Abstract
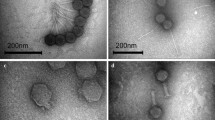
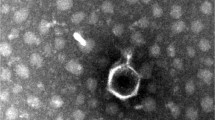
Five bacteriophages (Kpn5, Kpn12, Kpn13, Kpn17 and Kpn22), each having specificity against Klebsiella pneumoniae strain B5055, were isolated from sewage samples and characterized in terms of growth characteristics, genetic material, morphology and structural proteins. Adsorption rate as well as single step growth curve experiments showed variation among phages. Restriction enzyme digestion of DNA confirmed the presence of double stranded DNA as well as the heterogeneous nature of genetic material. RAPD-PCR was performed to further distinguish these closely related phages. Their genome fingerprint confirmed their diversity. Transmission electron microscopy, on the other hand, showed their morphological similarity; they were assigned to family Podoviridae, order Caudovirales on the basis of their head and tail morphology. Structural proteins resolved on SDS-PAGE showed the presence of similar major outer membrane proteins. The bacteriophages, belonging to Podoviridae family with short stumpy tails, were found to be nontoxic to mice. They showed maximum count in various organs at 6 h post inoculation, which persisted till 36 h. These phages thus have the potential to be used for phage therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFU:
-
colony forming units
- MDR:
-
multi drug resistant (bacteria)
- MOI:
-
multiplicity of infection
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PEG:
-
polyethylene glycol
- PFU:
-
plaque forming units
- RAPD:
-
random amplified polymorphic DNA
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TEM:
-
transmission electron microscopy
References
Ackermann H.W.: Frequency of morphological phage descriptions in the year 2000. Arch.Virol.146, 843–857 (2001).
Adam M.H.: Bacteriophages. Interscience Publishers, New York 1959.
Atterbury J., Connerton P.L., Dodd C.E.R., Rees C.E.D., Connerton I.F.: Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter bacteriophages from retail poultry. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.69, 4511–4518 (2003).
Barrangou R., Yoon S.S., Breidt F., Fleming H.P., Klenhammer T.R.: Characterization of six Leuconostoc fallax bacteriophages isolated from industrial sauerkraut fermentation. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.68, 5452–5458 (2002).
Benedict L.R.N., Flamiano R.S.: Use of bacteriophages as therapy for Escherichia coli-induced bacteremia in mouse models. Phil. J.Microbiol.Infect.Dis.33, 47–51 (2004).
Bogovazova G.G., Voroshilova N.N., Gorbatkova G.A., Bondarenko V.M., Kazakova T.B., Mamleeva A.G., Sirnov V.D., Glukharev I.A., Erastova E.I., Krylov I.A., Ovcherenko T.M., Baturo A.P., Yalsyk G.V., Arefyeva N.A.: Immunobiological properties and therapeutic effectiveness of preparations from Klebsiella bacteriophages. (In Russian) Zh.Mikrobiol.Epidemiol.Imunobiol.3, 30–33 (1992).
Carlton M.: Phage therapy: past history and future prospects. Arch.Immunol.Ther.Exp.(Warsaw)47, 267–274 (1999).
Cerveny K.E., Depaola A., Duckworth D.H., Gulig P.A.: Phage therapy of local and systemic disease caused by Vibrio vulnificus in iron-dextran-treated mice. Infect.Immun.70, 6251–6262 (2002).
Chakrabarti A.K., Ghosh A.N., Nair G.B., Niyogi S.K., Bhattacharya S.K., Sarkar B.L.: Development and evaluation of a phage typing scheme for Vibrio cholerae O139. J.Clin.Microbiol.38, 44–49 (2000).
Chang H.-C., Chen C.-R., Lin J.-W., Shen G.-H., Chang K.-M., Tseng Y.-H., Weng S.-F.: Isolation and characterization of novel giant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia phage ΦSMA5. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.71, 1387–1393 (2005).
Chhibber S., Kaur S., Kumari S.: Therapeutic potential of bacteriophage in treating Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055-mediated lobar pneumonia in mice. J.Med.Microbiol.57, 1508–1513 (2008).
Dabrowska K., Switala-Jelen K., Opolski A., Weber-Dabrowska B., Gorski A.: Bacteriophage penetration in vertebrates. J.Appl.Microbiol.98, 7–13 (2005).
Drake J.W., Hwang C.B.C.: On the mutation rate of herpes simplex virus type 1. Genetics170, 969–970 (2005).
Hanlon G.W.: Bacteriophages: an appraisal of their role in the treatment of bacterial infections. Internat.J.Antimicrob.Agents30, 118–128 (2007).
