Abstract
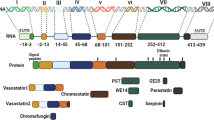
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a member of the granins, a family of acidic proteins found in abundance in (neuro)endocrine cells (e.g., in chromaffin cells) and in some tumors. Like other granins, CgA has a granulogenic role in secretory granule biogenesis and is stored in these organelles. CgA is partially processed differentially in various cell types to yield biologically active peptides, such as vasostatin, pancreastatin, catestatin, and serpinins. In this review, we describe the roles of CgA and several of its derived peptides. CgA, which is elevated in the blood of cancer patients, inhibits angiogenesis and exerts protective effects on the endothelial barrier function in tumors, thus affecting response to chemotherapy. Recent studies indicate that the serpinins promote cell survival and myocardial contractility and relaxation. Other peptides such as pancreastatin were found to have significant effects on inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and glucose up-take, induction of glycogenolysis in hepatocytes, and inhibition of lipogenesis. In contrast, catestatin has opposite effects to that of pancreastatin in glucose metabolism and lipogenesis. Catestatin appears to also play a significant role in cardiac function, blood pressure regulation, and mutations in the catestatin domain of the CgA gene are associated with hypertension in humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADD1:
-
Adipocyte determination and differentiation factor 1
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CST:
-
Catestatin
- CVLM:
-
Caudal ventrolateral medulla
- GLUT4:
-
Glucose transporter type 4
- Gpat:
-
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NTS:
-
Nucleus of the solitary tract
- Ppar-γ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- Srebp1c:
-
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
References
Ahren B, Bertrand G, Roye M, Ribes G (1996) Pancreastatin modulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. Acta Physiol Scand 158:63–70
Angelone T, Quintieri AM, Brar BK, Limchaiyawat PT, Tota B, Mahata SK, Cerra MC (2008) The antihypertensive chromogranin a peptide catestatin acts as a novel endocrine/paracrine modulator of cardiac inotropism and lusitropism. Endocrinology 149:4780–4793
Bartolomucci A, Possenti R, Mahata SK, Fischer-Colbrie R, Loh YP, Salton SR (2011) The extended granin family: structure, function, and biomedical implications. Endocr Rev 32:755–797
Belloni D, Scabini S, Foglieni C, Veschini L, Giazzon A, Colombo B, Fulgenzi A, Helle KB, Ferrero ME, Corti A, Ferrero E (2007) The vasostatin-I fragment of chromogranin A inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and migration. FASEB J 21:3052–3062
Blois A, Srebro B, Mandala M, Corti A, Helle KB, Serck-Hanssen G (2006) The chromogranin A peptide vasostatin-I inhibits gap formation and signal transduction mediated by inflammatory agents in cultured bovine pulmonary and coronary arterial endothelial cells. Regul Pept 135:78–84
Chen Y, Rao F, Rodriguez-Flores JL, Mahata M, Fung MM, Stridsberg M, Vaingankar SM, Wen G, Salem RM, Das M, Cockburn MG, Schork NJ, Ziegler MG, Hamilton BA, Mahata SK, Taupenot L, O’Connor DT (2008) Naturally occurring human genetic variation in the 3′-untranslated region of the secretory protein chromogranin A is associated with autonomic blood pressure regulation and hypertension in a sex-dependent fashion. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1468–1481
Chipuk JE, Green DR (2008) How do BCL-2 proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization? Trends Cell Biol 18:157–164
Colombo B, Curnis F, Foglieni C, Monno A, Arrigoni G, Corti A (2002) Chromogranin A expression in neoplastic cells affects tumor growth and morphogenesis in mouse models. Cancer Res 62:941–946
Corti A (2010) Chromogranin A and the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30:1163–1170
Corti A, Curnis F (2011) Tumor vasculature targeting through NGR peptide-based drug delivery systems. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12:1128–1134
Corti A, Gasparri A, Chen FX, Pelagi M, Brandazza A, Sidoli A, Siccardi AG (1996) Characterisation of circulating chromogranin A in human cancer patients. Br J Cancer 73:924–932
Corti A, Curnis F, Arap W, Pasqualini R (2008) The neovasculature homing motif NGR: more than meets the eye. Blood 112:2628–2635
Corti A, Pastorino F, Curnis F, Arap W, Ponzoni M, Pasqualini R (2012) Targeted drug delivery and penetration into solid tumors. Med Res Rev. doi:10.1002/med.20238
Curnis F, Sacchi A, Borgna L, Magni F, Gasparri A, Corti A (2000) Enhancement of tumor necrosis factor alpha antitumor immunotherapeutic properties by targeted delivery to aminopeptidase N (CD13). Nat Biotechnol 18:1185–1190
