Abstract
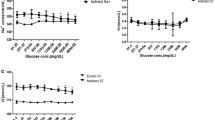
To determine the concentration of ionized calcium (iCa) collected in lithium heparin and gel tubes and to correlate the measured iCa with calculated iCa. Anaerobic fasting blood samples were simultaneously collected from healthy laboratory workers in lithium-heparin and gel tubes. iCa, pH, total calcium (CaT), total protein and albumin were measured. Ionized Ca was calculated with albumin and globulin values using an appropriate formula. Mean iCa in gel tubes showed a positive constant bias of 0.08 mmol/L (p < 0.001) when compared to lithium heparin results. The mean pH of blood taken in lithium heparin and gel tubes was non-significant (p = 0.3). Measured iCa poorly correlated with CaT (r = 0.2, p = 0.1) and calculated iCa (r = 0.2, p = 0.2). To evaluate the calcium status direct measurement of iCa must be done rather than using the formulae for iCa determination. In addition serum is recommended as the choice of sample for iCa determination in comparison to plasma samples.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- iCa:
-
Ionized calcium
- CaT:
-
Total calcium
- ISE:
-
Ion selective electrode
- PTH:
-
Parathyroid hormone
- CLSI:
-
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute
- IFCC:
-
International Federation of Clinical Chemistry
- SPSS:
-
Statistical Package of Social Sciences
References
Burnett RW, Christiansen TF, Covington AK, Fogh-Andersen N, Kulpmann WR, Lewenstam A, et al. IFCC recommended reference method for the determination of the substance concentration of ionized calcium in undiluted serum, plasma or whole blood. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2000;38(12):1301–14.
Kallner A. Preanalytical procedures in the measurement of ionized calcium in serum and plasma. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1996;34(1):53–8.
Baird GS. Ionized calcium. Clin Chim Acta. 2011;412(9–10):696–701.
Copp DH. Endocrine control of calcium homeostasis. J Endocrinol. 1969;43(1):137–61.
Robertson WG, Marshall RW. Calcium measurements in serum and plasma–total and ionized. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1979;11(3):271–304.
Seaton RD, Duncan KA, Pinnick RV, Diederich DA, Wiegmann TB. Regional citrate anticoagulation in chronic hemodialysis patients. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1983;29:414–8.
White TF, Farndon JR, Conceicao SC, Laker MF, Ward MK, Kerr DN. Serum calcium status in health and disease: a comparison of measured and derived parameters. Clin Chim Acta. 1986;157(2):199–213.
Thode J, Juul-Jorgensen B, Bhatia HM, Kjaerulf-Nielsen M, Bartels PD, Fogh-Andersen N, et al. Comparison of serum total calcium, albumin-corrected total calcium, and ionized calcium in 1213 patients with suspected calcium disorders. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1989;49(3):217–23.
Wang S, McDonnell EH, Sedor FA, Toffaletti JG. pH effects on measurements of ionized calcium and ionized magnesium in blood. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2002;126(8):947–50.
Bushinsky DA, Monk RD. Electrolyte quintet: Calcium. Lancet. 1998;352(9124):306–11.
Bjorkman MP, Sorva AJ, Tilvis RS. Calculated serum calcium is an insufficient surrogate for measured ionized calcium. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2009;49(3):348–50.
Haverstick DM, Brill LB 2nd, Scott MG, Bruns DE. Preanalytical variables in measurement of free (ionized) calcium in lithium heparin-containing blood collection tubes. Clin Chim Acta. 2009;403(1–2):102–4.
Boink AB, Buckley BM, Christiansen TF, Covington AK, Maas AH, Muller-Plathe O, et al. Recommendation on sampling, transport, and storage for the determination of the concentration of ionized calcium in whole blood, plasma, and serum. IFC Scientific Division, Working Group on Ion-Selective Electrodes (WGSE). J Int Fed Clin Chem. 1992;4(4):147–52.
Boink AB, Buckley BM, Christiansen TF, Covington AK, Maas AH, Muller-Plathe O, et al. IFCC recommendation on sampling, transport and storage for the determination of the concentration of ionized calcium in whole blood, plasma and serum. J Autom Chem. 1991;13(5):235–9.
Boink AB, Buckley BM, Christiansen TF, Covington AK, Maas AH, Muller-Plathe O, et al. International Federation of Clinical Chemistry (IFCC) scientific division IFCC recommendation. Recommendation on sampling, transport and storage for the determination of the concentration of ionized calcium in whole blood, plasma and serum. Ann Biol Clin (Paris). 1991;49(8):434–8.
NCCLS. Ionized calcium determinations: precollection variables, specimen choice, collection, and handling; approved guideline—second edition, vol 21. Wayne: NCCLS; 2001, p. C31–A2.
Sava L, Pillai S, More U, Sontakke A. Serum calcium measurement: Total versus free (ionized) calcium. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2005;20(2):158–61.
Dickerson RN, Henry NY, Miller PL, Minard G, Brown RO. Low serum total calcium concentration as a marker of low serum ionized calcium concentration in critically ill patients receiving specialized nutrition support. Nutr Clin Pract. 2007;22(3):323–8.
Dickerson RN, Alexander KH, Minard G, Croce MA, Brown RO. Accuracy of methods to estimate ionized and “corrected” serum calcium concentrations in critically ill multiple trauma patients receiving specialized nutrition support. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004;28(3):133–41.
Atsumi N, Abe M, Sakakibara Y, Terada Y, Jikuya T, Tsutsui T, et al. Influence of ionized calcium concentration during cardiopulmonary bypass on pediatric cardiac surgery. Kyobu Geka. 1994;47(7):544–8.
Shimeliovich IL, Lanskaia IM, Andrianova M, Lur’e GO, Mal’tseva A. The concentration of calcium and its fractions during heart surgery using extracorporeal circulation. Anesteziol Reanimatol. 1991;3:32–6.
Gauci C, Moranne O, Fouqueray B, de la Faille R, Maruani G, Haymann JP, et al. Pitfalls of measuring total blood calcium in patients with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(8):1592–8.
Calvi LM, Bushinsky DA. When is it appropriate to order an ionized calcium? J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19(7):1257–60.
Ong GS, Walsh JP, Stuckey BG, Brown SJ, Rossi E, Ng JL, et al. The Importance of Measuring Ionized Calcium in Characterizing Calcium Status and Diagnosing Primary Hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(9):3138–45.
Ladenson JH, Lewis JW, McDonald JM, Slatopolsky E, Boyd JC. Relationship of free and total calcium in hypercalcemic conditions. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1979;48(3):393–7.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
The study was given exemption by Ethical review committee (ERC) as per AKU ERC guidelines section B. http://www.aku.edu/res-office/res-erc.shtml.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafri, L., Khan, A.H. & Azeem, S. Ionized Calcium Measurement in Serum and Plasma by Ion Selective Electrodes: Comparison of Measured and Calculated Parameters. Ind J Clin Biochem 29, 327–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0360-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0360-x