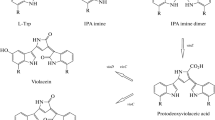
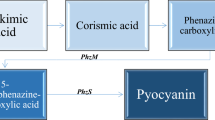
Abstract
C. violaceum appeared as important bacterium in different applications and mainly these aspects are related to the production of violacein. This review discusses the last reports on biosynthetic pathways, production, genetic aspects, biological activities, pathological effects, antipathogenic screening through quorum sensing, environmental effects and the products of C. violaceum with industrial interest. An important discussion is on biological applications in medicine and as industrial products such as textile and in cosmetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration (FDA or USFDA), an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services
- 5-FU:
-
5-fluorouracil
- QS:
-
quorum sensing
- VIO:
-
violacein
References
Ahmetagic A., Pemberton J.M.: Stable high level expression of the violacein indolocarbazole anti-tumour gene cluster and the Streptomyces lividans amyA gene in E. coli K12. Plasmid63, 79–85 (2010).
Ajithdoss D.K., Porter B.F., Calise D.V., Libal M.C., Edwards J.F.: Septicemia in a neonatal calf associated with Chromobacterium violaceum. Veter.Pathol.46, 71–74 (2009).
Al-Hussaini R., Mahasneh A.M.: Microbial growth and quorum sensing antagonist activities of herbal plants extracts. Molecules14, 3425–3435 (2009).
Alves O.L., Gimenez I.F., DE Azevedo M.M.M., Durán N., Melo P.S.: Phamacological use of cyclodextrine-Au-thiol-derivative/hydrophobic compound nanoparticles as antitumoral, antibacterial, antiviral and/or antiparasites, its obtention process and formulation. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 0502657-1 (2005).
Anah M.U., Udo J.J., Ochigbo S.O., Abia-Bassey L.N.: Neonatal septicemia in calabar, Nigeria. Tropical Doctor38, 126–128 (2008).
Andrighetti-frohner C.R., Kratz J.M., Antonio R.V., Creczynski-pasa T.B., Barardi C.R.M., Simoes C.M.O.: In vitro testing for genotoxicity of violacein assessed by Comet and Micronucleus assays. Mutat.Res.603, 97–103 (2006).
Antônio R.V., Creczynski-Pasa T.B.: Genetic analysis of violacein biosynthesis by Chromobacterium violaceum. Genet.Mol.Res.3, 85–91 (2004).
Antonisamy P., Kannan P., Ignacimuthu S.: Anti-diarrheal and ulcer-protective effects of violacein isolated from Chromobacterium violaceum in Wistar rats. Fundam.Clin.Pharmacol.23, 483–490 (2009).
Aoki S., Nomura T.: Violacein-containing natural bactericides, their manufacture, and cosmetics containing them. Japan Pat. JP 10139612 (1998).
Asamizu S., Kato Y., Igarashia Y., Onaka H.: VioE, a prodeoxyviolacein synthase involved in violacein biosynthesis, is responsible for intramolecular indole rearrangement. Tetrahedron Lett.48, 2923–2926 (2007).
Baek S.H., Kang H.S., Jang I.H., Lee J.S., Kim S.Y., Baek J.H., Kang J.G., Ahn J.M.: Insecticide and fungicide containing violacein, and their preparation method. Republ.Korean Pat. KR 20070 88150 A (2007).
Baker S., Campbell J.I., Stabler R., Nguyen H.V.M., To D.S., Nguyen D.V., Farrar J.: Fatal wound infection caused by Chromobacterium violaceum in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. J.Clin.Microbiol.46, 3853–3855 (2008).
Baldi M., Morales J.A., Hernandez G., Jimenez M., Alfaro A., Arquero-calvo e.: Chromobacterium violaceuminfection in a free-ranging Howler monkey in Costa Rica. J. Wildlife Dis.46, 306–310 (2010).
Balibar C.J., Walsh C.T.: In vitro biosynthesis of violacein from L-tryptophan by the enzymes VioA-E from Chromobacterium violaceum. Biochemistry45, 15444–15457 (2006).