Curnis F, Sacchi A, Corti A (2002a) Improving chemotherapeutic drug penetration in tumors by vascular targeting and barrier alteration. J Clin Invest 110:475–482
Curnis F, Arrigoni G, Sacchi A, Fischetti L, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Corti A (2002b) Differential binding of drugs containing the NGR motif to CD13 isoforms in tumor vessels, epithelia, and myeloid cells. Cancer Res 62:867–874
Dondossola E, Gasparri AM, Colombo B, Sacchi A, Curnis F, Corti A (2011) Chromogranin A restricts drug penetration and limits the ability of NGR-TNF to enhance chemotherapeutic efficacy. Cancer Res 71:5881–5890
Ferrero E, Scabini S, Magni E, Foglieni C, Belloni D, Colombo B, Curnis F, Villa A, Ferrero ME, Corti A (2004) Chromogranin A protects vessels against tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced vascular leakage. FASEB J 18:554–556
Fung MM, Salem RM, Mehtani P, Thomas B, Lu CF, Perez B, Rao F, Stridsberg M, Ziegler MG, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT (2010) Direct vasoactive effects of the chromogranin A (CHGA) peptide catestatin in humans in vivo. Clin Exp Hypertens 32:278–287
Gaede AH, Pilowsky PM (2010) Catestatin in rat RVLM is sympathoexcitatory, increases barosensitivity, and attenuates chemosensitivity and the somatosympathetic reflex. Am J Physiol 299:R1538–R1545
Gaede AH, Pilowsky PM (2012) Catestatin, a chromogranin A-derived peptide, is sympathoinhibitory and attenuates sympathetic barosensitivity and the chemoreflex in rat CVLM. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 302(3):R365–R372
Gaede AH, Lung MS, Pilowsky PM (2009) Catestatin attenuates the effects of intrathecal nicotine and isoproterenol. Brain Res 1305:86–95
Gayen JR, Gu Y, O’Connor DT, Mahata SK (2009a) Global disturbances in autonomic function yield cardiovascular instability and hypertension in the chromogranin a null mouse. Endocrinology 150:5027–5035
Gayen JR, Saberi M, Schenk S, Biswas N, Vaingankar SM, Cheung WW, Najjar SM, O’Connor DT, Bandyopadhyay G, Mahata SK (2009b) A novel pathway of insulin sensitivity in chromogranin A null mice: a crucial role for pancreastatin in glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem 284:28498–28509
Gayen JR, Zhang K, RamachandraRao SP, Mahata M, Chen Y, Kim HS, Naviaux RK, Sharma K, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT (2010) Role of reactive oxygen species in hyperadrenergic hypertension: biochemical, physiological, and pharmacological evidence from targeted ablation of the chromogranin a (Chga) gene. Circulation 3:414–425
Gonzalez-Yanes C, Sanchez-Margalet V (2000) Pancreastatin modulates insulin signaling in rat adipocytes: mechanisms of cross-talk. Diabetes 49:1288–1294
Gregorc V, Spreafico A, Floriani I, Colombo B, Ludovini V, Pistola L, Bellezza G, Vigano MG, Villa E, Corti A (2007) Prognostic value of circulating chromogranin A and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 110:845–853
Helle KB, Corti A, Metz-Boutigue MH, Tota B (2007) The endocrine role for chromogranin A: a prohormone for peptides with regulatory properties. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2863–2886
Hook V, Bark S, Gupta N, Lortie M, Lu WD, Bandeira N, Funkelstein L, Wegrzyn J, O’Connor DT, Pevzner P (2010) Neuropeptidomic components generated by proteomic functions in secretory vesicles for cell-cell communication. AAPS J 12:635–645
Kennedy BP, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Ziegler MG (1998) Mechanism of cardiovascular actions of the chromogranin A fragment catestatin in vivo. Peptides 19:1241–1248
Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Yergy AL, Loh YP (2011a) Role of pGlu-Serpinin, a novel chromogranin a-derived peptide in inhibition of cell death. J Mol Neurosci 45:294–303
Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Kim T, Yergey AL, Loh YP (2011b) Serpinin: a novel chromogranin A-derived, secreted peptide up-regulates protease nexin-1 expression and granule biogenesis in endocrine cells. Mol Endocrinol 25:732–744
Mahapatra NR, O’Connor DT, Vaingankar SM, Hikim AP, Mahata M, Ray S, Staite E, Wu H, Gu Y, Dalton N, Kennedy BP, Ziegler MG, Ross J, Mahata SK (2005) Hypertension from targeted ablation of chromogranin A can be rescued by the human ortholog. J Clin Invest 115:1942–1952
Mahata SK, O’Connor DT, Mahata M, Yoo SH, Taupenot L, Wu H, Gill BM, Parmer RJ (1997) Novel autocrine feedback control of catecholamine release. A discrete chromogranin a fragment is a noncompetitive nicotinic cholinergic antagonist. J Clin Invest 100:1623–1633
Mahata SK, Mahata M, Fung MM, O’Connor DT (2010) Catestatin: a multifunctional peptide from chromogranin A. Regul Pept 162:33–43
Marcucci F, Corti A (2012) How to improve exposure of tumor cells to drugs—promoter drugs increase tumor uptake and penetration of effector drugs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2011.09.007
