Abstract
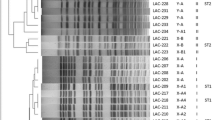
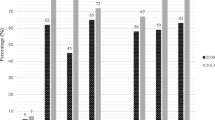
The investigation was carried out to elucidate the molecular characteristics and resistant mechanisms of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Thirty-seven isolates were collected from January 2007 to December 2007. The homology of the isolates was analyzed by both pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) and multilocus sequence typing (MLST). The genes of β-lactamases, adeB, and class 1 integron were polymerase chain reaction amplified. Genotype analysis of the 37 A. baumannii isolates by PFGE revealed the circulation of four PFGE types (A-D); the A- and B-type accounted for 48.6% and 40.5%, respectively. MLST showed the existence of three allelic profiles. The agar dilution method was carried out to determine the MIC of imipenem, in the absence or presence of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP, 10 μg/ml). The MICs of the strains to imipenem were between 16 μg/ml and 128 μg/ml. When CCCP was added, a MIC decrease of at least four-fold was observed in 20 isolates, which belonged to the A- or C-type. AdeB and bla PER-1 genes were each detected in 35 isolates, bla OXA-23 gene in 34 isolates and bla OXA-58-like gene in 24 isolates. All isolates harbored bla OXA-51-like genes. No isolates carried the bla IMP-1 gene. Integron was detected in 25 isolates, which mediated the resistance to aminoglycosides and rifampin. The epidemiologic data suggested that the increasing infection of A. baumannii in our hospital was mainly caused by the inter-hospital spread of two epidemic clones. The AdeABC efflux system may be the important factor that leads to the high level of imipenem-resistance in PFGE A-type.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afzal-Shah, M., N. Woodford, and D.M. Livermore. 2001. Characterization of OXA-25, OXA-26, OXA-27, molecular class D betalactamases associated with carbapenem resistance in clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumanni. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 583–588.
Bertini, A., A. Giordano, P. Varesi, L. Villa, C. Mancini, and A. Carattoli. 2006. First report of the plasmid-mediated carbapenemhydrolyzing oxacillinase OXA-58 in Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in Italy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 2268–2269.
Brown, S. and S. Amyes. 2006. OXA-lactamases in Acinetobacter: the story so far. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 57, 1–3.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2006. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Sixteenth Informational Supplement M100-S16. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, Pa, USA.
Cetin, E.S., R. Durmaz, T. Tetik, B. Otlu, S. Kaya, and A. Cali kan. 2009. Epidemiologic characterization of nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii infections in a Turkish university hospital by pulsedfield gel electrophoresis. Am. J. Infect Control. 37, 56–64.
Coelho, J., N. Woodford, M. Afzal-Shah, and D. Livermore. 2006. Occurrence of OXA-58-like carbapene-mases in Acinetobacter spp. Collected over 10 years in three continents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 756–758.
Dalla-Costa, L.M., J.M. Coelho, H.A. Souza, M.E. Castro, C.J. Stier, K.L. Bragagnolo, A. Rea-Neto, S.R. Penteado-Filho, D.M. Livermore, and N. Woodford. 2003. Outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23 enzyme in Curitiba, Brazil. J. Clin. Microbiol. 41, 3403–3406.
Dijkshoorn, L., H. Aucken, P. Gerner-Smidt, P. Janssen, M.E. Kaufmann, J. Garaizar, J. Ursing, and T.L. Pitt. 1996. Comparison of outbreak and nonoutbreak Acinetobacter baumannii strains by genotypic and phenotypic methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34, 1519–1525.
Gerner-Smidt, P. 1992. Ribotyping of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus Acinetobacter baumannii complex. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30, 2680–2685.
Gouby, A., M.J. Carles-Nurit, N. Bouziges, G. Bourg, R. Mesnard, and P.J. Bouvet. 1992. Use of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for investigation of hospital outbreaks of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30, 1588–1591.
Grundmann, H., S. Hori, M.C. Enright, C. Webster, A. Tami, E.J. Feil, and T. Pitt. 2002. Determining the genetic structure of the natural population of Staphylococcus aureus: a comparison of multilocus sequence typing with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis, and phage typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 4544–4546.
Grundmann, H.J., K.J. Towner, L. Dijkshoorn, P. Gerner-Smidt, M. Maher, H. Seifert, and M. Vaneechoutte. 1997. Multi-center study using standardized protocols and reagents for evaluation of reproducibility of PCR based fingerprinting of Acinetobacter spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 3071–3077.
Héritier, C., A. Dubouix, L. Poirel, N. Marty, and P. Nordmann. 2005. A nosocomial outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates expressing the carbapenem-hydrolysing oxacillinase OXA-58. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 55, 115–118.
Homan, W.L., D. Tribe, S. Poznanski, M. Li, G. Hogg, E. Spalburg, J.D. Van Embden, and R.J. Willems. 2002. Multilocus sequence typing scheme for Enterococcus faecium. J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 1963–1971.
