Abstract
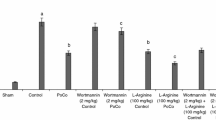
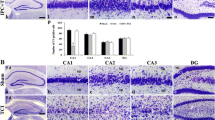
We tested the neuroprotective effect of milrinone, a phosphodiesterase III inhibitor, in pharmacological preconditioning. Bilateral carotid artery occlusion for 12 min followed by reperfusion for 24 h produced ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) cerebral injury in male Swiss albino mice. Cerebral infarct size was measured using triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. Memory was assessed using the Morris water maze test, and motor coordination was evaluated using the inclined beam walking test, rota-rod test, and lateral push test. Milrinone (50 μg/kg & 100 μg/kg i.v.) was administered 24 h before surgery in a separate group of animals to induce pharmacological preconditioning. I/R increased cerebral infarct size and impaired memory and motor coordination. Milrinone treatment significantly decreased cerebral infarct size and reversed I/R-induced impairments in memory and motor coordination. This neuroprotective effect was blocked by ruthenium red (3 mg/kg, s.c.), an intracellular ryanodine receptor blocker. These findings indicate that milrinone preconditioning exerts a marked neuroprotective effect on the ischemic brain, putatively due to increased intracellular calcium levels activating calcium-sensitive signal transduction cascades.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baim, D. S., McDowell, A. V., Cherniles, J., Monrad, E. S., Parker, J. A., Edelson J., Braunwald, E., and Grossman, W., Evaluation of a new bipyridine inotropic agentmilrinone in patients with severe congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med., 309, 748–756 (1983).
Bederson, J. B., Pitts, L. H., Tsuji, M., Nishimur, M. C., Davis, R. L., and Bartowski, H., Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke, 17, 472–476 (1986).
Bochelen, D., Rudin, M., and Sauter, A., Calcineurin inhibitors FK506 and SDZ ASM 981 alleviate the outcome of focal cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 288, 653–659 (1999).
Budde, T., Munsch, T., and Pape, H. C., Distribution of Ltype calcium channels in rat thalamic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci., 10, 586–597 (1998).
Carafoli, E., Santalla, L., Branca, D., and Brini, M., Generation, control and processing of cellular calcium signals. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 36, 107–260 (2001).
Conti, M., Phosphodiesterases and cyclic nucleotide signalling in endocrine cells. Mol. Endocrinol., 14, 1317–1327 (2000).
Davis, D. P. and Patel, P. M., Ischemic preconditioning in the brain. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol., 16, 447–452 (2003).
Dobkin, B. H., The rehabilitation of elderly stroke patients. Clin. Geriatr. Med., 7, 507–523 (1991).
Dunham, N. W. and Miya, T. S., A note on a simple apparatus for detecting neurological deficit in rats and mice. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. Am. Pharm. Assoc. (Baltim), 46, 208–209 (1957).
Edwards, R. J., Saurin, A. T., Rakhit, R. D., and Marber, M. S., Therapeutic potential of ischaemic preconditioning. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 50, 87–97 (2000).
Evans, D. B., Overview of cardiovascular physiologic and pharmacologic aspects of selective phosphodiesterase peak III inhibitors. Am. J. Cardiol., 63, 9A–11A (1989).
Fabiato, A., Time and calcium dependence of activation and inactivation of calcium-induced release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum of a skinned canine cardiac Purkinjee cell. J. Gen. Physiol., 85, 247–289 (1985).
Feeney, D. M., Boyeson, M. G., Linn, R. T., Murray, H. M., and Dail, W. G., Responses to cortical injury: I. Methodology and local effects of contusions in the rat. Brain Res., 211, 67–77 (1981).
Finkbeiner, S. and Greenberg, M. E., Calcium channel regulated neuronal gene expression. J. Neurobiol., 37, 171–189 (1998).
Fraticelli, A. T., Cholley, B. P., Losser, M. R., and Payen, D., Milrinone for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm after aneursymal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke, 39, 893–898 (2008).
Friedman, L. K., Calcium: A role for neuroprotection and sustained adaptation. Mol. Interv., 6, 315–329 (2006).
Gluckman, P. D., Wyatt, J. S., Azzopardi, D., Ballard, R., Edwards, A. D., Ferriero, D. M., Polin, R. A., Robertson, C. M., Thoresen, M., Whitelaw, A., and Gunn, A. J., Selective head cooling with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet, 365, 663–670 (2005).
Iwasaki, K., Egashira, N., Takagaki, Y., Yoshimitsu, Y., Hatip-Al-Khatib, I., Mishima, K., and Fujiwara, M., Nilvadipine prevents the impairment of spatial memory induced by cerebral ischemia combined with beta-amyloid in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 30, 698–701 (2007).
