Abstract
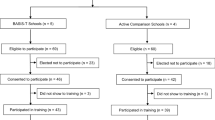
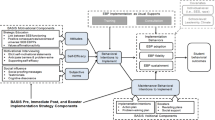
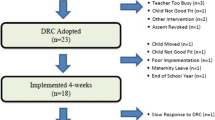
This study investigated the perceived feasibility and pattern of implementation following an online training for teachers delivering an integrated intervention encompassing two school-based universal preventive interventions: Promoting Alternative THinking Strategies (PATHS) curriculum and the PAX Good Behavior Game (GBG). Forty-five teachers from three urban elementary schools completed an online training consisting of didactics and video demonstration and received in-person coaching across a 31-week implementation period. Data from 65 teachers from three schools who received in-person training and coaching provided a benchmark for comparison. Most teachers in the online training + in-person coaching (OLT + IPC) condition reported that the technology was easy to use and that the course was as effective as an in-person workshop. Teachers in the OLT + IPC group reported positive attitudes regarding PATHS and the PAX GBG that generally were not significantly different from attitudes reported by teachers who received in-person training + in-person coaching (IPT + IPC). Importantly, teachers in the OLT + IPC condition achieved a high level of implementation quality similar to that demonstrated by teachers in the IPT + IPC condition. The frequency of intervention delivery by OLT + IPC teachers was also not significantly different than that of IPT + IPC teachers. These findings provide evidence that the internet is a promising component in a training sequence designed to teach teachers to deliver evidence-based preventive interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbaugh, J. (2005). Is there an optimal design for online MBA courses? Academy of Management Learning & Education, 4, 135–149.
Barrish, H., Saunders, M., & Wolf, M. (1969). Good behavior game: Effects of individual contingencies for group consequences on disruptive behavior in a classroom. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 2, 119–124.
Becker, K. D., Bradshaw, C., Domitrovich, C., & Ialongo, N. (2013). Coaching teachers to improve implementation of the good behavior game. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 40, 482–493.
Becker, K. D., Darney, D., Domitrovich, C., Keperling, J., & Ialongo, N. (2013). Supporting universal prevention programs: A two-phased coaching model. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 16, 213–228.
Beidas, R., Edmunds, J., Marcus, S., & Kendall, P. (2012). Training and consultation to promote implementation of an empirically supported treatment: A randomized trial. Psychiatric Services, 63, 660–665.
Bernard, R., Abrami, P., Lou, Y., Borokhovski, E., Wade, A., Wozney, L., et al. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta-analysis of the empirical literature. Review of Educational Research, 74, 379–439.
Bishop, D., Giles, S., & Bryant, K. (2005). Teacher receptiveness toward web-based training and support. Teaching and Teacher Education, 21, 3–14.
Boe, E., Shin, S., & Cook, L. (2007). Does teacher preparation matter for beginning teachers in either special or general education? Journal of Special Education, 41, 148–170.
Bradshaw, C., Zmuda, J., Kellam, S., & Ialongo, N. (2009). Longitudinal impact of two universal preventive interventions in first grade and educational outcomes in high school. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101, 926–937.
Buchanan, T., Sainter, P., & Saunders, G. (2013). Factors affecting faculty use of learning technologies: Implications for models of technology adoption. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 25, 1–11.
Catalano, R., Berglund, M., Ryan, J., Lonczak, H., & Hawkins, J. (2002). Positive youth development in the United States: Research findings on evaluations of positive youth development programs. Prevention & Treatment, 5, Article 15.
Cavanaugh, C. (2001). The effectiveness of interactive distance education technologies in K-12 learning: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Educational Telecommunications, 7, 73–78.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (1999). Initial impact of the Fast Track prevention trial for conduct problems: II. Classroom effects. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 648–657.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2010). The effects of a multi-year randomized clinical trial of a universal social-emotional learning program: The role of student and school characteristics. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 78, 156–168.
Darling-Hammond, L., Wei, R., Andree, A., Richardson, N., & Orphanos, S. (2009). Professional learning in the learning profession: A status report on teacher development in the United States and abroad. Oxford, OH: National Staff Development Council.
Derzon, J., Sale, E., Springer, J., & Brounstein, P. (2005). Estimating intervention effectiveness: Synthetic projection of field evaluation results. Journal of Primary Prevention, 26, 321–343.
