Abstract
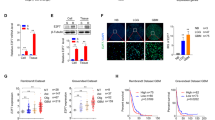
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the prevalent and most fatal brain tumor in adults. Invasion and a high rate of recurrence largely contribute to the poor prognosis of GBM. The current standard therapy for GBM includes surgery with maximum feasible resection, radiotherapy, and treatment with chemotherapeutic agent temozolomide. Annexin A5 reportedly promotes progression and chemoresistance in a variety of cancers. In the present study, we explored the effects of annexin A5 on GBM cell invasion and chemoresistance to temozolomide. Stable overexpression and knockdown of annexin A5 were performed in both U-87 MG and U-118 MG human GBM cell lines. Overexpression of annexin A5 in both cell lines significantly increased cell invasion, matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) expression/activity, Akt phosphorylation at serine 473, and the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of temozolomide and markedly decreased temozolomide-induced apoptosis, all of which were abolished by selective PI3K inhibitor BKM120. On the other hand, knockdown of annexin A5 markedly decreased cell invasion, MMP-2 expression/activity, Akt phosphorylation at serine 473, and the IC50 values of temozolomide and significantly increased temozolomide-induced apoptosis. In conclusion, our study provides the first evidence that annexin A5 promotes GBM cell invasion, MMP-2 expression/activity, and chemoresistance to temozolomide through a PI3K-dependent mechanism. It adds new insights not only into the biological function of annexin A5 but also into the molecular mechanisms underlying GBM progression and chemoresistance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dolecek TA, Propp JM, Stroup NE, Kruchko C. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neurooncol. 2012;14:v1–v49.
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–66.
Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507.
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M. Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:1624–36.
Berthois Y, Delfino C, Metellus P, Fina F, Nanni-Metellus I, Al Aswy H, et al. Differential expression of miR200a-3p and miR21 in grade II-III and grade IV gliomas: evidence that miR200a-3p is regulated by O 6-methylguanine methyltransferase and promotes temozolomide responsiveness. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15.
Moss SE, Morgan RO. The annexins. Genome Biol. 2004;5:219.
Laohavisit A, Davies JM. Multifunctional annexins. Plant Sci. 2009;177:532–9.
Peng B, Guo C, Guan H, Liu S, Sun MZ. Annexin A5 as a potential marker in tumors. Clin Chim Acta. 2014;427:42–8.
Tang S, Huang W, Zhong M, Yin L, Jiang H, Hou S, et al. Identification keratin 1 as a cDDP-resistant protein in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. J Proteome. 2012;75:2352–60.
Rajcevic U, Petersen K, Knol JC, Loos M, Bougnaud S, Klychnikov O, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomics profiling reveals increased metabolic activity and cellular cross-talk in angiogenic compared with invasive glioblastoma phenotype. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8:2595–612.
Wang B, Feng P, Xiao Z, Ren EC. LIM and SH3 protein 1 (Lasp1) is a novel p53 transcriptional target involved in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2009;50:528–37.
Feng Y, Hu J, Ma J, Feng K, Zhang X, Yang S, et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:2353–63.
Jo YK, Park SJ, Shin JH, Kim Y, Hwang JJ, Cho DH, et al. ARP101, a selective MMP-2 inhibitor, induces autophagy-associated cell death in cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;404:1039–43.
Qazi H, Shi ZD, Tarbell JM. Fluid shear stress regulates the invasive potential of glioma cells via modulation of migratory activity and matrix metalloproteinase expression. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20348.
Ding X, Zhang Z, Li S, Wang A. Combretastatin A4 phosphate induces programmed cell death in vascular endothelial cells. Oncol Res. 2011;19:303–9.
Li Y, Liao Q, Li K, Zhong D, Weng X, Mi M. Knockdown of endothelin A receptor expression inhibits osteosarcoma pulmonary metastasis in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5:1391–5.
Li B, Yang Y, Jiang S, Ni B, Chen K, Jiang L. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of BMP-9 inhibits human osteosarcoma cell growth and migration through downregulation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J Oncol. 2012;41:1809–19.
Liu ZL, Mao JH, Peng AF, Yin QS, Zhou Y, Long XH, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase suppresses osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration via downregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7:608–12.
Zhao G, Cai C, Yang T, Qiu X, Liao B, Li W, et al. MicroRNA-221 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in human osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 2013;8:e53906.
Wang TF, Wang H, Peng AF, Luo QF, Liu ZL, Zhou RP, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase suppresses U-2 OS cell invasion and migration via downregulating the activity of HER2/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;440:229–34.
Yao R, Jiang H, Ma Y, Wang L, Wang L, Du J, et al. PRMT7 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2014.
Wang J, Ou J, Guo Y, Dai T, Li X, Liu J, et al. TBLR1 is a novel prognostic marker and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:112–24.
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;114:97–109.
Pan SJ, Zhan SK, Pei BG, Sun QF, Bian LG, Sun BM. MicroRNA-149 inhibits proliferation and invasion of glioma cells via blockade of AKT1 signaling. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2012;25:871–81.
Ramaswamy P, Aditi Devi N, Hurmath Fathima K, Dalavaikodihalli Nanjaiah N. Activation of NMDA receptor of glutamate influences MMP-2 activity and proliferation of glioma cells. Neurol Sci. 2013.
Xiao Y, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhou K, Wen J, Wang Y, et al. Up-regulation of miR-200b in biliary atresia patients accelerates proliferation and migration of hepatic stallate cells by activating PI3K/Akt signaling. Cell Signal. 2014;26:925–32.
Hsieh CH, Cheng LH, Hsu HH, Ho TJ, Tu CC, Lin YM, et al. Apicidin-resistant HA22T hepatocellular carcinoma cells strongly activated the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and MMP-2 expression via the IGF-IR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway enhancing cell metastatic effect. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2013;77:2397–404.
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S, Stein H, Jaffe ES. WHO classification of tumours of hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Blood. 2011;117:5019–32.
Lossos IS, Morgensztern D. Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:995–1007.
Deng S, Wang J, Hou L, Li J, Chen G, Jing B, et al. Annexin A1, A2, A4 and A5 play important roles in breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and laryngeal carcinoma, alone and/or synergistically. Oncol Lett. 2013;5:107–12.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, L., Yang, L., Xiong, Y. et al. Annexin A5 promotes invasion and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioblastoma multiforme cells. Tumor Biol. 35, 12327–12337 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2545-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2545-1