Abstract
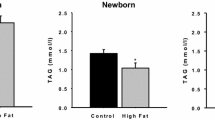
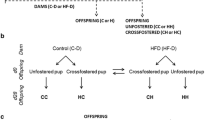
We investigated whether maternal over-nutrition during pregnancy and lactation affects the offspring’s lipid metabolism at weaning by assessing liver lipid metabolic gene expressions and analysing its mechanisms on the development of metabolic abnormalities. Female Sprague–Dawley rats were fed with standard chow diet (CON) or high-fat diet (HFD) for 8 weeks, and then continued feeding during gestation and lactation. The offspring whose dams were fed with HFD had a lower birth weight but an increased body weight with impaired glucose tolerance, higher serum cholesterol, and hepatic steatosis at weaning. Microarray analyses showed that there were 120 genes differently expressed between the two groups. We further verified the results by qRT-PCR. Significant increase of the lipogenesis (Me1, Scd1) gene expression was found in HFD (P<0.05), and up-regulated expression of genes (PPAR-α, Cpt1α, Ehhadh) involved in β-oxidation was also observed (P<0.05), but the Acsl3 gene was down-regulated (P<0.05). Maternal over-nutrition could not only primarily induce lipogenesis, but also promote lipolysis through an oxidation pathway as compensation, eventually leading to an increased body weight, impaired glucose tolerance, elevated serum cholesterol and hepatic steatosis at weaning. This finding may provide some evidence for a healthy maternal diet in order to reduce the risk of metabolic diseases in the early life of the offspring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dwairi A, Pabona JM, Simmen RC and Simmen FA 2012 Cytosolic malic enzyme 1 (ME1) mediates high fat diet-induced adiposity, endocrine profile, and gastrointestinal tract proliferation-associated biomarkers in male mice. PLoS One 7 e46716
Barker DJ 1990 The fetal and infant origins of adult disease. BMJ. 301 1111
Beck B, Richy S, Archer ZA and Mercer JG 2012 Early and persistent up-regulation of hypothalamic orexigenic peptides in rat offspring born to dams fed a high-carbohydrate supplement during gestation. Brain Res. 1477 10–18
Bu SY, Mashek MT and Mashek DG 2009 Suppression of long chain acyl-CoA synthetase 3 decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis through decreased transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 284 30474–30483
Cao HX and Fan JG 2011 Editorial: Fatty liver disease: a growing public health problem worldwide. J. Dig. Dis. 12 1–2
Chitturi S, Wong VW and Farrell G 2011 Nonalcoholic fatty liver in Asia: firmly entrenched and rapidly gaining ground. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 26 163–172
Cnop M, Foufelle F and Velloso LA 2012 Endoplasmic reticulum stress, obesity and diabetes. Trends Mol. Med. 18 59–68
Cunha Fda S, Dalle Molle R, Portella AK, Benetti Cda S, Noschang C, Goldani MZ and Silveira PP 2015 Both food restriction and high-fat diet during gestation induce low birth weight and altered physical activity in adult rat offspring: the "Similarities in the Inequalities" model. PLoS One 10 e0118586
Dudley KJ, Sloboda DM, Connor KL, Beltrand J and Vickers MH 2011 Offspring of mothers fed a high fat diet display hepatic cell cycle inhibition and associated changes in gene expression and DNA methylation. PLoS One 6 e21662
Dunn GA and Bale TL 2011 Maternal high-fat diet effects on third-generation female body size via the paternal lineage. Endocrinology 152 2228–2236
Fernandez Gianotti T, Burgueno A, Gonzales Mansilla N, Pirola CJ and Sookoian S 2013 Fatty liver is associated with transcriptional downregulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturase and impaired protein dimerization. PLoS One 8 e76912
Govindarajah V, Leung YK, Ying J, Gear R, Bornschein RL, Medvedovic M and Ho SM 2016 In utero exposure of rats to high-fat diets perturbs gene expression profiles and cancer susceptibility of prepubertal mammary glands. J. Nutr. Biochem. 29 73–82
Gugusheff J, Sim P, Kheng A, Gentili S, Al-Nussairawi M, Brand-Miller J and Muhlhausler B 2015 The effect of maternal and post-weaning low and high glycaemic index diets on glucose tolerance, fat deposition and hepatic function in rat offspring. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 10 1–10
Houten SM, Denis S, Argmann CA, Jia Y, Ferdinandusse S, Reddy JK and Wanders RJ 2012 Peroxisomal L-bifunctional enzyme (Ehhadh) is essential for the production of medium-chain dicarboxylic acids. J. Lipid Res. 53 1296–1303
Magliano DC, Bargut TC, De Carvalho SN, Aguila MB, Mandarim-De-Lacerda CA and Souza-Mello V 2013 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-alpha and gamma are targets to treat offspring from maternal diet-induced obesity in mice. PLoS One 8 e64258