Barreto E.S., Torres A.R., Barreto M.R., Vasconcelos A.T.R., Astolfi-filho S., Hungria M.: Diversity in antifungal activity of strains of Chromobacterium violaceum from the Brazilian Amazon. J.Ind.Microbiol.Biotechnol.35, 783–790 (2008).
Becker M.H., Brucker R.M., Schwantes C.R., Harris R.N., Minbiole K.P.C.: The bacterially produced metabolite violacein is associated with survival of amphibians infected with a lethal fungus. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.75, 6635–6638 (2009).
Bodini S.F., Manfredini S., Epp M., Valentini S., Santori F.: Quorum sensing inhibition activity of garlic extract and p-coumaric acid. Lett.Appl.Microbiol.49, 551–555 (2009).
Bosch F.J., Badenhorst L., Le Roux J.A., Louw V.J.: Successful treatment of Chromobacterium violacelum sepsis in South Africa. J.Med.Microbiol.57, 1293–1295 (2008).
Bosgelmez-Tinaz G., Ulusoy S., Ugur A., Ceylan O.: Inhibition of quorum sensing-regulated behaviors by Scorzonera sandrasica. Curr.Microbiol.55, 114–118 (2007).
Bowers A.A., Greshock T.J., West N., Schreiber S.L., Wiest O., Williams R.M., Bradner J.E.: Synthesis and conformation-activity relationships of the peptide isosters of FK228 and largazole. J.Am.Chem.Soc.131, 2901–2905 (2009).
Brandl H., Lehmann S., Faramarzi M.A., Martinelli D.: Biomobilization of silver, gold, and platinum from solid waste materials by HCN-forming microorganisms. Hydrometallurgy94, 14–17 (2008).
Brown A.G.: Discovery and development of new β-lactam antibiotics. Pure Appl.Chem.59, 475–484 (1987).
Brucker R.M., Harris R.N., Schwantes C.R., Gallaher T.N., Flaherty D.C., Lam B.A., Minbiole K.P.C.: Amphibian chemical defense: antifungal metabolites of the microsymbiont Janthinobacterium lividum on the salamander Plethodon cinereus. J.Chem.Ecol.34, 1422–1429 (2008).
Byrd L.C., Marcucci G., Parthun M.R., Xiao J.J., Klisovic R.B., Moran M., Lin T.S., Liu S., Sklenar A.R., Davis M.E., Lucas D.M., Fischer B., Shank R., Tejaswi S.L., Binkley P., Wright J., Chan K.K., Grever M.R.: A phase 1 and pharmacodynamic study of depsipeptide (FK228) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood105, 959–967 (2005).
Cao W., Chen W., Sun S., Guo P., Song J., Tian C., Cao W., Chen W., Sun S., Guo P., Song J., Tian C.: Investigating the antioxidant mechanism of violacein by density functional theory method. Investigating the antioxidant mechanism of violacein by density functional theory method. J.Mol.Struct.Theochem.817, 1–4 (2007).
Carminatti C.A., Oliveira I.L., Recouvreux D.O.S., Antonio R.V., Porto L.M.: Anthranilate synthase subunit organization in Chromobacterium violaceum. Genet.Mol.Res.7, 830–838 (2008).
Carter E., Cain K., Rutland B.: Chromobacterium violaceum cellulitis and sepsis following cutaneous marine trauma. Cutis81, 269–272 (2008).
Chen C.N., Chen C.J., Liao C.T., Lee C.Y.: A probable aculeacin A acylase from the Ralstonia solanacearum GMI1000 is N-acylhomoserine-lactone acylase with quorum-quenching activity. BMC Microbiol.9, 89 doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-89 (2009).
Cooper R., Unger S.: Novel potentiators of β-lactam antibiotics. Structures of SQ 28504 and SQ 28546. J.Org.Chem.51, 3942–3946 (1986).
