Abstract
Aim
Our aim was to identify psychological and behavioral characteristics of women affected by normal weight obese (NWO) syndrome.
Methods
Anthropometric, body composition, eating behavior and physical activity were evaluated in 79 women.
Results
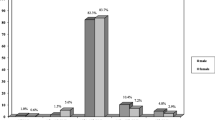
48.10 % of the subjects were found to be normalweight obese (NWO), 22.79 % normalweight lean (NWL), and 29.11 % pre-obese-obese (PreOB/OB) according to BMI and body composition. Significant differences (p < 0.001) among the groups were identified on analysis of the subscales of the Eating Disorder Inventory-2 (EDI-2), suggesting progressively increased presence of psychopathology relative to body composition. In a further analysis, results of the subscales of the EDI-2 were compared with body composition parameters, revealing that BMI co-varied with body composition variables and psychological responses. %TBFat co-varied exclusively with body composition variables (height, weight, BMI, KgTBFat, and a decrease of KgTBLean (R 2 = 0.96; Q 2 = 0.94). The NWO was discriminated from PreOB/OB group (compared to BMI) only on the basis of body composition variables (R 2 = 0.68; Q 2 = 0.60).
Conclusion
NWO women appeared to find themselves at a cognitive crossroads, attaining intermediate scores on the EDI-2 between normal weight lean women and pre-obese or obese women, in particular in terms of drive for thinness and body dissatisfaction. The NWO syndrome not only conveys an increased risk of cardiovascular and metabolic disease, but may also significantly overlap with other eating disorders in terms of psychological symptomatology, the correct identification of which may be the key in the successful management of these patients.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01890070



Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (1998) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report on a WHO Consultation of Obesity
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Ogden CL (2012) Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. JAMA 307:491–497. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.39
Mensah GA, Mokdad AH, Ford E, Narayan KM, Giles WH, Vinicor F, Deedwania PC (2004) Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: emerging epidemics and their cardiovascular implications. Cardiol Clin 22(4):485–504. doi:10.1016/j.ccl.2004.06.005
Dixon JB (2010) The effect of obesity on health outcomes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316:104–108. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2009.07.008
Report of a WHO consultation (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 894:i–xii, 1–253
De Lorenzo A, Nardi A, Iacopino L, Domino E, Murdolo G, Gavrila C, Minella D, Scapagnini G, Di Renzo L (2014) A new predictive equation for evaluating women body fat percentage and obesity-related cardiovascular disease risk. J Endocrinol Invest 37(6):511–524. doi:10.1007/s40618-013-0048-3
De Lorenzo A, Bianchi A, Maroni P, Iannarelli A, Di Daniele N, Iacopino L, Di Renzo L (2013) Adiposity rather than BMI determines metabolic risk. Int J Cardiol 166(1):111–117. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.10.006
De Lorenzo A, Martinoli R, Vaia F, Di Renzo L (2006) Normal weight obese (NWO) women: an evaluation of candidate new syndrome. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 16(8):513–523. doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2005.10.010
Oliveros E, Somers VK, Sochor O, Goel K, Lopez-Jimenez F (2014) The concept of normal weight obesity. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 56(4):426–433. doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2013.10.003
Di Renzo L, Del Gobbo V, Bigioni M, Premrov MG, Cianci R, De Lorenzo A (2006) Body composition analyses in normal weight obese women. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 10(4):191–196
Di Renzo L, Sarlo F, Petramala L, Iacopino L, Monteleone G, Colica C, De Lorenzo A (2013) Association between -308 G/A TNF-α polymorphism and appendicular skeletal muscle mass index as a marker of sarcopenia in normal weight obese syndrome. Dis Markers 35(6):615–623. doi:10.1155/2013/983424
Di Renzo L, Gratteri S, Sarlo F, Cabibbo A, Colica C, De Lorenzo A (2014) Individually tailored screening of susceptibility to sarcopenia using p53 codon 72 polymorphism, phenotypes, and conventional risk factors. Dis Markers. doi:10.1155/2014/743634
Di Renzo L, Marsella L, Sarlo F, Soldati L, Gratteri S, Abenavoli L, De Lorenzo A (2014) C677T gene polymorphism of MTHFR and metabolic syndrome: response to dietary intervention. J Transl Med 12:329. doi:10.1186/s12967-014-0329-4
Romero-Corral A, Somers VK, Sierra-Johnson J, Korenfeld Y, Boarin S, Korinek J, Jensen MD, Parati G, Lopez-Jimenez F (2010) Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. Eur Heart J 31(6):737–746. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehp487
Marques-Vidal P, Pécoud A, Hayoz D, Paccaud F, Mooser V, Waeber G, Vollenweider P (2008) Prevalence of normal weight obesity in Switzerland: effect of various definitions. Eur J Nutr 47(5):251–257. doi:10.1007/s00394-008-0719-6
