Abstract
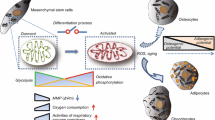
Due to a rapidly expanding aging population, the incidence of age-related or degenerative diseases has increased, and efforts to handle the issue with regenerative medicine via adult stem cells have become more important. And it is now clear that the mitochondrial energy metabolism is important for stem cell differentiation. When stem cells commit to differentiate, glycolytic metabolism is being shifted to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) to meet an increased cellular energy demand required for differentiated cells. However, the nature of cellular metabolisms during the differentiation process of periosteum-derived mesenchymal stem cells (POMSC) is still unclear. In the present study, we investigated mitochondrial biogenesis during the adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic differentiation of POMSCs. Both mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) contents and mitochondrial proteins (VDAC and mitochondrial OXPHOS complex subunits) were increased during all of these mesenchymal lineage differentiations of POMSCs. Interestingly, glycolytic metabolism is reduced as POMSCs undergo osteogenic differentiation. Furthermore, reducing mtDNA contents by ethidium bromide treatments prevents osteogenic differentiation of POMSCs. In conclusion, these results indicate that mitochondrial biogenesis and OXPHOS metabolism play important roles in the differentiation of POMCS and suggest that pharmaceutical modulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and/or function can be a novel regulation for POMSC differentiation and regenerative medicine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angelova PR, Barilani M, Lovejoy C, Dossena M, Vigano M, Seresini A, Piga D, Gandhi S, Pezzoli G, Abramov AY, Lazzari L (2018) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinsonian mesenchymal stem cells impairs differentiation. Redox Biol 14:474–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.016
Berebichez-Fridman R, Gomez-Garcia R, Granados-Montiel J, Berebichez-Fastlicht E, Olivos-Meza A, Granados J, Velasquillo C, Ibarra C (2017) The holy grail of orthopedic surgery: mesenchymal stem cells-their current uses and potential applications. Stem Cells Int 2017:2638305. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2638305
Breitbart AS, Grande DA, Kessler R, Ryaby JT, Fitzsimmons RJ, Grant RT (1998) Tissue engineered bone repair of calvarial defects using cultured periosteal cells. Plast Reconstr Surg 101:567–574. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-199803000-00001
Brunt KR, Weisel RD, Li RK (2012) Stem cells and regenerative medicine—future perspectives. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1139/y2012-007
Chen CT, Shih YR, Kuo TK, Lee OK, Wei YH (2008) Coordinated changes of mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant enzymes during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 26:960–968. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2007-0509
Choudhery MS, Badowski M, Muise A, Pierce J, Harris DT (2014) Donor age negatively impacts adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell expansion and differentiation. J Transl Med 12:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-12-8
Chung JE, Park JH, Yun JW, Kang YH, Park BW, Hwang SC, Cho YC, Sung IY, Woo DK, Byun JH (2016) Cultured human periosteum-derived cells can differentiate into osteoblasts in a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated fashion via bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Int J Med Sci 13:806–818. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.16484
Dao LT, Park EY, Lim SM, Choi YS, Jung HS, Jun HS (2014) Transplantation of insulin-producing cells differentiated from human periosteum-derived progenitor cells ameliorate hyperglycemia in diabetic mice. Transplantation 98:1040–1047. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000000388
De Bari C, Dell’Accio F, Luyten FP (2001) Human periosteum-derived cells maintain phenotypic stability and chondrogenic potential throughout expansion regardless of donor age. Arthritis Rheum 44:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1%3c85:AID-ANR12%3e3.0.CO;2-6
De Bari C, Dell’Accio F, Vanlauwe J, Eyckmans J, Khan IM, Archer CW, Jones EA, Mcgonagle D, Mitsiadis TA, Pitzalis C, Luyten FP (2006) Mesenchymal multipotency of adult human periosteal cells demonstrated by single-cell lineage analysis. Arthritis Rheum 54:1209–1221. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.21753
Duchamp de Lageneste O, Julien A, Abou-Khalil R, Frangi G, Carvalho C, Cagnard N, Cordier C, Conway SJ, Colnot C (2018) Periosteum contains skeletal stem cells with high bone regenerative potential controlled by Periostin. Nat Commun 9:773. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03124-z