Jeon, B., S.H. Jeong, I.K. Bae, S.B. Kwon, K. Lee, D. Young, J.H. Lee, J.S. Song, and S.H. Lee. 2005. Investigation of a nosocomial outbreak of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii producing the OXA-23-lactamase in Korea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 2241–2245.
Koeleman, J.G., J. Stoof, M.W. Van Der Bijl, C.M. Vandenbroucke-Grauls, and P.H. Savelkoul. 2001. Identification of epidemic strains of Acinetobacter baumannii by Integrase Gene PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 39, 8–13.
Lévesque, C., L. Piché, C. Larose, and P.H. Roy. 1995. PCR mapping of integrons reveals several novel combinations of resistance genes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39, 185–191.
Magnet, S., P. Courvalin, and T. Lambert. 2001. Resistancenodulation-cell division-type efflux pump involved in aminoglycoside resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii strain BM4454. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45, 3375–3380.
Maiden, M.C., J.A. Bygraves, E. Feil, G. Morelli, J.E. Russell, R. Urwin, Q. Zhang, J. Zhou, K. Zurth, D.A. Caugant, I.M. Feavers, M. Achtman, and B.G. Spratt. 1998. Multilocus sequence typing: a portable approach to the identification of clones within populations of pathogenic microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3140–3145.
Marchand, I., L. Damier-Piolle, P. Courvalin, and T. Lambert. 2004. Expression of the RND-type efflux pump AdeABC in Acinetobacter baumannii is regulated by the AdeRS two-component system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48, 3298–3304.
Poirel, L., A. Karim, A. Mermat, I. Le Thomas, H. Vahaboglu, C. Richard, and P. Nordmann. 1999. Extended-spectrum betalactamase-producing strain of Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from a patient in France. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 43, l57–165.
Poirel, L. and P. Nordmann. 2006. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: mechanisms and epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 12, 826–836.
Pournaras, S., A. Markogiannakis, A. Ikonomidis, L. Kondyli, K. Bethimouti, A.N. Maniatis, N.J. Legakis, and A. Tsakris. 2006. Outbreak of multiple clones of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates expressing OXA-58 carbapenemase in an intensive care unit. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 57, 557–561.
Riccio, M.L., N. Franceschini, L. Boschi, B. Caravelli, G. Cornaglia, R. Fontana, G. Amicosante, and G.M. Rossolini. 2000. Characterization of the metallo-beta-lactamase determinant of Acinetobacter baumannii AC-54/97 reveals the existence of bla(IMP) allelic variants carried by gene cassettes of different phylogeny. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44, 1229–1235.
Sergio, G.B., H. Seifert, C. Hippler, M.A. Luzon, H. Wisplinghoff, and F. Rodríguez-Valera. 2005. Development of a multilocus sequence typing scheme for characterization of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 43, 4382–4390.
Shi, W.F., J.P. Jiang, N. Xu, Z.M. Huang, and Y.Y. Wang. 2005. Inhibitory effects of reserpine and carbonyl cyanidem-chlorophenylhydrazone on fluoroquinolone resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii. Clin. Med. J. (Engl). 118, 340–343.
Tenover, F.C., R.D. Arbeit, R.V. Goering, P.A. Mickelsen, B.E. Murray, D.H. Persing, and B. Swaminathan. 1995. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 33, 2233–2239.
Tian, S.F., B.Y. Chen, Y.Z. Chu, and S. Wang. 2008. Prevalence of rectal carriage of extended-spectrum -lactamase-producing Escherichia coli among elderly people in community settings in China. Can. J. Microbiol. 54, 781–785.
Vahaboglu, H., F. Budak, M. Kasap, G. Gacar, S. Torol, A. Karadenizli, F. Kolayli, and C. Eroglu. 2006. High prevalence of OXA-51-type class D-lactamases among ceftazidime-resistant clinical isolates of Acinetobacter spp.: co-existence with OXA-58 in multiple centers. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 58, 537–542.
Van, L.M., H. Goossens, and ARPAC Steering Group. 2004. Antimicrobial resistance of Acinetobacter spp. in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 10, 684–704.
Wang, H., M. Chen, Y. Ni, Y. Liu, H. Sun, Y. Yu, X. Yu, Y. Mei, M. Liu, Z. Sun, Y. Chu, Z. Hu, and X. Huang. 2005. Antimicrobial resistance analysis among nosocomial Gram-negative bacilli from 10 teaching hospitals in China. Chin. J. Lab. Med. 28, 1295–1303.
Wang, H., P. Guo, H. Sun, H. Wang, Q. Yang, M. Chen, Y. Xu, and Y. Zhu. 2007. Molecular epidemiology of clinical isolates of carbapenemresistant Acinetobacter spp. from Chinese hospitals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51, 4022–4028.
Yoo, J.H., J.H. Choi, W.S. Shin, D.H. Huh, Y.K. Cho, K.M. Kim, M.Y. Kim, and M.W. Kang. 1999. Application of infrequentrestriction-site PCR to clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii and Serratia marcescens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37, 3108–3112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.P., Zhu, W., Tian, S.F. et al. Molecular characteristics and resistant mechanisms of imipenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in Shenyang, China. J Microbiol. 48, 689–694 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0137-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-0137-3