Costa F.T.M., Justo G.Z., Duran N., Nogueira P.A., Lopes S.C.P.: Uso da violaceina na forma livre ouencapsulada em sistemas polimericos como antimalárico. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 056399-0 (2005).
de Azevedo M.B.M., Alderete J.B., Rodriguez J.A., DE Souza A.O., Rettori D., Torsoni M.A., Faljoni-alario A., Haun M., Durán N.: Biological activities of violacein: a new antitumoral indole derivative in an inclusion complex with β-cyclodextrin. J.Incl.Phenom.Macrocyclic Chem.37, 93–101 (2000a).
de Azevedo M.B.M., Melo P.S., Almeida A.B.A., Souza-brito A.R.M., Haun M., Durán N.: Antiulcerogenic activity of violacein/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes and violacein. Proc.Intern.Symp.Control.Rel.Bioact.Mater.27, 508–509 (2000b).
de Carvalho D.D., Costa F.T.M., Durán N., Haun M.: Cytotoxic activity of violacein in human colon cancer cells. Toxicol. in Vitro20, 1514–1521 (2006).
de Moss R.D.: Violacein. Antibiotics2, 77–81 (1967).
Deines P., Matz C., Jurgens K.: Toxicity of violacein-producing bacteria fed to bacterivorous freshwater plankton. Limnol.Oceanogr.54, 1343–1352 (2009).
Dessaux Y., Elmerich C., Faure D.: Violacein: a molecule of biological interest originating from the soil-borne bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum. Rev.Med.Internat.25, 659–662 (2004).
Dobretsov S., Dahms H.U., Huang Yili H., Wahl M., Qian P.Y.: The effect of quorum-sensing blockers on the formation of marine microbial communities and larval attachment. FEMS Microbiol.Ecol.60, 177–188 (2007).
Dufosse L.: Microbial production of food grade pigments. Food Technol.Biotechnol.44, 313–321 (2006).
Durán N.: Violacein: an antibiotic discovery. Ciencia Hoje11, 58–80 (1990).
Durán N., DE Azevedo M.M.M.: Compound incorporated in a polymeric nanoparticle with pharmaceutical or a cosmetic, its preparation process and cosmetic or pharmaceutical formulations. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 0404306-5 (2004).
Durán N., DE Souza A.O.: Process of violacein application as antimycobacterial compound. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 0101346-7 (2001).
Durán N., Haun M.: Production, obtention and purification process and antitumoral activity of 3-[1,2-dihydro-5-(5-hydroxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-2-oxo-3H-pyrrol-3-ylidene]-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 9702918 (1997).
Durán N., Menck C.F.M.: Chromobacterium violaceum: a review of farmacological and indutrial perspectives. Crit.Rev.Microbiol.27, 201–222 (2001).
Durán N., Rettori D., Menck C.F.M.: Who is Chromobacterium violaceum? Biotecnol.Ciên.Desenvol.20, 38–43 (2001).
Durán N., Justo G.Z., Melo P.S., DE Azevedo M.B.M., Souza-Brito A.R.M., Almeida A.B.A., Haun M.: Evaluation of the antiulcerogenic activity of violacein and its modulation by the inclusion complexation with β-cyclodextrin.Can.J.Physiol.Pharmacol.81, 387–396 (2003).
Durán N., Justo G.Z., Melo P.S., Martins D. Jr., CORDI L.: Violacein: properties and biological activities. Biotechnol.Appl.Biochem.48, 127–133 (2007).
Durán N., Marcato P.D., Alves O.L., DA Silva J.P.S., DE Souza G.I.H., Rodrigues F.A., Espósito E.: Ecosystem protection by effluent bioremediation: silver nanoparticles impregnation in a textile fabrics process. J.Nanopart.Res.12, 285–292 (2010).
Fairbrother L., Shapter J., Brugger J., Southam G., Pring A., Reith F.: Effect of the cyanide-producing bacterium Chromobacterium violaceum on ultraflat Au surfaces. Chem.Geol.265, 313–320 (2009).