Fernandez-Moreno M, Hermida-Gomez T, Gallardo ME, Dalmao-Fernandez A, Rego-Perez I, Garesse R, Blanco FJ (2016) Generating rho-0 cells using mesenchymal stem cell lines. PLoS ONE 11:e0164199. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0164199
Ferretti C, Mattioli-Belmonte M (2014) Periosteum derived stem cells for regenerative medicine proposals: boosting current knowledge. World J Stem Cells 6:266–277. https://doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v6.i3.266
Forni MF, Peloggia J, Trudeau K, Shirihai O, Kowaltowski AJ (2016) Murine mesenchymal stem cell commitment to differentiation is regulated by mitochondrial dynamics. Stem Cells 34:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2248
Gonzalez-Gil AB, Lamo-Espinosa JM, Muinos-Lopez E, Ripalda-Cemborain P, Abizanda G, Valdes-Fernandez J, Lopez-Martinez T, Flandes-Iparraguirre M, Andreu I, Elizalde MR, Stuckensen K, Groll J, De-Juan-Pardo EM, Prosper F, Granero-Molto F (2019) Periosteum-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells in engineered implants promote fracture healing in a critical-size defect rat model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 13:742–752. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2821
Hah YS, Joo HH, Kang YH, Park BW, Hwang SC, Kim JW, Sung IY, Rho GJ, Woo DK, Byun JH (2014) Cultured human periosteal-derived cells have inducible adipogenic activity and can also differentiate into osteoblasts in a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-mediated fashion. Int J Med Sci 11:1116–1128. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.9611
Hock MB, Kralli A (2009) Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Annu Rev Physiol 71:177–203. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.010908.163119
Hofmann AD, Beyer M, Krause-Buchholz U, Wobus M, Bornhauser M, Rodel G (2012) OXPHOS supercomplexes as a hallmark of the mitochondrial phenotype of adipogenic differentiated human MSCs. PLoS ONE 7:e35160. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035160
Hsu YC, Wu YT, Yu TH, Wei YH (2016) Mitochondria in mesenchymal stem cell biology and cell therapy: from cellular differentiation to mitochondrial transfer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 52:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.02.011
Hutmacher DW, Sittinger M (2003) Periosteal cells in bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng 9(Suppl 1):S45–S64. https://doi.org/10.1089/10763270360696978
Ito K, Suda T (2014) Metabolic requirements for the maintenance of self-renewing stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:243–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3772
Lee JH, Hah YS, Cho HY, Kim JH, Oh SH, Park BW, Kang YH, Choi MJ, Shin JK, Rho GJ, Jeon RH, Lee HC, Kim GC, Kim UK, Kim JR, Lee CI, Byun JH (2014) Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34-positive endothelial progenitor cells stimulate osteoblastic differentiation of cultured human periosteal-derived osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A 20:940–953. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEA.2013.0329
Mara CS, Sartori AR, Duarte AS, Andrade AL, Pedro MA, Coimbra IB (2011) Periosteum as a source of mesenchymal stem cells: the effects of TGF-beta3 on chondrogenesis. Clinics 66:487–492. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1807-59322011000300022
Marycz K, Kornicka K, Maredziak M, Golonka P, Nicpon J (2016) Equine metabolic syndrome impairs adipose stem cells osteogenic differentiation by predominance of autophagy over selective mitophagy. J Cell Mol Med 20:2384–2404. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12932
Murphy MP, Hartley RC (2018) Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for common pathologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 17:865–886. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2018.174
Palomaki S, Pietila M, Laitinen S, Pesala J, Sormunen R, Lehenkari P, Koivunen P (2013) HIF-1alpha is upregulated in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 31:1902–1909. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.1435
Park BW, Hah YS, Kim DR, Kim JR, Byun JH (2007) Osteogenic phenotypes and mineralization of cultured human periosteal-derived cells. Arch Oral Biol 52:983–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2007.04.007
Park BW, Hah YS, Kim DR, Kim JR, Byun JH (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in cultured periosteal-derived cells. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 105:554–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2007.08.018