O’Connor DT, Bernstein KN (1984) Radioimmunoassay of chromogranin A in plasma as a measure of exocytotic sympathoadrenal activity in normal subjects and patients with pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med 311:764–770
O’Connor DT, Deftos LJ (1986) Secretion of chromogranin A by peptide-producing endocrine neoplasms. N Engl J Med 314:1145–1151
O’Connor DT, Kailasam MT, Kennedy BP, Ziegler MG, Yanaihara N, Parmer RJ (2002) Early decline in the catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin in humans at genetic risk of hypertension. J Hypertens 20:1335–1345
O’Connor DT, Cadman PE, Smiley C, Salem RM, Rao F, Smith J, Funk SD, Mahata SK, Mahata M, Wen G, Taupenot L, Gonzalez-Yanes C, Harper KL, Henry RR, Sanchez-Margalet V (2005) Pancreastatin: multiple actions on human intermediary metabolism in vivo, variation in disease, and naturally occurring functional genetic polymorphism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:5414–5425
Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 72:219–246
Portela-Gomes GM, Grimelius L, Wilander E, Stridsberg M (2010) Granins and granin-related peptides in neuroendocrine tumours. Regul Pept 165:12–20
Rao F, Wen G, Gayen JR, Das M, Vaingankar SM, Rana BK, Mahata M, Kennedy BP, Salem RM, Stridsberg M, Abel K, Smith DW, Eskin E, Schork NJ, Hamilton BA, Ziegler MG, Mahata SK, O’Connor DT (2007) Catecholamine release-inhibitory peptide catestatin (chromogranin A(352-372)): naturally occurring amino acid variant Gly364Ser causes profound changes in human autonomic activity and alters risk for hypertension. Circulation 115:2271–2281
Sacchi A, Gasparri A, Gallo-Stampino C, Toma S, Curnis F, Corti A (2006) Synergistic antitumor activity of cisplatin, paclitaxel, and gemcitabine with tumor vasculature-targeted tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Cancer Res 12:175–182
Sanchez-Margalet V, Gonzalez-Yanes C, Santos-Alvarez J, Najib S (2000) Pancreastatin. Biological effects and mechanisms of action. Adv Exp Med Biol 482:247–262
Sanchez-Margalet V, Gonzalez-Yanes C, Najib S, Santos-Alvarez J (2010) Metabolic effects and mechanism of action of the chromogranin A-derived peptide pancreastatin. Regul Pept 161:8–14
Tatemoto K, Efendic S, Mutt V, Makk G, Feistner GJ, Barchas JD (1986) Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature 324:476–478
Taupenot L, Harper KL, O’Connor DT (2003) The chromogranin-secretogranin family. N Engl J Med 348:1134–1149
Theurl M, Schgoer W, Albrecht K, Jeschke J, Egger M, Beer AG, Vasiljevic D, Rong S, Wolf AM, Bahlmann FH, Patsch JR, Wolf D, Schratzberger P, Mahata SK, Kirchmair R (2010) The neuropeptide catestatin acts as a novel angiogenic cytokine via a basic fibroblast growth factor-dependent mechanism. Circ Res 107:1326–1335
Tota B, Angelone T, Mazza R, Cerra MC (2008) The chromogranin A-derived vasostatins: new players in the endocrine heart. Curr Med Chem 15:1444–1451
Tota B, Pasqua T, Gentile S, Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Cerra MC, Loh YP, Angelone T (2011) C-terminal Chromogranin A-derived serpinin and pyroglutaminated serpinin as novel cardiac ß-adrenergic agonists. In: 62nd Meeting of The Italian Physiological Society, p 154. Sorrento, (Italy): Acta Physiologica
Tota B, Gentile S, Pasqua T, Bassino E, Koshimizu H, Cawley NX, Cerra MC, Loh YP, Angelone T (2012) The novel Chromogranin A-derived serpinin and pyroglutaminated serpinin peptides are positive cardiac beta-adrenergic-like inotropes (Submitted).
Veschini L, Crippa L, Dondossola E, Doglioni C, Corti A, Ferrero E (2011) The vasostatin-1 fragment of chromogranin A preserves a quiescent phenotype in hypoxia-driven endothelial cells and regulates tumor neovascularization. FASEB J 25:3906–3914
Wen G, Mahata SK, Cadman P, Mahata M, Ghosh S, Mahapatra NR, Rao F, Stridsberg M, Smith DW, Mahboubi P, Schork NJ, O’Connor DT, Hamilton BA (2004) Both rare and common polymorphisms contribute functional variation at CHGA, a regulator of catecholamine physiology. Am J Hum Genet 74:197–207
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Niamh Cawley (NIH) for helpful discussions. This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA (YPL, YC). S.K.M. is supported by grants from the VA Merit Review and the National Institutes of Health. B.T. was supported by a grant from the University of Calabria (Cosenza), Italy. A.C. was supported by a grant from Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) of Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loh, Y.P., Cheng, Y., Mahata, S.K. et al. Chromogranin A and Derived Peptides in Health and Disease. J Mol Neurosci 48, 347–356 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9728-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9728-2