Ferreira C.V., Bos C.L., Versreeg H.H., Justo G.Z., Durán N., Peppelenbosch M.P.: Molecular mechanism of violacein-mediated human promyelocytic leukemia cell-specific cytotoxicity. Blood104, 1459–1464 (2004).
Gimenez I.F., Anazetti M.C., Melo P.S., Haun M., De Azevedo M.M.M., Durán N., Alves O.L.: Cytotoxicity on V79 and HL60 cell lines by thiolated-β-cyclodextrin-Au/violacein nanoparticles. J.Biomed.Nanotechnol.1, 352–358 (2005).
Gootz T.D.: Discovery and development of new antimicrobial agents. Clin.Microbiol.Rev.3, 13–31 (1990).
Gregory A., Ribollet D., Pailla K., Bourgade M., Alma S.: Chromobacterium violaceum septicemia: first case report in the French West Indies. Méd.Malad.Infect.37, 613–615 (2007).
Greshock T.J., Johns D.M., Noguchi Y., Williams R.M.: Improved total synthesis of the potent HDAC inhibitor FK228 (FR-901228). Org.Lett.10, 613–616 (2008).
Guevara A., Salomon M., Oliveros M., Guevara E., Guevara M., Medina Z.: Sepsis caused by pigmented and no pigmented Chromobacterium violaceum. Rev.Chilena Infect.24, 402–406 (2007).
Gupta R., Shah P., Swiatlo E.: Differential gene expression in Streptococcus pneumoniae in response to various iron sources. Microb.Pathogen.47, 101–109 (2009).
Hakvag S., Fjaervik E., Klinkenberg G., Borgos S.E.F., Josefsen K.D., Ellingsen T.E., Zotchev S.B.: Violacein-producing Collimonas sp. from the sea surface microlayer of costal waters in Trondelag, Norway. Marine Drugs7, 576–588 (2009).
Harris R.N., Brucker R.M., Walke J.B., Becker M.H., Schwantes C.R., Flaherty D.C., Lam B.A., Woodhams D.C., Briggs C.J., Vredenburg V.T., Minbiole K.P.C.: Skin microbes on frogs prevent morbidity and mortality caused by a lethal skin fungus. ISME J.3, 818–824 (2009).
Haun M., Pereira M.F., Hoffman M.F., Riveros R., Joyas A., Campos V., Durán N.: Bacterial chemistry — VI. Biological activities and cyto-toxicity of 1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one derivatives. Biol.Res.25, 21 (1992).
Hirano S., Asamizu S., Onaka H., Shiro Y., Nagano S.: Crystal structure of VioE, a key player in the construction of the molecular skeleton of violacein. J.Biol.Chem.283, 6459–6466 (2008).
Kato H., Hata T., Shirata A., Tsukamoto T.: Improvement of lightfastness of fibers or fiber products dyed with violacein or deoxyviolacein bluish purple dyes by treating the dyed fibers with thiourea. Japan Pat. JP 1115 2687 A (1999).
Khan M.S.A., Zahin M., Hasan S., Husain F.M., Ahmad I.: Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functions by plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Lett.Appl.Microbiol.49, 354–360 (2009).
Kita Y., Nishikawa H., Ike M., Takemoto T.: Enhancement of Au dissolution by microorganisms using an accelerating cathode reaction. Metallurg.Mat.Trans.B40B, 2009–2044 (2009).
Kodach L.L., Bos C.L., Durán N., Peppelenbosh M.P., Ferreira C.V., Hardwick J.C.H.: Inhibition of Akt-mediated signal transduction in human colorectal cancer cells by violacein abrogates 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance. Carcinogenesis27, 508–516 (2006).
Konzen M., DE Marco D., Cordova C.A.S., Vieira T.O., Antonio R.V., Creczynski-Pasa T.B.: Antioxidant properties of violacein: possible relation on its biological function. Bioorg.Med.Chem.14, 8307–8313 (2006).
Kubo H., Kotani H., Yamamoto Y., Hazato T.: Involvement of sperm proteases in the binding of sperm to the vitelline envelope in Xenopus laevis. Zoolog.Sci.25, 80–87 (2008).
