ state and unfavorable prognosis in breast cancer patients. Med Oncol 28:745–752
Pece S, Tosoni D, Confalonieri S, Mazzarol G, Vecchi M, Ronzoni S, Bernard L, Viale G, Pelicci PG, Di Fiore PP (2010) Biological and molecular heterogeneity of breast cancers correlates with their cancer stem cell content. Cell 140:62–73
Keller PJ, Lin AF, Arendt LM, Klebba I, Jones AD, Rudnick JA, Dimeo TA, Gilmore H, Jefferson DM, Graham RA, Naber SP, Schnitt S, Kuperwasser C (2010) Mapping the cellular and molecular heterogeneity of normal and malignant breast tissues and cultured cell lines. Breast Cancer Res 12:R87
Li X, Lewis MT, Huang J, Gutierrez C, Osborne CK, Wu MF, Hilsenbeck SG, Pavlick A, Zhang X, Chamness GC, Wong H, Rosen J, Chang JC (2008) Intrinsic resistance of tumorigenic breast cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:672–679
Phillips TM, McBride WH, Pajonk F (2006) The response of CD24(-/low)/CD44 + breast cancer-initiating cells to radiation. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1777–1785
Diehn M, Cho RW, Lobo NA, Kalisky T, Dorie MJ, Kulp AN, Qian D, Lam JS, Ailles LE, Wong M, Joshua B, Kaplan MJ, Wapnir I, Dirbas FM, Somlo G, Garberoglio C, Paz B, Shen J, Lau SK, Quake SR, Brown JM, Weissman IL, Clarke MF (2009) Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature 458:780–783
Rich JN (2007) Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res 67:8980–8984
Dean M (2009) ABC transporters drug resistance and cancer stem cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 14:3–9
Keshet GI, Goldstein I, Itzhaki O, Cesarkas K, Shenhav L, Yakirevitch A, Treves AJ, Schachter J, Amariglio N, Rechavi G (2008) MDR1 expression identifies human melanoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368:930–936
Lee JH, Jung C, Javadian-Elyaderani P, Schweyer S, Schutte D, Shoukier M, Karimi-Busheri F, Weinfeld M, Rasouli-Nia A, Hengstler JG, Mantilla A, Soleimanpour-Lichaei HR, Engel W, Robson CN, Nayernia K (2010) Pathways of proliferation and antiapoptosis driven in breast cancer stem cells by stem cell protein piwil2. Cancer Res 70:4569–4579
Yule SM, Boddy AV, Cole M, Price L, Wyllie R, Tasso MJ, Pearson AD, Idle JR (1995) Cyclophosphamide metabolism in children. Cancer Res 55:803–809
Lan KH, Lu CH, Yu D (2005) Mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance and their clinical implications. Ann NY Acad Sci 1059:70–75
Miller KD (2004) The role of ErbB inhibitors in trastuzumab resistance. Oncologist 9(3):16–19
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M, Baselga J, Norton L (2001) Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med 344:783–792
Nahta R, Esteva FJ (2006) HER2 therapy: molecular mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance. Breast Cancer Res 8:215
Nagata Y, Lan KH, Zhou X, Tan M, Esteva FJ, Sahin AA, Klos KS, Li P, Monia BP, Nguyen NT, Hortobagyi GN, Hung MC, Yu D (2004) PTEN activation contributes to tumor inhibition by trastuzumab and loss of PTEN predicts trastuzumab resistance in patients. Cancer Cell 6:117–127
Berns K, Horlings HM, Hennessy BT, Madiredjo M, Hijmans EM, Beelen K, Linn SC, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Stemke-Hale K, Hauptmann M, Beijersbergen RL, Mills GB, van de Vijver MJ, Bernards R (2007) A functional genetic approach identifies the PI3 K pathway as a major determinant of trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 12:395–402
Cicalese A, Bonizzi G, Pasi CE, Faretta M, Ronzoni S, Giulini B, Brisken C, Minucci S, Di Fiore PP, Pelicci PG (2009) The tumor suppressor p53 regulates polarity of self-renewing divisions in mammary stem cells. Cell 138:1083–1095
Korkaya H, Kim G, Davis A, Malik F, Henry NL, Ithimakin S, Quraishi AA, Tawakkol N, D’Angelo R, Paulson A, Chung S, Luther T, Paholak HS, Liu S, Hassan K, Zen Q, Clouthier SG, Wicha MS (2012) Activation of an IL-6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2 overexpressing breast cancers by expanding the cancer stem cell population. Molecular Cell (In print)
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G, Struhl K (2011) Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:1397–1402
