Abstract
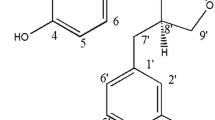
Eugenol, a member of the phenylpropanoids class of chemical compounds, is a clear to pale yellow oily liquid extracted from certain essential oils especially from clove oil, nutmeg, cinnamon, and bay leaf. The antibacterial activity of eugenol and its mechanism of bactericidal action against Proteus mirabilis were evaluated. Treatment with eugenol at their minimum inhibitory concentration [0.125 % (v/v)] and minimum bactericidal concentration [0.25 % (v/v)] reduced the viability and resulted in complete inhibition of P. mirabilis. A strong bactericidal effect on P. mirabilis was also evident, as eugenol inactivated the bacterial population within 30 min exposure. Chemo-attractant property and the observance of highest antibacterial activity at alkaline pH suggest that eugenol can work more effectively when given in vivo. Eugenol inhibits the virulence factors produced by P. mirabilis as observed by swimming motility, swarming behavior and urease activity. It interacts with cellular membrane of P. mirabilis and makes it highly permeable, forming nonspecific pores on plasma membrane, which in turn directs the release of 260 nm absorbing materials and uptake of more crystal violet from the medium into the cells. SDS–polyacrylamide gel, scanning electron microscopy and Fourier transform infrared analysis further proves the disruptive action of eugenol on the plasma membrane of P. mirabilis. The findings reveal that eugenol shows an excellent bactericidal activity against P. mirabilis by altering the integrity of cell membrane.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, S.M., A.A. Khan, I. Ahmed, M. Musaddiq, K.S. Ahmed, H. Polasa, et al. 2005. Antimicrobial activities of eugenol and cinnamaldehyde against the human gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials 4: 20.
Al-Quadiri, H.M., N.I. Al-Alami, M.A. Al-Holy, and B.A. Rasco. 2008. Using Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) absorbance spectroscopy and multivariate analysis to study the effect of chlorine-induced bacterial injury in water. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 56: 8992–8997.
Allison, C., L. Emody, N. Coleman, and C. Hughes. 1994. The role of swarm cell differentiation and multicellular migration in the uropathogenicity of Proteus mirabilis. Journal of Infectious Diseases 169: 1155–1158.
Aiyegoro, O.A., A.J. Afolayan, and A.I. Okoh. 2009. In vitro antibacterial time kill studies of leaves extracts of Helichrysum longifolium. Journal of Medicinal Plant Research 3: 462–467.
Benli, M., N. Yigit, F. Geven, K. Guney, and U. Bingol. 2008. Antimicrobial activity of endemic Crataegus tanacetifolia (Lam.) Pers and observation of the inhibition effect on bacterial cells. Cell Biochemistry and Function 26: 844–851.
Blaszyk, M., and R.A. Holley. 1998. Interaction of monolaurin, eugenol and sodium citrate on growth of common meat spoilage and pathogenic organisms. International Journal of Food Microbiology 39: 175–183.
Burall, L.S., J.M. Harro, X. Li, C.V. Lockatell, S.D. Himpsl, J.R. Hebel, D.E. Johnson, and H.L. Mobley. 2004. Proteus mirabilis genes that contribute to pathogenesis of urinary tract infection: Identification of 25 signature-tagged mutants attenuated at least 100-fold. Infection and Immunity 72: 2922–2938.
Burt, S. 2004. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. International Journal of Food Microbiology 94: 223–253.
Carson, C.F., K.A. Hammer, and T.V. Riley. 1995. Broth microdilution method for determining the susceptibility of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus to the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree oil). Microbios 82: 181–185.
Christensen, W.B. 1946. Urea decomposition as a means of differentiating Proteus and paracolon cultures from each other and from Salmonella and Shigella. Journal of Bacteriology 52: 461.
Cosentino, S., C.I.G. Tuberoso, B. Pisano, M. Satta, V. Mascia, E. Arzedi, and F. Palmas. 1999. In vitro antimicrobial activity and chemical composition of Sardinian Thymus essential oils. Letters in Applied Microbiology 29: 130–135.
Culafic, D.M., B.V. Gacic, J.K. Vukcevic, S. Stankovic, and D. Simic. 2005. Comparative study on the antibacterial activity of volatiles from sage (Salvia officinalis L.). Archives of Biological Science 57: 173–178.
Dattelbaum, J.D., C.V. Lockatell, D.E. Johnson, and H.L.T. Mobley. 2003. The transcriptional activator of the Proteus mirabilis urease gene cluster, is required for urease activity and virulence in experimental urinary tract infections. Infection and Immunity 71: 1026–1030.
Dayton, T.M., K.A. Diefenbach, L.M. Fuller, J. Valtos, and E.C. Niederhoffer. 1996. Production of superoxide dismutases from Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris. BioMetals 9: 131–137.