Lai M.T., Yang C.C., Lin T.Y., Tsai F.J., Chen W.C.: Depsipeptide (FK228) inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells. Urol. Oncol.Sem.Orig.Invest.26, 182–189 (2008).
Leon L.L., Miranda C.C., De Souza A.O., Durán N.: Antileishmanial activity of the violacein extracted from Chromobacterium violaceum. J.Antimicrob.Chemother.48, 449–450 (2001).
Lim I.W.M., Stride P.J., Horvath R.L., Hamilton-Craig C.R., Chau P.P.: Chromobacterium violaceum endocarditis and hepatic abscesses treated successfully with meropenem and ciprofloxacin. Med.J.Austral.190, 386–387 (2009).
Lima-Bittencourt C.I., Astolfi-Filho S., Chartone-Souza E., Santos F.R., Nascimento A.M.A.: Analysis of Chromobacterium sp. natural isolates from different Brazilian ecosystems. BMC Microbiol.7, 58 doi:10.1186/1471-2180-7-58 (2007).
Lopes S.C.P., Blanco Y.C., Justo G.Z., Nogueira P.A., Rodrigues F.L.S., Goelnitz U., Wunderlich G., Facchini G., Brocchi M., Durán N., Costa F.T.M.: Violacein extracted from Chromobacterium violaceum inhibits Plasmodium growth in vitro and in vivo. Antimocrob.Agents Chemother.53, 2149–2152 (2009).
Lu Y., Wang L., Xue Y., Zhang C., Xing X.H., Lou K., Zhang Z., Li Y., Zhang G., Bi J., Su Z.: Production of violet pigment by a newly isolated psychrotrophic bacterium from a glacier in Xinjiang, China. Biochem.Eng.J.43, 135–141 (2009).
Manjunath M.: Fatal septicemia due to Chromobacterium violaceum. West Indian Med.J.56, 380–381 (2007).
Martins D., Frungillo L., Anazzetti M.C., Melo P.S., Durán N.: Antitumoral activity of L-ascorbic acid-poly-d,l-(lactide-coglycolide) nanoparticles containing violacein. Internat.J.Nanomed.5, 77–85 (2010).
Masuoka Y., Shindoh N., Inamura N.: Histone deacetylase inhibitors from microorganisms: the Astellas experience, in F. Petersen, R. Amstutz: Natur.Comp.Drugs2, 335–359 (2008).
Matz C., Webb J.S., Schupp P.J., Phang S.Y., Penesyan A., Egan S., Steinberg P., Kjelleberg S.: Marine biofilm bacteria evade eukaryotic predation by targeted chemical defense. PLoS One3, e2744, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002744(2008).
Meiring U., Lanzendoerfer G., Riedel H., Kallmayer V., Viala S., Mocigemba N., Schaefer J.: Cosmetic preparations containing violacein as dye. Ger.Pat. DE 102 005 051 869 A1 (2007).
Melo P.S., Justo G.Z., DE Azevedo M.B.M., Durán N., Haun M.: Violacein and its β-cyclodextrin complexes induce apoptosis and differentiation in HL60 cells. Toxicology186, 217–225 (2003).
Melo P.S., DE Azevedo M.M.M., Frungillo L., Anazetti M.C., Marcato P.D., Durán N.: Nanocytotoxicity: violacein and violacein-loaded poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles acting on human leukemic cells. J.Biomed.Nanotechnol.5, 192–201 (2009).
Mendes A.S., DE Carvalho J.E., Duarte M.C.T., Durán N., Bruns R.E.: Optimized production process of violacein and deoxyviolacein by Chromobacterium violaceum by factorial design and response surface methodology. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 0100199-0 (2001a).
Mendes A.S., DE Carvalho J.E., Duarte M.C.T., Durán N., Bruns R.E.: Factorial design and response surface optimization of crude violacein for Chromobacterium violaceum production. Biotechnol.Lett.23, 1963–1969 (2001b).