Patil R, Kumar BM, Lee WJ, Jeon RH, Jang SJ, Lee YM, Park BW, Byun JH, Ahn CS, Kim JW, Rho GJ (2014) Multilineage potential and proteomic profiling of human dental stem cells derived from a single donor. Exp Cell Res 320:92–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.10.005
Pattappa G, Heywood HK, De Bruijn JD, Lee DA (2011) The metabolism of human mesenchymal stem cells during proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Physiol 226:2562–2570. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22605
Pessoa LV, Bressan FF, Chiaratti MR, Pires PR, Perecin F, Smith LC, Meirelles FV (2015) Mitochondrial DNA dynamics during in vitro culture and pluripotency induction of a bovine rho0 cell line. Genet Mol Res 14:14093–14104. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.October.29.29
Pietila M, Palomaki S, Lehtonen S, Ritamo I, Valmu L, Nystedt J, Laitinen S, Leskela HV, Sormunen R, Pesala J, Nordstrom K, Vepsalainen A, Lehenkari P (2012) Mitochondrial function and energy metabolism in umbilical cord blood- and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 21:575–588. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2011.0023
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S, Marshak DR (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5411.143
Ryu YM, Hah YS, Park BW, Kim DR, Roh GS, Kim JR, Kim UK, Rho GJ, Maeng GH, Byun JH (2011) Osteogenic differentiation of human periosteal-derived cells in a three-dimensional collagen scaffold. Mol Biol Rep 38:2887–2894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-9950-3
Scarpulla RC (2011) Metabolic control of mitochondrial biogenesis through the PGC-1 family regulatory network. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:1269–1278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.019
Shen Y, Wu L, Wang J, Wu X, Zhang X (2018) The role of mitochondria in methamphetamine-induced inhibitory effects on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol 826:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.02.049
Tormos KV, Anso E, Hamanaka RB, Eisenbart J, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B, Chandel NS (2011) Mitochondrial complex III ROS regulate adipocyte differentiation. Cell Metab 14:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.007
Varum S, Rodrigues AS, Moura MB, Momcilovic O, Easley CA, Ramalho-Santos J, Van Houten B, Schatten G (2011) Energy metabolism in human pluripotent stem cells and their differentiated counterparts. PLoS ONE 6:e20914. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020914
Wanet A, Remacle N, Najar M, Sokal E, Arnould T, Najimi M, Renard P (2014) Mitochondrial remodeling in hepatic differentiation and dedifferentiation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 54:174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2014.07.015
Wang YL, Hong A, Yen TH, Hong HH (2018) Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human alveolar periosteum and effects of vitamin D on osteogenic activity of periosteum-derived cells. J Vis Exp 135:e57166. https://doi.org/10.3791/57166
Wisnovsky S, Lei EK, Jean SR, Kelley SO (2016) Mitochondrial chemical biology: new probes elucidate the secrets of the powerhouse of the cell. Cell Chem Biol 23:917–927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.06.012
Woo DK, Green PD, Santos JH, D’souza AD, Walther Z, Martin WD, Christian BE, Chandel NS, Shadel GS (2012) Mitochondrial genome instability and ROS enhance intestinal tumorigenesis in APC(Min/+) mice. Am J Pathol 180:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.003
Younger EM, Chapman MW (1989) Morbidity at bone graft donor sites. J Orthop Trauma 3:192–195. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005131-198909000-00002
Zhang X, Naik A, Xie C, Reynolds D, Palmer J, Lin A, Awad H, Guldberg R, Schwarz E, Okeefe R (2005) Periosteal stem cells are essential for bone revitalization and repair. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 5:360–362
Zhang Y, Marsboom G, Toth PT, Rehman J (2013) Mitochondrial respiration regulates adipogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS ONE 8:e77077. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077077
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea (Grants #: NRF-2016R1D1A1B03931722 and NRF-2017R1D1A1B03035996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, A.R., Moon, D.K., Siregar, A. et al. Involvement of mitochondrial biogenesis during the differentiation of human periosteum-derived mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes, chondrocytes and osteocytes. Arch. Pharm. Res. 42, 1052–1062 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01198-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01198-x