Devi, K.P., S.A. Nisha, R. Sakthivel, and S.K. Pandian. 2010. Eugenol (an essential oil of clove) acts as an antibacterial agent against Salmonella typhi by disrupting the cellular membrane. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 130: 107–115.
Garg, A.D., and D.V. Kanitkar. 2006. Chemical-gradient motility Agar (CGMA): A system, demonstrating chemoreceptor mediated chemotaxis. In 12th national symposium biotechcellence ‘06 at Centre for Biotechnology, Anna University, Chennai (unpublished result).
Helander, I.M., H.L. Alakomi, K.L. Kala, T.M. Sandholm, I. Pol, E.J. Smid, L.G.M. Gorris, and A.V. Wright. 1998. Characterization of the action of selected essential oil components on gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 46: 3590–3595.
Holt, J.G., N.R. Krieg, P.H.A. Sneath, J.T. Staley, S.T. Williams, and W.R. Hensyl (eds.). 1994. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th ed, 184–185. Baltimore, MD, USA: Williams and Wilkins.
Jay, J.M. 2000. Modern food microbiology, 6th ed. Gaithersburg, MD: Aspen.
Kim, J., M.R. Marshall, and C.I. Wei. 1995. Antibacterial activity of some essential oil components against five food borne pathogens. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 43: 2839–2845.
Liaw, S.J., H.C. Lai, S.W. Ho, K.T. Luh, and W.B. Wang. 2001. Characterization of p-notrophenyl glycerol—Resistant P. mirabilis super-swarming mutants. Journal of Medical Microbiology 50: 1039–1048.
Mobley, H.L., and R.P. Hausinger. 1989. Microbial ureases: Significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiological Reviews 53: 85–108.
Nostro, A., G. Bisignano, M.A. Cannatelli, G. Crisafi, M.P. Germano, and V. Alonzo. 2001. Effects of Helichrysum italicum extract on growth and enzymatic activity of Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 17: 517–520.
Pearson, M.M., M. Sebaihia, C. Churcher, M.A. Quail, A.S. Seshasayee, N.M. Luscombe, Z. Abdellah, C. Arrosmith, B. Atkin, T. Chillingworth, H. Hauser, K. Jagels, S. Moule, K. Mungall, H. Norbertczak, E. Rabbinowitsch, D. Walker, S. Whithead, N.R. Thomson, P.N. Rather, J. Parkhill, and H.L. Mobley. 2008. Complete genome sequence of uropathogenic Proteus mirabilis, a master of both adherence and motility. Journal of Bacteriology 190: 4027–4037.
Sosa, V., and P. Zunino. 2009. Effect of Ibicella lutea on uropathogenic Proteus mirabilis growth, virulence and biofilm formation. The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 3: 762–770.
Tippayatum, P., and V. Chonhenchob. 2007. Antibacterial activities of thymol, eugenol and nisin against some food spoilage bacteria. Kasetsart Journal (Natural Science) 41: 319–323.
Vaara, M., and T. Vaara. 1981. Outer membrane permeability barrier disruption by polymixin in polymixin-susceptible and resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 19: 578–583.
Vázquez, B.I., C. Fente, C.M. Franco, M.J. Vázquez, and A. Cepeda. 2001. Inhibitory effect of eugenol and thymol on Penicillium citrinum strains in culture media and cheese. International Journal of Food Microbiology 67: 157–163.
Vuotto, M.L., A. Basile, V. Moscatiello, P.D. Sole, R.C. Cobianchi, E. Laghi, and M.T.L. Ielpo. 2000. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activites of Feijoa sellowiana fruit. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 13: 197–201.
Wang, W.B., H.C. Lai, P.R. Hsueh, Y.R. Chiou, S.B. Lin, and S.J. Liaw. 2006. Inhibition of swarming and virulence factor expression in Proteus mirabilis by resveratrol. Journal of Medical Microbiology 55: 1313–1321.
Wu, G., J. Ding, H. Li, L. Li, R. Zhao, X. Fan, and Z. Shen. 2008. Effects of cations and pH on antimicrobial activity of thanatin and S-thanatin against Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and B. subtilis ATCC 21332. Current Microbiology 57: 552–557.
Zhou, K., W. Zhou, P. Li, G. Liu, J. Zhang, and Y. Dai. 2008. Mode of action of pentocin 31-1: An antilisteria bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus pentosus from Chinese traditional ham. Food Control 19: 817–822.
Acknowledgments
K.P.D. wishes to thank UGC, India for the financial support. The authors gratefully acknowledge the computational and bioinformatics facility provided by the Alagappa University Bioinformatics Infrastructure Facility (funded by Department of Biotechnology, Government of India; Grant No. BT/BI/25/001/2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devi, K.P., Sakthivel, R., Nisha, S.A. et al. Eugenol alters the integrity of cell membrane and acts against the nosocomial pathogen Proteus mirabilis . Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 282–292 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0028-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0028-3