Mantzaris MD, Tsianos EV and Galaris D 2011 Interruption of triacylglycerol synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum is the initiating event for saturated fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in liver cells. FEBS J. 278 519–530
Ntambi JM and Miyazaki M 2004 Regulation 01of stearoyl-CoA desaturases and role in metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 43 91–104
Plagemann A, Harder T, Schellong K, Schulz S and Stupin JH 2012 Early postnatal life as a critical time window for determination of long-term metabolic health. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 26 641–653
Poppelreuther M, Rudolph B, Du C, Grossmann R, Becker M, Thiele C, Ehehalt R and Fullekrug J 2012 The N-terminal region of acyl-CoA synthetase 3 is essential for both the localization on lipid droplets and the function in fatty acid uptake. J. Lipid Res. 53 888–900
Pruis MG, Lendvai A, Bloks VW, Zwier MV, Baller JF, De Bruin A, Groen AK and Plosch T 2014 Maternal western diet primes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adult mouse offspring. Acta. Physiol. 210 215–227
Reynolds CM, Segovia SA, Zhang XD, Gray C and Vickers MH 2015 Maternal high-fat diet-induced programing of gut taste receptor and inflammatory gene expression in rat offspring is ameliorated by CLA supplementation. Physiol. Rep. 3 10
Silbernagel G, Kovarova M, Cegan A, Machann J, Schick F, Lehmann R, Haring HU, Stefan N, et al. 2012 High hepatic SCD1 activity is associated with low liver fat content in healthy subjects under a lipogenic diet. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97 E2288–E2292
Sohi G, Revesz A and Hardy DB 2011 Permanent implications of intrauterine growth restriction on cholesterol homeostasis. Semin. Reprod. Med. 29 246–256
Stergiou E, Diamanti E, Agakidis C, Sarafidis K, Mantzou E and Drossou V 2012 Effect of gestational diabetes and intrauterine growth restriction on the offspring's circulating galanin at birth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97 E238–E242
Strakovsky RS, Zhang X, Zhou D and Pan YX 2011 Gestational high fat diet programs hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression and histone modification in neonatal offspring rats. J. Physiol. 589 2707–2717
Takasaki M, Honma T, Yanaka M, Sato K, Shinohara N, Ito J, Tanaka Y, Tsuduki T, et al. 2012 Continuous intake of a high-fat diet beyond one generation promotes lipid accumulation in liver and white adipose tissue of female mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 23 640–645
Tanaka T, Masuzaki H and Nakao K 2005 Role of PPARs in the pathophysiology of nonalcoholoic fatty liver disease. Nihon Rinsho. 63 700–706
Uauy R, Kain J and Corvalan C 2011 How can the Developmental Origins of Health and Disease (DOHaD) hypothesis contribute to improving health in developing countries? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 94 1759s–1764s
Yamaguchi R, Nakagawa Y, Liu YJ, Fujisawa Y, Sai S, Nagata E, Sano S, Satake E, et al. 2010 Effects of maternal high-fat diet on serum lipid concentration and expression of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors in the early life of rat offspring. Horm. Metab. Res. 42 821–825
Zhang J, Wang C, Terroni PL, Cagampang FR, Hanson M and Byrne CD 2005 High-unsaturated-fat, high-protein, and low-carbohydrate diet during pregnancy and lactation modulates hepatic lipid metabolism in female adult offspring. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 288 R112–R118
Zhang J, Zhang F, Didelot X, Bruce KD, Cagampang FR, Vatish M, Hanson M, Lehnert H, et al. 2009 Maternal high fat diet during pregnancy and lactation alters hepatic expression of insulin like growth factor-2 and key microRNAs in the adult offspring. BMC Genomics 10 478
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance provided by Shanghai Jiao Tong University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Huang Y, Ye T, Liu C, Fang F, Chen Y and Dong Y 2017 Maternal high-fat diet during pregnancy and lactation affects hepatic lipid metabolism in early life of offspring rat. J. Biosci. 42 XXX–XXX]
Supplementary materials pertaining to this article are available on the Journal of Biosciences Website.
Yanhong Huang and Tingting Ye contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 62 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Ye, T., Liu, C. et al. Maternal high-fat diet during pregnancy and lactation affects hepatic lipid metabolism in early life of offspring rat. J Biosci 42, 311–319 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9675-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9675-8