Johansson M.L., Quednau M., Molin G., Ahrne S.: Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) for rapid typing of Lactobacillus plantarum strains. Lett.Appl.Microbiol.21, 155–159 (1999).
Jothikumar N., Reddy C.G., Sundari R.B., Saigopal D.V.R.: Isolation of coliphages specific to enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC). J.Environ.Monit.2, 372–374 (2000).
Kumari S., Harjai K., Chhibber S.: Bacteriophage treatment of burn wound infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO in BALB/c mice. Am.J.BioMed.Sci.1, 385–394 (2009a).
Kumari S., Harjai K., Chhibber S.: Efficacy of bacteriophages treatment in murine burn wound infection induced by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J.Microbiol.Biotechnol.19, 622–628 (2009b).
Kumari S., Harjai K., Chhibber S.: Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO specific bacteriophages isolated from sewage samples. Am.J.BioMed.Sci.1, 91–102 (2009c).
Kurzępa A., Dąbrowska K., Świtała-Jeleń K., Górski A.: Molecular modification of T4 bacteriophage proteins and its potential application — review. Folia Microbiol.54, 5–15 (2009).
Laemmli U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature22, 680–685 (1970).
Letkiewicz S., Międzybrodzki R., Fortuna W., Weber-Dąbrowska B., Górski A.: Eradication of Enterococcus faecalis by phage therapy in chronic prostatitis — case report. Folia Microbiol.54, 457–462 (2009).
Malik R., Chhibber S.: Protection with bacteriophages Kϕ1 Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced burn wound infection in mice. J.Microbiol. Immunol.Infect.42, 134–140 (2009).
Matsuzaki S., Rashel M., Uchiyama J., Sakurai S., Ujihara T., Kuroda M., Ikeuchi M., Tani T., Fujieda M., Wakiguchi H., Imai S.: Bacteriophage therapy: a revitalized therapy against bacterial infectious diseases. J.Infect.Chemother.11, 211–219 (2005).
Mcvay C., Velasquez S.M., Fralick J.A.: Phage therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in a mouse burn wound model. Antimicrob. Agents Chem.51, 1934–1938 (2007).
Mitra K., Ghosh A.N.: Characterization of Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor typing phage S5. Arch.Virol.152, 1775–1786 (2007).
Niemann H., Kwiatkowski B., Westphal U., Stirm S.: Klebsiella serotype 25 capsular polysaccharide: primary structure and depolymerization by a bacteriophage-borne glycanase. J.Bacteriol.130, 366–374 (1977).
Nordeen R.O., Morgan M.K., Currier T.C.: Isolation and partial characterization of bacteriophages of the phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.45, 1890–1898 (1983).
Pajunen M., Kiljunen S., Skrunik M.: Bacteriophage YeO3-12, specific for Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:3, is related to coliphages T3 and T7. J.Bacteriol.182, 5114–5120 (2000).
Podschun R., Ullmann U.: Klebsiella spp. as nosocomial pathogens: epidemiology, taxonomy, typing methods, and pathogenicity factors. Clin.Microbiol.Rev.11, 589–603 (1998).
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F., Maniatis T.: Molecular Cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor (NY, USA) 1989.
Sen A., Ghosh A.N.: Physicochemical characterization of vibriophage N5. Virol.J.2, 27 (2005).
Shukla I., Tiwari R., Agrawal M.: Prevalence of extended spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a tertiary care hospital. Ind.J.Med.Microbiol.22, 87–91 (2004).
Skurnik M., Pajunen M., Kiljunen S.: Biotechnological challenges of phage therapy. Biotechnol.Lett.29, 995–1003 (2007).
Verma V., Harjai K., Chhibber S.: Characterization of a T7-like lytic bacteriophage of Klebsiella pneumoniae B5055: a potential therapeutic agent. Curr.Microbiol.59, 274–281 (2009).
Watnick P., Kolter R.: Biofilm, city of microbes. J.Bacteriol.182, 2675–2679 (2000).
Wu L.T., Chang S.Y., Yen M.R., Yang T.C., Tseng Y.H.: Characterization of extended-host-range pseudo-T-even bacteriophage Kpp95 isolated on Klebsiella pneumoniae. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.73, 2532–2540 (2007).
Yamamoto K.R., Alberts B.M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G.: Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large scale virus purification. Virology40, 734–744 (1970).
Yoon S.-S., Barrangou-Poueys R., Breid F. Jr., Fleming H.P.: Detection and characterization of a lytic Pediococcus bacteriophage from the fermenting cucumber brine. J.Microbiol.Biotechnol.17, 262–270 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, S., Harjai, K. & Chhibber, S. Isolation and characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae specific bacteriophages from sewage samples. Folia Microbiol 55, 221–227 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0032-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0032-7