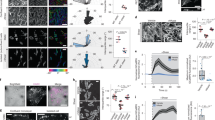
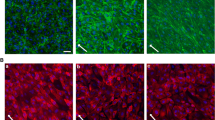
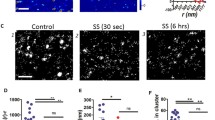
Abstract
There is now a large body of evidence demonstrating that fluid mechanical forces generated by blood flowing through the vasculature play a direct role in regulating endothelial cell structure and function. Integrin receptors that localize to the basal surface of the endothelium participate in both outside-in and inside-out signaling events that influence endothelial gene expression and morphology in response to flow. Our analyses of apical plasma membranes derived from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells revealed that integrins are also expressed on this cell surface. Here, we tested whether these integrins participate in mechanotransduction events that are known to occur on the endothelial cell luminal/apical membrane. We found that apically expressed β1 integrins are rapidly activated in response to acute shear stress. Blockade of β1 integrin activation attenuated a shear-induced signaling cascade involving Src-family kinase, PI3-kinase, Akt and eNOS on this cell surface. In addition, β1 integrin activation and associated signaling events were dependent on the structural integrity of caveolae but not the actin cytoskeleton. Taken together, these data indicate that endothelial responses to shear stress are mediated by spatially distinct pools of integrins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berk, B. C., M. A. Corson, T. E. Peterson, and H. Tseng. Protein kinases as mediators of fluid shear stress stimulated signal transduction in endothelial cells: a hypothesis for calcium-dependent and calcium-independent events activated by flow. J. Biomech. 28:1439–1450, 1995.
Bhullar, I. S., Y. S. Li, H. Miao, E. Zandi, M. Kim, J. Y. Shyy, and S. Chien. Fluid shear stress activation of IkappaB kinase is integrin-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 273:30544–30549, 1998.
Carlile Klusacek, M., and V. Rizzo. Endothelial cytoskeletal reorganization in response to protease activated receptor-1 (Par1) stimulation is mediated by membrane rafts but not caveolae. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 293:H366–H375, 2007.
Chachisvilis, M., Y. L. Zhang, and J. A. Frangos. G protein-coupled receptors sense fluid shear stress in endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 103:15463–15468, 2006.
Gutierrez, J., and E. Brandan. A novel mechanism of sequestering fibroblast growth factor 2 by glypican in lipid rafts, allowing skeletal muscle differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 30:1634–1649, 2010.
Hooper, N. M. Glypican-1 facilitates prion conversion in lipid rafts. J. Neurochem. 116:721–725, 2011.
Jin, Z. G., H. Ueba, T. Tanimoto, A. O. Lungu, M. D. Frame, and B. C. Berk. Ligand-independent activation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 by fluid shear stress regulates activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circ. Res. 93:354–363, 2003.
Katsumi, A., A. W. Orr, E. Tzima, and M. A. Schwartz. Integrins in mechanotransduction. J. Biol. Chem. 279:12001–12004, 2004.
Koshida, R., P. Rocic, S. Saito, T. Kiyooka, C. Zhang, and W. M. Chilian. Role of focal adhesion kinase in flow-induced dilation of coronary arterioles. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25:2548–2553, 2005.
Lee, H. J., and G. Y. Koh. Shear stress activates Tie2 receptor tyrosine kinase in human endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 304:399–404, 2003.
Li, S., M. Kim, Y. L. Hu, S. Jalali, D. D. Schlaepfer, T. Hunter, S. Chien, and J. Y. Shyy. Fluid shear stress activation of focal adhesion kinase. Linking to mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 272:30455–30462, 1997.
Liu, Y., B. P. Chen, M. Lu, Y. Zhu, M. B. Stemerman, S. Chien, and J. Y. Shyy. Shear stress activation of SREBP1 in endothelial cells is mediated by integrins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22:76–81, 2002.
Loufrani, L., and D. Henrion. Role of the cytoskeleton in flow (shear stress)-induced dilation and remodeling in resistance arteries. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 46:451–460, 2008.
Luque, A., M. Gomez, W. Puzon, Y. Takada, F. Sanchez-Madrid, and C. Cabanas. Activated conformations of very late activation integrins detected by a group of antibodies (HUTS) specific for a novel regulatory region (355–425) of the common beta 1 chain. J. Biol. Chem. 271:11067–11075, 1996.
Matthews, B. D., D. R. Overby, R. Mannix, and D. E. Ingber. Cellular adaptation to mechanical stress: role of integrins, Rho, cytoskeletal tension and mechanosensitive ion channels. J. Cell Sci. 119:508–518, 2006.
Matthews, B. D., C. K. Thodeti, J. D. Tytell, A. Mammoto, D. R. Overby, and D. E. Ingber. Ultra-rapid activation of TRPV4 ion channels by mechanical forces applied to cell surface beta1 integrins. Integr. Biol. (Camb) 2:435–442, 2009.
Monaghan-Benson, E., C. C. Mastick, and P. J. McKeown-Longo. A dual role for caveolin-1 in the regulation of fibronectin matrix assembly by uPAR. J. Cell Sci. 121:3693–3703, 2008.
