Abstract
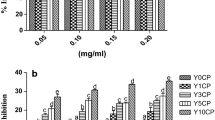
In this study a new wheat bread was designed whose sugars were replaced with S. rebaudiana Bertoni aqueous extract. The impact of the S. rebaudiana Bertoni aqueous extract on nutritional and sensory quality, its ability to reduce sugar intake and its antioxidant properties were investigated. Functional bread with 50 % of sugars replaced with S. rebaudiana extract was compared with traditional wheat bread. The extract demonstrated alpha amylase (IC50 = 198.40 μg/mL) glucosidase (596.77 μg/mL) inhibition. The radical scavenging activity exhibited an IC50 value of 335.94 mg/mL. In comparison with the control, the bread with stevia extract was softer and had lower microbial growth during the shelf-life study. The sensory test showed that the substitution of 50 % stevia extract was more acceptable when comparing with all quality characteristics. Regarding the nutritional contribution, the content of dietary fiber and digestible carbohydrates in the bread with stevia extract was higher and lower respectively, so caloric intake was significantly reduced. The results showed that the biological properties of S. rebaudiana extract were retained after the bread making process and that the proposed bread is suitable as functional food in human nutrition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam J, Talukder MU, Rahman MN, Prodhan UK, Huq AKO (2013) Evaluation of the nutritional and sensory quality of functional breads prepared from whole wheat and soybean flour. Annals Food Sci Technol 14(2):171–175
American Association of Cereal Chemistis-AACC (2000) Approved methods of analysis of the AACC. 10. ed. St. Paul
Annunziata A, Vecchio R (2011) Functional foods development in the European market: a concumer perspective. J Func Foods 3:223–228
Association of Official Analytical Chemists-AOAC (1997) Official Methods of Analysis, AOAC, Arlington, VA, USA. Secs. 920.39, 923.03, 925.09, 954.01, 962.09, 992.16
Belda-Galbis CM, Pina-Pérez MC, Espinosa J, Marco-Celdrán A, Martínez A, Rodrigo D (2014) Use of the modified Gompertz equation to assess the Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni antilisterial kinetics. Food Microbiol 38:56–61
Bischoff H (1994) Pharmacology of alpha-glucosidase inhibition. Eur J Clin Invest 24:3–10
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C (1995) Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm Wiss Technology 28:25–30
Chen L, Kang YH (2013) In vitro inhibitory effect of oriental melon (Cucumis melo L. var. mauka Makino) seed on key enzyme linked to type 2 diabetes. J Func Foods 5:981–986
Cirillo G, Puoci F, Iemma F, Curcio M, Parisi OI, Spizzirri UG, Altimari I, Picci N (2011) Starch-quercetin conjugate by radical grafting: synthesis and biological characterization. Pharm Develop Technol 17(4):466–476
Criado MN, Barba FJ, Frígola A, Rodrigo D (2013) Effect of Stevia rebaudiana on oxidative enzyme activity and its correlation with antioxidant capacity and bioactive compounds. Food Bioprocess Technol 7(5):1518–1525
Czuchajowska Z, Pomeranz Y, Jeffers HC (1989) Water activity and moisture content of dough and bread. Cereal Chem 66:128–132
Dewanto V, Wu X, Adom KK, Liu RH (2002) Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem 50:3010–3014
Dineshkumar B, Mitra A, Manjunatha M (2010) Studies on the anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic potentials of mangiferin (Xanthone glucoside) in streptozotocin-induced type 1 and type 2 diabetic model rats. Int J Advan Pharm Sci 1:75–85
Dziki D, Rozylo R, Gawlik-Dziki U, Swieca M (2014) Current trends in the enhancement of antioxidant activity of wheat bread by the addition of plant materials rich in phenolic compounds. Trends Food Sci Technol 40:48–61
FAO⁄WHO⁄UNU Expert Consultation (1994) Food Nutrients Requirements, Report of a Joint FAO⁄WHO⁄UNU Expert Consultation. World Health Organization Technical Report Series. 724. Geneva: WHO
Ghanta S, Banerjee A, Poddar A, Chattopadhyay S (2007) Oxidative DNA damage preventive activity and antioxidant potential of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni), a natural Sweetener. J Agric Food Chem 55:10962–10967
Gupta E, Purwar S, Sandaram S, Gai GK (2013) Nutritional and therapeutic values of Stevia rebaudiana: a review. J Med Plants Res 7:3343–3353
Han H-M, Koh B-K (2011) Antioxidant activity of hard wheat flour, dough and bread prepared using various processes with the addition of different phenolic acids. J Sci Food Agric 91:604–608
Hirano R, Sasamoto W, Matsumoto A, Itakura H, Igarashi O, Kondo K (2001) Antioxidant ability of various flavonoids against DPPH radicals and LDL oxidation. J Nut Sci Vitaminol 47:357–362
Jideani V, Onwubali F (2009) Optimisation of wheat-sprouted soybean flour bread using response surface methodology. Afr J Biotechnol 8:6364–6373
John KMM, Rajesh J, Mandal AKA, Natarajan S (2011) Antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of individual catechin molecules: a comparative study between gallated and epimerized catechin molecules. Eur J Exp Biol 1(3):145–153