Jenkins, L. W., Povlishock, J. T., Lewelt, W., Miller, J. D., and Becker, D. P., The role of postischemic recirculation in the development of ischemic neuronal injury following complete cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol., 55, 205–220 (1981).
Kaur, S., Jaggi, A. S., and Singh, N., Molecular aspects of ischemic postconditioning. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 23, 521–536 (2009a).
Kaur, S., Rehni, A. K., Singh, N., and Jaggi, A. S., Studies on cerebral protection of digoxin against ischemia/reperfusion Injury in Mice. Yakugaku Zasshi, 129, 435–443 (2009b).
Kitagawa, K., Matsumoto, M., Tagaya, M., Hata, R., Ueda, H., Niinobe, M., Handa, N., Fukunaga, R., Kimura, K., and Mikoshiba, K., ’Ischemic tolerance’ phenomenon found in the brain. Brain Res., 528, 21–24 (1990).
Kobayashi, T., Sugawara, Y., Ohkubo, T., Imamura, H., and Makuuchi, M., Effects of amrinone on hepatic ischemiareperfusion injury in rats. J. Hepatol., 37, 31–38 (2002).
Kucuk, C., Akcan, A., Akyyldyz, H., Akgun, H., Muhtaroglu, S., and Sozuer, E., Effects of amrinone in an experimental model of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Surg. Res., 151, 74–79 (2009).
Kume, M., Banafsche, R., Yamamoto, Y., Yamaoka, Y., Nobling, R., Gebhard, M. M., and Klar, E., Dynamic changes of post-ischemic hepatic microcirculation improved by a pretreatment of phosphodiesterase III inhibitor, milrinone. J. Surg. Res., 136, 209–218 (2006).
Lang, S. C., Elsasser, A., Scheler, C., Vetter, S., Tiefenbacher, C. P., Kubler, W., Katus, H. A., and Vogt, A. M., Myocardial preconditioning and remote renal preconditioning—identifying a protective factor using proteomic methods? Basic Res. Cardiol., 101, 149–158 (2006).
Lee, J. H., Lee, Y. K., Ishikawa, M., Koga, K., Fukunaga, M., Miyakoda, G., Mori, T., Hosokawa, T., and Hong, K. W., Cilostazol reduces brain lesion induced by focal cerebral ischemia in rats-an MRI study. Brain Res., 994, 91–98 (2003).
Lugnier, C., Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) superfamily: A new target for the development of specific therapeutic agents. Pharmacol. Ther., 109, 366–398 (2006).
Lukyanenko, V., Gyorke, I., Subramanian, S., Smirnov, A., Weisner, T. F., and Gyorke, S., Inhibition of Ca2+ sparks by Ruthenium red in permeabilized rat ventricular myocytes. Biophys. J., 79, 1273–1284 (2000).
McCormick, P. H., Chen, G., Tlerney, S., Kelly, C. J., and Bouchier-Hayes, D. J., Clinically relevant thermal preconditioning attenuates ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Surg. Res., 109, 24–30 (2003).
Mcgarry, S. J. and Williams, A. J., Digoxin activates sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release channels: possible role in cardiac inotropy. Br. J. Pharmacol., 108, 1043–1050 (1993).
Miyawaki, H. and Ashraf, M., Calcium as a mediator of ischemic preconditioning. Circ. Res., 80, 790–799 (1997).
Miyawaki, H., Zhou, X., and Ashraf, M., Calcium preconditioning elicits strong protection against ischemic injury via protein kinase C signaling pathway. Circ. Res., 79, 137–146 (1996).
Morris, R., Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods, 11, 47–60 (1984).
Murray, C. E., Jennings, R. B., and Reimer, K. A., Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation, 74, 1124–1136 (1986).
Neumar, R. W., Molecular mechanisms of ischemic neuronal injury. Ann. Emerg. Med., 36, 483–506 (2000).
Parle, M. and Singh, N., Animal models for testing memory. Asia Pacific. J. Pharmacol., 16, 101–120 (2004).
Pateliya, B. B., Singh, N., and Jaggi, A. S., Possible role of opioids and KATP channels in neuroprotective effect of postconditioning in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 31, 1755–1760 (2008).
Peralta, C., Serafin, A., Fernandez-Zabalegui, L., Wu, Z. Y., and Rosello-Catafau, J., Liver ischemic preconditioning: a new strategy for the prevention of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant. Proc., 35, 1800–1802 (2003).
Rehni, A. K. and Singh, N., Role of phosphoinositide 3- kinase in ischemic postconditioning-induced attenuation of cerebral ischemia-evoked behavioral deficits in mice. Pharmacol. Rep., 59, 197–198 (2007).