Muller, J. M., W. M. Chilian, and M. J. Davis. Integrin signaling transduces shear stress–dependent vasodilation of coronary arterioles. Circ. Res. 80:320–326, 1997.
Muriel, O., A. Echarri, C. Hellriegel, D. M. Pavon, L. Beccari, and M. A. Del Pozo. Phosphorylated filamin A regulates actin-linked caveolae dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 124:2763–2776, 2011.
Nauli, S. M., Y. Kawanabe, J. J. Kaminski, W. J. Pearce, D. E. Ingber, and J. Zhou. Endothelial cilia are fluid shear sensors that regulate calcium signaling and nitric oxide production through polycystin-1. Circulation 117:1161–1171, 2008.
Paszek, M. J., D. Boettiger, V. M. Weaver, and D. A. Hammer. Integrin clustering is driven by mechanical resistance from the glycocalyx and the substrate. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5:e1000604, 2009.
Radel, C., M. Carlile-Klusacek, and V. Rizzo. Participation of caveolae in beta1 integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 358:626–631, 2007.
Radel, C., and V. Rizzo. Integrin mechanotransduction stimulates caveolin-1 phosphorylation and recruitment of Csk to mediate actin reorganization. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 288:H936–H945, 2005.
Rizzo, V., D. P. McIntosh, P. Oh, and J. E. Schnitzer. In situ flow activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase in luminal caveolae of endothelium with rapid caveolin dissociation and calmodulin association. J. Biol. Chem. 273:34724–34729, 1998.
Rizzo, V., C. Morton, N. DePaola, J. E. Schnitzer, and P. F. Davies. Recruitment of endothelial caveolae into mechanotransduction pathways by flow conditioning in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 285:H1720–H1729, 2003.
Rizzo, V., A. Sung, P. Oh, and J. E. Schnitzer. Rapid mechanotransduction in situ at the luminal cell surface of vascular endothelium and its caveolae. J. Biol. Chem. 273:26323–26329, 1998.
Saliez, J., C. Bouzin, G. Rath, P. Ghisdal, F. Desjardins, R. Rezzani, L. F. Rodella, J. Vriens, B. Nilius, O. Feron, J. L. Balligand, and C. Dessy. Role of caveolar compartmentation in endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated relaxation: Ca2+ signals and gap junction function are regulated by caveolin in endothelial cells. Circulation 117:1065–1074, 2008.
Shyy, J. Y., and S. Chien. Role of integrins in endothelial mechanosensing of shear stress. Circ. Res. 91:769–775, 2002.
Singh, R. D., D. L. Marks, E. L. Holicky, C. L. Wheatley, T. Kaptzan, S. B. Sato, T. Kobayashi, K. Ling, and R. E. Pagano. Gangliosides and beta1-integrin are required for caveolae and membrane domains. Traffic 11:348–360, 2010.
Tarbell, J. M., and M. Y. Pahakis. Mechanotransduction and the glycocalyx. J. Intern. Med. 259:339–350, 2006.
Thodeti, C. K., B. Matthews, A. Ravi, A. Mammoto, K. Ghosh, A. L. Bracha, and D. E. Ingber. TRPV4 channels mediate cyclic strain-induced endothelial cell reorientation through integrin-to-integrin signaling. Circ. Res. 104:1123–1130, 2009.
Tzima, E., M. Angel del Pozo, S. Shattil, S. Shein, and M. Schwartz. Activation of integrins in endothelial cells by fluid shear stress mediates Rho-dependent cytoskeletal alignment. EMBO 20:4639-4647, 2001
Tzima, E., M. Irani-Tehrani, W. B. Kiosses, E. Dejana, D. A. Schultz, B. Engelhardt, G. Cao, H. DeLisser, and M. A. Schwartz. A mechanosensory complex that mediates the endothelial cell response to fluid shear stress. Nature 437:426–431, 2005.
Wang, Y., E. L. Botvinick, Y. Zhao, M. W. Berns, S. Usami, R. Y. Tsien, and S. Chien. Visualizing the mechanical activation of Src. Nature 434:1040–1045, 2005.
Wang, Y., H. Miao, S. Li, K. D. Chen, Y. S. Li, S. Yuan, J. Y. Shyy, and S. Chien. Interplay between integrins and FLK-1 in shear stress-induced signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 283:C1540–C1547, 2002.
Yamamoto, K., R. Korenaga, A. Kamiya, and J. Ando. Fluid shear stress activates Ca(2+) influx into human endothelial cells via P2X4 purinoceptors. Circ. Res. 87:385–391, 2000.
Yang, B., C. Radel, D. Hughes, S. Kelemen, and V. Rizzo. p190 RhoGTPase-activating protein links the beta1 integrin/caveolin-1 mechanosignaling complex to RhoA and actin remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 31:376–383, 2011.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Chris Radel and Dr. Jackcy Jacobs for their technical assistance. This work was supported by NIH grant RO1 HL086551to VR.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Jeffrey Fredberg oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Rizzo, V. Shear Stress Activates eNOS at the Endothelial Apical Surface Through β1 Containing Integrins and Caveolae. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 6, 346–354 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-013-0276-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-013-0276-9