Ginestier C, Liu S, Diebel ME, Korkaya H, Luo M, Brown M, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Charafe-Jauffret E, Birnbaum D, Guan JL, Dontu G, Wicha MS (2010) CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts. J Clin Invest 120:485–497
Hartman ZC, Yang XY, Glass O, Lei G, Osada T, Dave SS, Morse MA, Clay TM, Lyerly HK (2011) HER2 overexpression elicits a proinflammatory IL-6 autocrine signaling loop that is critical for tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 71:4380–4391
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F, Raman V, Ramirez N, Oberyszyn TM, Hall BM (2009) Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28:2940–2947
Salgado R, Junius S, Benoy I, Van Dam P, Vermeulen P, Van Marck E, Huget P, Dirix LY (2003) Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer 103:642–646
Bachelot T, Ray-Coquard I, Menetrier-Caux C, Rastkha M, Duc A, Blay JY (2003) Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer 88:1721–1726
Korkaya H, Liu S, Wicha MS (2011) Regulation of cancer stem cells by cytokine networks: attacking cancer’s inflammatory roots. Clin Cancer Res 17:6125–6129
Korkaya H, Liu S, Wicha MS (2011) Breast cancer stem cells cytokine networks and the tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest 121:3804–3809
Radtke F, Clevers H (2005) Self-renewal and cancer of the gut: two sides of a coin. Science 307:1904–1909
Vermeulen L, De Sousa EMF, van der Heijden M, Cameron K, de Jong JH, Borovski T, Tuynman JB, Todaro M, Merz C, Rodermond H, Sprick MR, Kemper K, Richel DJ, Stassi G, Medema JP (2010) Wnt activity defines colon cancer stem cells and is regulated by the microenvironment. Nat Cell Biol 12:468–476
Korkaya H, Wicha MS (2010) Cancer stem cells: nature versus nurture. Nat Cell Biol 12:419–421
Sigurdsson V, Hilmarsdottir B, Sigmundsdottir H, Fridriksdottir AJ, Ringner M, Villadsen R, Borg A, Agnarsson BA, Petersen OW, Magnusson MK, Gudjonsson T (2011) Endothelial induced EMT in breast epithelial cells with stem cell properties. PLoS ONE 6:e23833
Pierce BL, Ballard-Barbash R, Bernstein L, Baumgartner RN, Neuhouser ML, Wener MH, Baumgartner KB, Gilliland FD, Sorensen BE, McTiernan A, Ulrich CM (2009) Elevated biomarkers of inflammation are associated with reduced survival among breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol 27:3437–3444
Mantovani A, Romero P, Palucka AK, Marincola FM (2008) Tumour immunity: effector response to tumour and role of the microenvironment. Lancet 371:771–783
Mantovani A, Pierotti MA (2008) Cancer and inflammation: a complex relationship. Cancer Lett 267:180–181
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F (2008) Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 454:436–444
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357:539–545
Michaud DS, Daugherty SE, Berndt SI, Platz EA, Yeager M, Crawford ED, Hsing A, Huang WY, Hayes RB (2006) Genetic polymorphisms of interleukin-1B (IL-1B) IL-6 IL-8 and IL-10 and risk of prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66:4525–4530
Zou W (2005) Immunosuppressive networks in the tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat Rev Cancer 5:263–274
Pardoll D (2003) Does the immune system see tumors as foreign or self? Annu Rev Immunol 21:807–839
Dunn GP, Bruce AT, Ikeda H, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2002) Cancer immunoediting: from immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat Immunol 3:991–998
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K (2009) An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB Lin28 Let-7 MicroRNA and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 139:693–706
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk ML, Struhl (2010) K STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to cancer. Mol Cell 39:493–506
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P, Marcu KB, Chieco P, Bonafe M (2007) IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland. J Clin Invest 117:3988–4002
Liu H, Patel MR, Prescher JA, Patsialou A, Qian D, Lin J, Wen S, Chang YF, Bachmann MH, Shimono Y, Dalerba P, Adorno M, Lobo N, Bueno J, Dirbas FM, Goswami S, Somlo G, Condeelis J, Contag CH, Gambhir SS, Clarke MF (2010) Cancer stem cells from human breast tumors are involved in spontaneous metastases in orthotopic mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:18115–18120