Dimeff, L., Koerner, K., Woodcock, E., Beadnell, B., Brown, M., Skutch, J., et al. (2009). Which training method works best? A randomized controlled trial comparing three methods of training clinicians in dialectical behavior therapy skills. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 47, 921–930.
Domitrovich, C., Bradshaw, C., Greenberg, M., Embry, D., Poduska, J., & Ialongo, N. (2010). Integrated models of school-based prevention: Logic and theory. Psychology in the Schools, 47, 71–88.
Domitrovich, C., Greenberg, M., Schaffer, K., Darney, D., Rouiller, S., & Ialongo, N. (2006). The PATHS to PAX implementation rubric. Unpublished technical report. Johns Hopkins University.
Durlak, J., & DuPre, E. (2011). Implementation matters: A review of research on the influence of implementation on program outcomes and the factors affecting implementation. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 327–350.
Durlak, J., Weissberg, R., Dymnicki, A., Taylor, R., & Schellinger, K. (2011). The impact of enhancing students’ social and emotional learning: A meta-analysis of school-based universal interventions. Child Development, 82, 405–432.
Embry, D., Staatemeier, G., Richardson, C., Lauger, K., & Mitich, J. (2003). The PAX good behavior game (1st ed.). Center City, MN: Hazelden.
Fixsen, D., Naoom, S., Blasé, K., Friendman, R., & Wallace, F. (2005). Implementation research: A synthesis of the literature. Tampa, FL: The National Implementation Research Network, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, University of South Florida.
Gottfredson, D., & Wilson, D. (2003). Characteristics of effective school-based substance abuse prevention. Prevention Science, 4, 27–38.
Greenberg, M., Domitrovich, C., & Bumbarger, B. (2001). The prevention of mental disorders in school-aged children: Current state of the field. Prevention & Treatment, 4, 1–64.
Greenberg, M., & Kusche, C. (2006). Building social and emotional competence: The PATHS curriculum. In S. R. Jimerson & M. J. Furlong (Eds.), Handbook of school violence and school safety: From research to practice (pp. 395–412). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Greenberg, M., Kusche, C., Cook, E., & Quamma, J. (1995). Promoting emotional competence in school-aged children: The effects of the PATHS curriculum. Development and Psychopathology, 7, 117–136.
Hahn, R., Fuqua-Whitley, D., Wethington, H., Lowy, J., Crosby, A., Fullilove, M., et al. (2007). Effectiveness of universal school-based programs to prevent violent and aggressive behavior: A systematic review. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 33, s114–s129.
Hamre, B., Pianta, R., Burchinal, M., Field, S., LoCasale-Crouch, J., Downer, J. T., et al. (2012). A course on effective teacher–child interactions: Effects on teacher beliefs, knowledge, and observed practice. American Educational Research Journal, 49, 88–123.
Ialongo, N., Poduska, J., Werthamer, L., & Kellam, S. (2001). The distal impact of two first-grade preventive interventions on conduct problems and disorder in early adolescence. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 9, 146–160.
Ialongo, N., Werthamer, L., Kellam, S., Brown, C., Wang, S., & Lin, Y. (1999). Proximal impact of two first-grade preventive interventions on the early risk behaviors for later substance abuse, depression, and anti-social behavior. American Journal of Community Psychology, 27, 599–641.
Ingersoll, R., & Smith, T. (2003). The wrong solution to the teacher shortage. Educational Leadership, 60, 30–33.
Joyce, B., & Showers, B. (2002). Student achievement through staff development (3rd ed.). Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development.
Justice, L., Chow, S., Capellini, C., Flanigan, K., & Colton, S. (2003). Emergent literacy intervention for vulnerable preschoolers: Relative effects of two approaches. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 12, 320–332.
Kam, C., Greenberg, M., & Kusche, C. (2004). Sustained effects of the PATHS curriculum on the social and psychological adjustment of children in special education. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 12, 66–78.
Kellam, S., Brown, C., Poduska, J., Ialongo, N., Wang, W., Toyinbo, P., et al. (2008). Effects of a universal classroom behavior management program in first and second grades on young adult behavioral, psychiatric, and social outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 95S, S5–S28.
Kellam, S., Ling, X., Merisca, R., Brown, C., & Ialongo, N. (1998). The effect of the level of aggression in the first grade classroom on the course and malleability of aggressive behavior into middle school. Development and Psychopathology, 10, 165–185.