Morohoshi T., Kato M., Fukamachi K., Kato N., Ikeda T.: N-Acylhomoserine lactone regulates violacein production in Chromobacterium violaceum type strain ATCC 12472. FEMS Microbiol.Lett.279, 124–130 (2008).
Nomura T.: Natural dye violacein manufacture with Chromobacterium and Janthinobacterium. Japan Pat. JP 0625 3864 A (1994).
Pantanella F., Berlutti F., Passariello C., Sarli S., Morea C., Schippa S.: Violacein and biofilm production in Janthinobacterium lividum. J.Appl.Microbiol.102, 992–999 (2007).
Pearson R.N.: Chromobacterium violaceum endocarditis and hepatic abscesses treated successfully with meropenem and ciprofloxacin. Med.J.Austral.191, 416 (2009).
Perpetuo E.A., Marques R.C.P., Mendes M.A., DE Lima W.C., Menck C.F.M., DO Nascimento C.A.O.: Characterization of the phenol monooxygenase gene from Chromobacterium violaceum: potential use for phenol biodegradation. Biotechnol.Bioproc. Eng.14, 694–701 (2009).
Pham V.A., Ting Y.P.: Gold bioleaching of electronic waste by cyanogenic bacteria and its enhancement with bio-oxidation. Adv.Mat. Res.71–73 (Biohydrometallurgy) 661–664 (2009).
Philip D.S., Sarovich D.S., Pemberton J.M.: pPSY: a vector for the stable cloning and expression of streptomycete single gene phenotypes in Escherichia coli. Plasmid60, 53–58 (2008).
Philip D.S., Sarovich D.S., Pemberton J.M.: Complete sequence and analysis of the stability functions of pPSX, a vector that allows stable cloning and expression of streptomycete genes in Escherichia coli K12. Plasmid62, 39–43 (2009).
Praneenararat T., Geske G.D., Blackwell H.E.: Efficient synthesis and evaluation of quorum-sensing modulators using small molecule macroarrays. Org.Lett.11, 4600–4603 (2009).
Rettori D., Durán N.: Stationary tray bioreactor for the bacterial metabolite production. Brazil.Pat. PIBr 9702986-6 (1997).
Ryan K.S., Balibar C.J., Turo K.E., Walsh C.T., Drennan C.L.: The violacein biosynthetic enzyme VioE shares a fold with lipoprotein transporter proteins. J.Biol.Chem.283, 6467–6475 (2008).
Sanchez C., Braña A.F., Mendez C., Salas J.A.: Reevaluation of the violacein biosynthetic pathway and its relationship to indolocarbazole biosynthesis. ChemBioChem.7, 1231–1240 (2006).
Sarovich D.S., Pemberton J.M.: pPSX: a novel vector for the cloning and heterologous expression of antitumor antibiotic gene clusters. Plasmid57, 306–313 (2007).
Shinoda K., Hasegawa T., Sato H., Shinozaki M., Kuramoto H., Takamiya Y., Sato T., Nikaidou N., Watanabe T., Hoshino T.: Biosynthesis of violacein: a genuine intermediate, protoviolaceinic acid, produced by VioABDE, and insight into VioC function. Chem.Commun. 4140–4142 (2007).
Shirata A., Tsukamoto T., Yasui H., Kato H., Hayasaka S., Kojima A.: Production of bluish-purple pigments by Janthinobacterium lividum isolated from the raw silk and dyeing with them. Nippon Sanshigaku Zasshi66, 377–385 (1997).
Shirata A., Tsukamoto T., Kato H., Hata T., Yasui T., Kojima A.: Blue purple pigment manufacture with microorganism and applications of the pigment. Japan Kokai Tokkyo Koho JP 10113169 A (1998).
Shukla S.R., Damle A.J.: Colorants from microorganisms. Asian Dyer4, 33–34, 36–38 (2007).
Singh B.N., Singh B.R., Singh R.L., Prakash D., Dhakarey R., Upadhyay G., Singh H.B.: Oxidative DNA damage protective activity, antioxidant and anti-quorum sensing potentials of Moringa oleifera. Food Chem.Toxicol.47, 1109–1116 (2009).