Rehni, A. K., Singh, N., and Singh, A. S., Possible role of insulin, endogenous opioids and calcitonin gene related peptide in remote ischemic preconditioning of brain. Yakugaku Zasshi, 127, 1013–1020 (2007).
Rehni, A. K., Bhateja, P., Singh, N., and Jaggi, A.S., Implication of mast cell degranulation in ischemic precondition ing induced prevention of cerebral injury. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 22, 179–188 (2008a).
Rehni, A. K., Singh, T. G., Singh, N., and Jaggi, A. S., Pharmacological preconditioning of the brain: a possible interplay between opioid and calcitonin gene related peptide transduction systems. Pharmacol. Rep., 60, 904–913 (2008b).
Rump, A. F., Acar, D., and Klaus, W., A quantitative comparison of functional and anti-ischemic effects of the phosphodiesterase-inhibitors, amrinone, milrinone and levosimendan in rabbit isolated hearts. Br. J. Pharmacol., 112, 757–762 (1994).
Saltman, A. E., Gaudette, G. R., Levitsky, S., and Krukenkamp, I. B., Amrinone preconditioning in the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Ann. Thorac. Surg., 70, 609–613 (2000).
Schulz, R., Post, H., Vahlhaus, C., and Heusch, G., Ischemic preconditioning in pigs: a graded phenomenon; its relation to adenosine and bradykinin. Circulation, 98, 1022–1029 (1998).
Schulz, R., Gres, P., and Heusch, G., Role of endogenous opioids in ischemic preconditioning but not in short-term hibernation in pigs. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 280, H2175–H2181 (2001).
Setoyama, K., Kamimura, R., Fujiki, M., Misumi, K., Miyahara, K., and Sakamoto, H., Effects of olprinone on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci., 68, 865–868 (2006).
Somers, S., Lacerda, L., Suleman, N., Opie, L., and Lecour, S., Critical role of age, strain and number of cycles in ischemic postconditioniong. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 42, S186–S187 (2007).
Ueda, T., Mizushige, K., Yukiiri, K., Takahashi, T., and Kondoh, M., Improvement of cerebral blood flow by olprinone, a phosphodiesterase-3 inhibitor, in mild heart failure. Cerebrovasc. Dis., 16, 396–401 (2003).
Wang, S. Q., Song, L. S., Lakatta, E. G., and Cheng, H., Ca2+ signaling between single L-type Ca2+ channels and ryanodine receptors in heart cells. Nature, 410, 592–596 (2001).
Warner, D. S., McFarlane, C., Todd, M. M., Ludwig, P., and McAllister, A. M., Sevoflurane and halothane reduce focal ischemic brain damage in the rat: Possible influence on thermoregulation. Anesthesiology, 79, 985–992 (1993).
Yang, X. M., Proctor, J. B., Cui, L., Krieg, T., Downey, J. M., and Cohen, M. V., Multiple, brief coronary occlusions during early reperfusion protect rabbit hearts by targeting cell signaling pathways. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 44, 1103–1110 (2004).
Yanpallewar, S. U., Hota, D., Rai, S., Kumar, M., and Acharya, S. B., Nimodipine attenuates biochemical, behavioral and histopathological alterations induced by acute transient and long-term bilateral common carotid occlusion in rats. Pharmacol. Res., 49, 143–150 (2004).
Yellon, D. M. and Dana, A., The preconditioning phenomenon: a tool for the scientist or a clinical reality? Circ. Res., 87, 543–550 (2000).
Ye, Y. L., Shi, W. Z., Zhang, W. P., Wang, M. L., Zhou, Y., Fang, S. H., Liu, L. Y., Zhang, Q., Yu, Y. P., and Wei, E. Q., Cilostazol, a phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor, protects mice against acute and late ischemic brain injuries. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 557, 23–31 (2007).
Zhai, P., Eurell, T. E., Cotthaus, R., Jeffery, E. H., Bahr, J. M., and Gross, D. R., Effect of estrogen on global myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in female rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol., 279, H2766–H2775 (2000).
Zhao, P., Peng, L., Li, L., Xu, X., and Zuo, Z., Isoflurane preconditioning improves long-term neurologic outcome after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology, 107, 963–970 (2007).
Zheng, S. and Zuo, Z., Isoflurane preconditioning induces neuroprotection against ischemia via activation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol. Pharmacol., 65, 1172–1180 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saklani, R., Jaggi, A. & Singh, N. Pharmacological preconditioning by milrinone: Memory preserving and neuroprotective effect in ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 33, 1049–1057 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0711-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-010-0711-6