Magnifico A, Albano L, Campaner S, Delia D, Castiglioni F, Gasparini P, Sozzi G, Fontanella E, Menard S, Tagliabue E (2009) Tumor-initiating cells of HER2-positive carcinoma cell lines express the highest oncoprotein levels and are sensitive to trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res 15:2010–2021
Korkaya H, Wicha MS (2009) HER-2 notch and breast cancer stem cells: targeting an axis of evil. Clin Cancer Res 15:1845–1847
Pece S, Serresi M, Santolini E, Capra M, Hulleman E, Galimberti V, Zurrida S, Maisonneuve P, Viale G, Di Fiore PP (2004) Loss of negative regulation by Numb over Notch is relevant to human breast carcinogenesis. J Cell Biol 167:215–221
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, Beachy PA (2002) Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to smoothened genes. Dev 16:2743–2748
Clement V, Sanchez P, de Tribolet N, Radovanovic I, Altaba A Ruiz i (2007) HEDGEHOG-GLI1 signaling regulates human glioma growth cancer stem cell self-renewal and tumorigenicity. Curr Biol 17:165–172
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A, Isaacs JT, Berman DM, Beachy PA (2004) Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 431:707–712
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Yajnik V, Antoniu B, McMahon M, Warshaw AL, Hebrok M (2003) Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 425:851–856
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, Parker AR, Shimada Y, Eshleman JR, Watkins DN, Beachy PA (2003) Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature 425:846–851
Rudin CM, Hann CL, Laterra J, Yauch RL, Callahan CA, Fu L, Holcomb T, Stinson J, Gould SE, Coleman B, LoRusso PM, Von Hoff DD, de Sauvage FJ, Low JA (2009) Treatment of medulloblastoma with hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449. N Engl J Med 361:1173–1178
Kelly OG, Pinson KI, Skarnes WC (2004) The Wnt co-receptors Lrp5 and Lrp6 are essential for gastrulation in mice. Development 131:2803–2815
Huelsken J, Vogel R, Brinkmann V, Erdmann B, Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W (2000) Requirement for beta-catenin in anterior-posterior axis formation in mice. J Cell Biol 148:567–578
Li Y, Welm B, Podsypanina K, Huang S, Chamorro M, Zhang X, Rowlands T, Egeblad M, Cowin P, Werb Z, Tan LK, Rosen JM, Varmus HE (2003) Evidence that transgenes encoding components of the Wnt signaling pathway preferentially induce mammary cancers from progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15853–15858
Lepourcelet M, Chen YN, France DS, Wang H, Crews P, Petersen F, Bruseo C, Wood AW, Shivdasani RA (2004) Small-molecule antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf/beta-catenin protein complex. Cancer Cell 5:91–102
Liu M, Sakamaki T, Casimiro MC, Willmarth NE, Quong AA, Ju X, Ojeifo J, Jiao X, Yeow WS, Katiyar S, Shirley LA, Joyce D, Lisanti MP, Albanese C, Pestell RG (2010) The canonical NF-kappaB pathway governs mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice and tumor stem cell expansion. Cancer Res 70:10464–10473
Joshi PA, Jackson HW, Beristain AG, Di Grappa MA, Mote PA, Clarke CL, Sting LJ, Waterhouse PD, Khokha R (2010) Progesterone induces adult mammary stem cell expansion. Nature 465:803–807
Asselin-Labat ML, Vaillant F, Sheridan JM, Pal B, Wu D, Simpson ER, Yasuda H, Smyth GK, Martin TJ, Lindeman GJ, Visvader JE (2010) Control of mammary stem cell function by steroid hormone signalling. Nature 465:798–802
Hassane DC, Sen S, Minhajuddin M, Rossi RM, Corbett CA, Balys M, Wei L, Crooks PA, Guzman ML, Jordan CT (2010) Chemical genomic screening reveals synergism between parthenolide and inhibitors of the PI-3 kinase and mTOR pathways. Blood 116:5983–5990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Korkaya, H., Malik, F. (2013). Breast Cancer Stem Cells: Responsible for Therapeutic Resistance and Relapse?. In: Ahmad, A. (eds) Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5647-6_21
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5647-6_21
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-5646-9
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-5647-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)