Slesak G., Douangdala P., Inthalad S., Silisouk J., Vongsouvath M., Sengduangphachanh A., Moore C.E., Mayxay M., Matsuoka H., Newton P.N.: Fatal Chromobacterium violaceum septicaemia in northern Laos, a modified oxidase test and post-mortem forensic family G6PD analysis. Ann.Clin.Microbiol.Antimicrob.8, 24 doi:10.1186/1476-0711-8-24 (2009).
Swem L.R., Swem D.L., O’Loughlin C.T., Gatmaitan R., Zhao B., Ulrich S.M., Bassler B.L.: A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity. Mol.Cell35, 143–153 (2009).
Tan T.L., Montforts F.P., Meyer D.: Microbiological method for the biosynthesis of natural blue-violet colorants violacein and desoxyviolacein. PCT Internat.Appl. WO 20020 50299 A2 (2002).
Teasdale M.E., Liu J.Y., Wallace J., Akhlaghi F., Rowley D.C.: Secondary metabolites produced by the marine bacterium Halobacillus salinus that inhibit quorum sensing-controlled phenotypes in Gram-negative bacteria. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.75, 567–572 (2009).
Uroz S., Oger P., Chhabra S.R., Cámara M., Williams P., Dessaux Y.: N-Acylhomoserine lactones are degraded via an amidolytic activity in Comamonas sp. strain D1. Arch.Microbiol.187, 249–256 (2007).
Vasconcelos A.T.R.et al. (Brazilian National Genome Project Consortium; 109 authors): The complete genome of Chromobacterium violaceum reveals remarkable and exploitable bacterial adaptability. Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA100, 11660–11665 (2003).
Vattem D.A., Mihalik K., Crixell S.H., Mclean R.J.C.: Dietary phytochemicals as quorum sensing inhibitors. Fitoterapia78, 302–310 (2007).
Vijayan A.P., Anand M.R., Remesh P.: Chromobacterium violaceum sepsis in an infant. Indian Pedriat.46, 721–722 (2009).
Wang Y., Ikawa A., Okaue S., Taniguchi S., Osaka I., Yoshimoto A., Kishida Y., Arakawa R., Enomoto K.: Quorum sensing signaling molecules involved in the production of violacein by Pseudoalteromonas. Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem.72, 1958–1961 (2008).
Wang H., Jiang P., Lu Y., Ruan Z., Jiang R., Xin-hui Xing X.H., Lou K., Wei D.: Optimization of culture conditions for violacein production by a new strain of Duganella sp. B2. Biochem.Eng.J.44, 119–124 (2009).
Watine J., Courtade A., Pham E., Lievrouw C., Dubourdieu B., Guerin B., Gineston J.L.: Chromobacterium violaceum peritonitis: case report and literature review. Ann.Biol.Clin.64, 327–330 (2006).
Yada S., Wang Y., Zou Y., Nagasaki K., Hosokawa K., Osaka I., Arakawa R., Enomoto K.: Isolation and characterization of two groups of novel marine bacteria producing violacein. Marine Biotechnol.10, 128–132 (2008).
Yang L.H., Xiong H., Lee O.O., Qi S.H., Qian P.Y.: Effect of agitation on violacein production in Pseudoalteromonas luteoviolacea isolated from a marine sponge. Lett.Appl.Microbiol.44, 625–630 (2007).
Yurek-george A., Cecil A.R.L., Mo A.H.K., Wen S., Rogers H., Habens F., Maeda S., Yoshida M., Packham G., Ganesan A.: The first biologically active synthetic analogues of FK228, the depsipeptide histone deacetylase inhibitor. J.Med.Chem.50, 5720–5726 (2007).
Zhu H., Sun S.J.: Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing-regulated behaviors by Tremella fuciformis extract. Curr.Microbiol.57, 418–422 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durán, M., Faljoni-Alario, A. & Durán, N. Chromobacterium violaceum and its important metabolites — review. Folia Microbiol 55, 535–547 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0088-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0088-4