Abstract
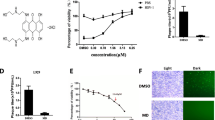
To investigate the inhibitory effects of Ginsenoside Rb1 (GRb1) on apoptosis caused by Herpes Simplex Virus-1(HSV-1) in Human Glioma Cells (U251), U251 cells were infected by HSV-1 at a multiplicity of infection of 5 and GRb1, GRb1+HSV-1, HSV-1 and control groups. MTT and cell apoptosis assays were used to detect the inhibitory effects of GRb1 on the apoptosis of U251 cells that caused by HSV-1 infection for various concentrations of drug and virus treatments by MTT assay. We found that in the 400 μg/mL GRb1 and 400 μg/mL GRb1+HSV-1 groups, MTT values were higher than control group at all times (P<0. 05). Moreover, the apoptosis rate in the 400 μg/mL GRb1+HSV-1 group was lower than the HSV-1 group (P<0. 05). These results confirmed that, at appropriate concentrations, GRb1 could inhibit nerve cell apoptosis in HSV-1 infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barcia C, Sanderson N S, Barrett R J, et al. 2008. T cells’ immunological synapses induce polarization of brain astrocytes in vivo and in vitro: A novel astrocyte response mechanism to cellular injury. PLoS One, 3(8): e2977.
Benishin C G. 1992. Actions of ginsenoside rb1 on choline uptake in central cholinergic nerve endings. Neurochem Int, 21(1): 1–5.
Carr D J, Veress L A, Noisakran S, et al. 1998. Astrocyte-targeted expression of ifn-alpha1 protects mice from acute ocular herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. J Immunol, 161(9): 4859–4865.
Chen L W, Wang Y Q, Wei L C, et al. 2007. Chinese herbs and herbal extracts for neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons and potential therapeutic treatment of parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets, 6(4): 273–281.
Gao X Q, Yang C X, Chen G J, et al. 2010. Ginsenoside rb1 regulates the expressions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and caspase-3 and induces neurogenesis in rats with experimental cerebral ischemia. J Ethnopharmacol, 132(2): 393–399.
Hsu M J, Wu C Y, Chiang H H, et al. 2010. Pi3k/akt signaling mediated apoptosis blockage and viral gene expression in oral epithelial cells during herpes simplex virus infection. Virus Res, 153(1): 36–43.
Jia Z, Yin Z, Guan P, et al. 2009. The association between polymorphisms of xpd and susceptibility of lung cancer: A meta analysis. HChin J Lung CancH, 12(10): 1079–1084.(in Chinese)
Kim E H, Jang M H, Shin M C, et al. 2003. Protective effect of aqueous extract of ginseng radix against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis in pc12 cells. Biol Pharm Bull, 26(12): 1668–1673.
Lee S D, Lo M J. 2010. Ginsenoside rb1 promotes pc12 cell cycle kinetics through an adenylate cyclase-dependent protein kinase a pathway. Nutr Res, 30(9): 660–666.
Liang W, Ge S, Yang L, et al. 2010. Ginsenosides rb1 and rg1 promote proliferation and expression of neurotrophic factors in primary schwann cell cultures. Brain Res, 1357: 19–25.
Liao B, Newmark H, Zhou R. 2002. Neuroprotective effects of ginseng total saponin and ginsenosides rb1 and rg1 on spinal cord neurons in vitro. Exp Neurol, 173(2): 224–234.
Liu F Z, Shi H, Shi Y J, et al. 2010. Pharmacodynamic experiment of the antivirus effect of houttuynia cordata injection on influenza virus in mice. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 45(3): 399–402. (in Chinese)
Nishiyama N, Cho S I, Kitagawa I, et al. 1994. Malonylginsenoside rb1 potentiates nerve growth factor (ngf)-induced neurite outgrowth of cultured chick embryonic dorsal root ganglia. Biol Pharm Bull, 17(4): 509–513.
Rivera E, Hu S, Concha C. 2003. Ginseng and aluminium hydroxide act synergistically as vaccine adjuvants. Vaccine, 21(11–12): 1149–1157.
Rivera E, Daggfeldt A, Hu S. 2003. Ginseng extract in aluminium hydroxide adjuvanted vaccines improves the antibody response of pigs to porcine parvovirus and erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Vet Immunol Immunopathol, 91(1): 19–27.
Rivera E, Ekholm Pettersson F, Inganas M, et al. 2005. The rb1 fraction of ginseng elicits a balanced th1 and th2 immune response. Vaccine, 23(46–47): 5411–5419.
Salim K N, McEwen B S, Chao H M. 1997. Ginsenoside rb1 regulates chat, ngf and trka mrna expression in the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res, 47(1–2): 177–182.
Setinek U, Wondrusch E, Jellinger K, et al. 1995. Cytomegalovirus infection of the brain in aids: A clinicopathological study. Acta Neuropathol, 90(5): 511–515.
Song X, Bao S, Wu L, et al. 2009. Ginseng stem-leaf saponins (gsls) and mineral oil act synergistically to enhance the immune responses to vaccination against foot-and-mouth disease in mice. Vaccine, 27(1): 51–55.
Tang H Y, Yan D, Zhang S F, et al. 2010. Agglutinated activity bioassay method for the determination of antivirus potency of banlangen granula]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 45(4): 479–483. (in Chinese)
Wen S, Huifu X, Hao H. 2011. In vitro anti-influenza a h1n1 effect of extract of bupleuri radix. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol, 33(3): 433–437.
Wiley C A, Nelson J A. 1988. Role of human immunodeficiency virus and cytomegalovirus in aids encephalitis. Am J Pathol, 133(1): 73–81.
Xue J F, Liu Z J, Hu J F, et al. 2006. Ginsenoside rb1 promotes neurotransmitter release by modulating phosphorylation of synapsins through a camp-dependent protein kinase pathway. Brain Res, 1106(1): 91–98.
Yang C X, Liu J X, Sun Z L, et al. 2008. Effects of ginsenoside rb1 on neural cell apoptosis and expressions of bcl-2 and bax in rats following subjected to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. J Sichuan Univ(Med Sci Edi), 39(2): 214–217. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation items: Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81070501 and 30770105), and Shandong Provincial Outstanding Medical Academic Professional Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, YY., Wang, B., Qian, DM. et al. Inhibitory effects of Ginsenoside Rb1 on apoptosis caused by HSV-1 in Human Glioma Cells. Virol. Sin. 27, 19–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-012-3220-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-012-3220-6