Di Renzo L, Bigioni M, Bottini FG, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Cianci R, De Lorenzo A (2006) Normal Weight Obese syndrome: role of single nucleotide polymorphism of IL-15R-alpha and MTHFR 677CT genes in the relationship between body composition and resting metabolic rate. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 10(5):235–245. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2006.11.002
Di Renzo L, Bigioni M, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Barbini U, Di Lorenzo N, De Lorenzo A (2007) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor antagonist gene poymorphism in normal weight obese syndrome: relationship to body composition and IL-1α and β plasma levels. Pharmacol Res 55(2):131–138. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2006.11.002
Di Renzo L, Bertoli A, Bigioni M, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Calabrese V, Di Daniele N, De Lorenzo A (2008) Body composition and -174 G/C Interleukin-6 promoter gene polymorphism: association with progression of insulin resistance in normal weight obese syndrome. Curr Pharm Des 14:2699–2706. doi:10.2174/138161208786264061
Di Renzo L, Galvano F, Orlandi C, Bianchi A, Di Giacomo C, La Fauci L, Acquaviva R, De Lorenzo A (2010) Oxidative stress in normal-weight obese syndrome. Obes (Silver Spring). 18(11):2125–2130. doi:10.1038/oby.2010.50
Kang S, Kyung C, Park JS, Kim S, Lee SP, Kim MK, Kim HK, Kim KR, Jeon TJ, Ahn CW (2014) Subclinical vascular inflammation in subjects with normal weight obesity and its association with body Fat: an 18 F-FDG-PET/CT study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 13(1):70. doi:10.1186/1475-2840-13-70
Madeira FB, Silva AA, Veloso HF, Goldani MZ, Kac G, Cardoso VC, Bettiol H, Barbieri MA (2013) Normal weight obesity is associated with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in young adults from a middle-income country. PLoS One 8(3):e60673. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060673
Haines J, Neumark-Sztainer D (2006) Prevention of obesity and eating disorders: a consideration of shared risk factors. Health Educ Res 21(6):770–782. doi:10.1093/her/cyl094
Villarejo C, Jiménez-Murcia S, Álvarez-Moya E et al (2014) Loss of control over eating: a description of the eating disorder/obesity spectrum in women. Eur Eat Disord Rev 22(1):25–31. doi:10.1002/erv.2267
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R (1998) Anthropometric standardization reference manual. Champaign, IL, Human Kinetics
Hansen RD, Raja C, Aslani A, Smith RC, Allen BJ (1999) Determination of skeletal muscle and fat-free mass by nuclear and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry methods in men and women aged 51–84 years (1–3). Am J Clin Nutr 70:228–233
Garner DM (1991) Eating disorder inventory-2 professional manual. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Rizzardi M, Trombini G (1995) EDI-2. Organizzazioni Speciali, Firenze
Vanderheyden DA, Boland MA (1987) A comparison of normals, mild, moderate, and severe binge eaters, and binge vomiters using discriminant function analysis. Int J Eat Disord 6(3):331–337. doi:10.1002/1098-108X(198705)6:3<331::AID-EAT2260060302>3.0.CO;2-M
Rosen JC, Gross J, Vara L (1987) Psychological adjustment of adolescents attempting to lose or gain weight. J Consult Clin Psych 55(5):742–747. doi:10.1037//0022-006X.55.5.742
Martens HA, Anderssen E, Flatberg A, Gidskehaug LH, Høy M, Westad F, Thybo A, Martens M (2005) Regression of a data matrix on descriptors of both its rows and of its columns via latent variables: L-PLSR. Comput Stat Data Ana l48(1):103–123
De Lorenzo A, Del Gobbo V, Premrov MG, Bigioni M, Galvano F, Di Renzo L (2007) Normal-weight obese syndrome: early inflammation? Am J Clin Nutr 85:40–45
Lasserre AM, Glaus J, Vandeleur CL, Marques-Vidal P, Vaucher J, Bastardot F, Waeber G, Vollenweider P, Preisig M (2014) Depression with atypical features and increase in obesity, body mass index, waist circumference, and fat mass. JAMA Psychiatry 71(8):880–888. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.411
Rosenblat JD, Cha DS, Mansur RB, McIntyre RS (2014) Inflamed moods: a review of the interactions between inflammation and mood disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 53C:23–34. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.01.013
Ramacciotti CE, Coli E, Bondi E, Burgalassi A, Massimetti G, Dell’osso L (2008) Shared psychopathology in obese subjects with and without binge-eating disorder. Int J Eat Disord 41(7):643–649. doi:10.1002/eat.20544
Boschi V, Siervo M, D’Orsi P, Margiotta N, Trapanese E, Basile F, Nasti G, Papa A, Bellini O, Falconi C (2003) Body composition, eating behaviour, food-body concerns and eating disorders in adloescent girls. Ann Nutr Metab 47:284–293. doi:10.1159/000072401
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to all the subjects who volunteered in the study.
This study was supported by grants from Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Forestry (D.M.; 2017188).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures of the study were performed in accordance with the1964 Helsinki declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Renzo, L., Tyndall, E., Gualtieri, P. et al. Association of body composition and eating behavior in the normal weight obese syndrome. Eat Weight Disord 21, 99–106 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-015-0215-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-015-0215-y