Kähkönen MP, Hopia AI, Vuorela HJ, Rauha J-P, Pihlaja K, Kujala TS, Heinonen M (1999) Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 47:3954–3962
Krentz A, Bailey C (2005) Oral antidiabetic agents: current role in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs 65:385–411
Kwon Y, Apostolidis E, Shetty K (2007) Evaluation of pepper (Capsicum annuum) for management of diabetes and hypertension. J Food Biochem 31:370–385
Lemus-Mondaca R, Vega-Gálvez A, Zura-Bravo L, Ah-Hen K (2012) Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, source of a high-potency natural sweetener: a comprehensive review on the bichemical, nutritional and functional aspects. Food Chem 132:1121–1132
Mishra N (2011) An Analysis of antidiabetic activity of Stevia rebaudiana extract on diabetic patient. J Nat Sci Res 1(3):1–9
Montgomery D (2004) Diseño y análisis de experimentos. Limusa-Wiley, México
Nair SS, Kavrekar V, Mishra A (2012) In vitro studies on alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory activities of selected plant extracts. Eur J Exp Biol 3(1):128–132
NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-247-SSA1-2008, Productos y servicios. Cereales y sus productos. Cereales, harinas de cereales, sémolas o semolinas. Alimentos a base de: cereales, semillas comestibles, de harinas, sémolas o semolinas o sus mezclas. Productos de panificación. Disposiciones y especificaciones sanitarias y nutrimentales. Métodos de prueba
Ognean M, Darie N, Ognean CF (2006) Studies about obtaining low calorie and high fiber content bakery product using wheat bran. Acta Universitatis Cibiniensis Seria F Chemia 9(1):55–66
Önal S, Timmur S, Okuttucu B, Zihnioglu F (2005) Inhibition of alpha-glucosidase by aqueous extracts of some potent antidiabetic medicinal herbs. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 35:29–36
Preethi D, Sridhar TM, Josthna P, Naidu CV (2011) Studies on antibacterial activity, phytochemical analysis of Stevia rebaudiana (Bert.). An important calorie free biosweetner. J Ecobiotechnol 3(7):5–10
Prosky L, Asp N, Schweitzer T, Debris S, Furda I (1998) Determination of insoluble, soluble and total dietary fiber in food and food products: interlaboratory study. J AOAC 71:1017–1023
Puoci F, Malanchin R, Piangiolino C, Restuccia D, Curcio M, Parisi OI, Cirillo G, Picci N (2013) Maca flour: a powerful ingredient for functionally enhanced bread. Int Food Res J 20(3):1293–1300
Ramírez JG, Avilés BW, Moguel OY, Góngora GS, May LC (2011) Estevia (Stevia rebaudiana, Bertoni), un cultivo con potencial productivo en México. Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Forestales, Agrícolas y Pecuarias. Centro de Investigación Regional sureste
Rao GN, Rao PP, Balaswamy K, Satyanarayana A (2014) Antioxidant activity of Stevia (Stevia rebaudiana L.) leaf powder and a commercial stevioside powder. J Food Pharm Sci 2:32–38
Reyes-Carmona J, Yousef GG, Martinez-Peniche RA, Lila MA (2005) Antioxidant capacity of fruit extracts of blackberry (Rubus sp.) produced in different climatic regions. J Food Sci 70:497–503
Schleißinger M, Meyer AL, Afsar N, György Nagy Á, Dieker V, Schmitt JJ (2013) Impact of dietary fibers on moisture and crumb firmness of brown bread. Advan J Food Sci Technol 5(10):1281–1284
Sharma R, Yadav R, Manivannan E (2012) Study of effect of Stevia rebaudiana bertoni on oxidative stress in type-2 diabetic rat models. Biomed Aging Pathol 2:126–131
Shimada K, Fujikawa K, Yahara K, Nakamura T (1992) Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the autioxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J Agric Food Chem 40:945–948
Sigh S, Garg V, Yadav D (2013) Antihyperglucemic and antioxidative ability of Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni) leaves in diabetes induced mice. Int J Pharm Sci 5(2):297–302
Singleton VL, Rossi JA (1965) Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am J Enol Vitic 16(3):144–158
Swieca M, Gawlik-Dziki U, Dziki D, Baraniak B, Czyz J (2013) The influence of protein-flavonoid interactions on protein digestibility in vitro and the antioxidant quality of breads enriched with onion skin. Food Chem 141:451–458
Torricella MR, Zamora UE, Pulido AH (1989) Evaluación sensorial aplicada al desarrollo de la calidad en la industria alimentaria. Instituto de Investigaciones para la Industria Alimenticia. La Habana, Cuba
Woelwer RU, Lankes C, Wawrzun A, Wüst M (2010) Improved HPLC method for evaluation of the major steviol glycosides in leaves of Stevia rebaudiana. Eur Food Res Technol 231:581–588
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz-Ruiz, J.C., Moguel-Ordoñez, Y.B., Matus-Basto, A.J. et al. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of Stevia rebaudiana extracts (Var. Morita) and their incorporation into a potential functional bread. J Food Sci Technol 52, 7894–7903 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1883-3
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1883-3