Kellam, S., Rebok, G., Ialongo, N., & Mayer, L. (1994). The course and malleability of aggressive behavior from early first grade into middle school: Results of a developmental epidemiologically-based preventive trial. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 35, 259–281.
Kusche, C., & Greenberg, M. (1995). The PATHS curriculum. Seattle, WA: Developmental Research and Programs.
Mikami, A., Gregory, A., Allen, J., Pianta, R., & Lun, J. (2011). Effects of a teacher professional development intervention on peer relationships in secondary classrooms. School Psychology Review, 40, 367–385.
Murray, D., Varnell, S., & Blitstein, J. (2004). Design and analysis of group-randomized trials: A review of recent methodological developments. American Journal of Public Health, 94, 423–432.
Office of National Drug Control Policy. (2004). The economic costs of drug abuse in the United States, 1992–2002. Washington, DC: Executive Office of the President (Publication No. 207303).
Petras, H., Kellam, S., Brown, C., Muthén, B., Ialongo, N., & Poduska, J. (2008). Developmental epidemiological courses leading to antisocial personality disorder and violent and criminal behavior: Effects by young adulthood of a universal preventive intervention in first- and second-grade classrooms. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 95(Suppl. 1), 45–59.
Pianta, R., & Hamre, B. (2001). Students, teachers, and relationship support. Lutz. FL: Psychological Assessment Resources. Online: www.parinc.com.
Pianta, R., Mashburn, A., Downer, J., Hamre, B., & Justice, L. (2008). Effects of web-mediated professional development resources on teacher–child interactions in pre-kindergarten classrooms. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 23, 431–451.
Reinke, W., Stormont, M., Herman, K., Puri, R., & Goel, N. (2011). Supporting children’s mental health in schools: Teacher perceptions of needs, roles, and barriers. School Psychology Quarterly, 26, 1–13.
Riggs, N., Greenberg, M., Kusche, C., & Pentz, M. (2006). The mediational role of neurocognition in the behavioral outcomes of a social-emotional prevention program in elementary school students: Effects of the PATHS curriculum. Prevention Science, 7, 91–102.
Schaffer, K., Darney, D., Rouiller, S., Embry, D., & Ialongo, N. (2006). The PAX good behavior game implementation rubric. Unpublished technical report. Johns Hopkins University.
Sholomskas, D., Syracuse-Stewart, G., Rounsaville, B., Ball, S., Nuro, K., & Carroll, K. (2005). We don’t train in vain: A dissemination trial of three strategies of training clinicians in cognitive-behavioral therapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73, 106–115.
Sitzmann, T., Kraiger, K., Stewart, D., & Wisher, R. (2006). The comparative effectiveness of web-based and classroom instruction: A meta-analysis. Personnel Psychology, 59, 623–644.
U.S. Department of Education, Office of Planning, Evaluation, and Policy Development. (2010). Evaluation of evidence-based practices in online learning: A meta-analysis and review of online learning studies. Washington, D.C.: Author.
Wehby, J., Maggin, D., Partin, T., & Robertson, R. (2012). The impact of working alliance, social validity, and teacher burnout on implementation fidelity of the good behavior game. School Mental Health, 4, 22–33.
Weingardt, K., Villafranca, S., & Levin, C. (2006). Technology-based training in cognitive behavioral therapy for substance abuse counselors. Substance Abuse, 27, 19–26.
Wilson, S., & Lipsey, M. (2007). School-based interventions for aggressive and disruptive behavior: Update of a meta-analysis. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 33, S130–S143.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by grants from the Institutes for the Education Sciences (R305A080326) and the National Institute of Mental Health (P30 MH086043 T32 MH018834). We wish to acknowledge the wonderful contributions of our teacher and administrator colleagues in the Baltimore City Public School System and the invaluable contributions of Dennis Embry, Ph.D. and Mark Greenberg, Ph.D.
Conflict of interest
Dr. Domitrovich is an author of the PATHS Curriculum and has a royalty agreement with Channing-Bete, Inc. She receives income from PATHS Training, LLC. This has been reviewed and managed by Penn State’s Individual Conflict of Interest Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, K.D., Bohnenkamp, J., Domitrovich, C. et al. Online Training for Teachers Delivering Evidence-Based Preventive Interventions. School Mental Health 6, 225–236 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-014-9124-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-014-9124-x