Abstract
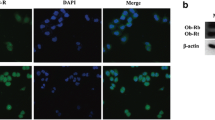
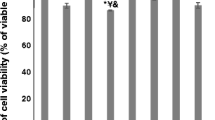
Adiponectin, the hormone produced and secreted by adipocytes, has been shown to promote migration of the epithelial cells and angiogenesis in these cells. We sought to determine if adiponectin could induce the cellular migration and growth factor expression in breast cancer cells grown in vitro. The breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-436 and MFM-223 (estrogen-independent) were treated with adiponectin for different time periods. Supernatants of the cell cultures were obtained by centrifugation and were assayed for growth factor expression by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Becton–Dickinson-Falcon Transwell systems were used to assay adiponectin-induced migration. Adiponectin significantly induced the expression of various growth factors, including vascular endothelial growth factor, transforming growth factor-β1, and basic fibroblast growth factor in MDA-MB-436 and MFM-223 cells. Adiponectin also enhanced the migration of breast cancer cells which were inhibited about 50–70 % by the inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Adiponectin treatment of the cancer cell induced an increased expression of different growth factors and migration of the cells. These effects are likely to contribute to the progression of breast cancer, implying that change in adiponectin levels associated with obesity may be considered as a high risk factor in breast cancer patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Kruijsdijk, R., van der Wall, E., & Visseren, F. (2009). Obesity and cancer: The role of dysfunctional adipose tissue. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, 18(10), 2569–2578.
Schlienger, J. L., et al. (2009). Obesity and cancer. Revue de Medecine Interne, 30(9), 776–782.
Calle, E. E., et al. (2003). Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. New England Journal of Medicine, 348(17), 1625–1638.
Neugut, A. I., Chen, A. C., & Petrylak, D. P. (2004). The “skinny” on obesity and prostate cancer prognosis. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 22(3), 395–398.
Dalamaga, M., Diakopoulos, K. N., & Mantzoros, C. S. (2012). The role of adiponectin in cancer: A review of current evidence. Endocrine Reviews, 33(4), 547–594.
Kelesidis, I., Kelesidis, T., & Mantzoros, C. (2006). Adiponectin and cancer: A systematic review. British Journal of Cancer, 94(9), 1221–1225.
Tian, Y. F., et al. (2007). Anthropometric measures, plasma adiponectin, and breast cancer risk. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 14(3), 669–677.
Cnop, M., et al. (2003). Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia, 46, 459–469.
Perrier, S., & Jarde, T. (2012). Adiponectin, an anti-carcinogenic hormone? A systematic review on breast, colorectal, liver and prostate cancer. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 19(32), 5501–5512.
Wu, M. H., et al. (2009). Circulating levels of leptin, adiposity and breast cancer risk. British Journal of Cancer, 100(4), 578–582.
Sun, C. A., et al. (2010). Adipocytokine resisting and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, 123(3), 869–876.
Grossmann, M. E., et al. (2008). Balance of adiponectin and leptin modulates breast cancer cell growth. Cell Research, 18(11), 1154–115625.
Prieto-Hontoria, P. L., et al. (2011). Role of obesity-associated dysfunctional adipose tissue in cancer: A molecular nutrition approach. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Bioenergetics, 1807(6SI), 664–678.
Zhang, X. T., et al. (2012). Estrogen receptor-alpha 36 mediates mitogenic antiestrogen signaling in ER-negative breast cancer cells. PLoS One, 7(1), e30174. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030174.
Grossmann, M. E., et al. (2008). Effects of adiponectin on breast cancer cell growth and signaling. British Journal of Cancer, 98, p370–p379.
Körner, A., et al. (2007). Total and high molecular weight adiponectin in breast cancer: In vitro and in vivo studies. J Clin Endocrinol & Metabolism, 92(3), 1041–1048.
Lijnen, H. R., & Scroyen, I. (2013). Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 antagonism on adiposity in obese mice. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 50(3), 319–324.
Moon, H. S., et al. (2013). Salutary effects of adiponectin on colon cancer: In vivo and in vitro studies in mice. Gut, 62(4), 561–570.
Hu, D., et al. (2013). Adiponectin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression in macrophages via Syk-ERK pathway. PLOS One, 8, e560712.
Fayad, R., et al. (2007). Adiponectin deficiency protects mice from chemically induced colonic inflammation. Gastroenterology, 132(2), 601–614.
Du, B. W., et al. (2013). The transcription factor paired-related homeobox 1 (Prrx1) inhibits adipogenesis by activating transforming growth factor-beta (TGF beta) signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(5), 3036–3047.
Wanninger, J., et al. (2011). Adiponectin induces the transforming growth factor decoy receptor BAMBI in human hepatocytes. FEBS Letters, 585(9), 1338–1344.
Masuda, H., et al. (2012). Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment,. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2289-9.
Miyoshi, Y., et al. (2003). Association of serum adiponectin levels with breast cancer risk. Clinical Cancer Research, 9, 5699–5704.
Hou, W. K., et al. (2007). Adipocytokines and breast cancer risk. Chinese Medical Journal (English Edition), 120, 1592–1596.
Kang, J. H., et al. (2007). Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 22, 117–121. doi:10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.117.
Mantzoros, C., et al. (2004). Adiponectin and breast cancer risk. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 89, 1102–1107. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-031804.
Tworoger, S. S., et al. (2007). Plasma adiponectin concentrations and risk of incident breast cancer. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 92, 1510–1516. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-1975.
Gaudet, M. M., et al. (2010). Do adipokines underlie the association between known risk factors and breast cancer among a cohort of United States women. Cancer Epidemiology, 34, 580–586. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2010.05.014.
Miyatani, Y., et al. (2008). Associations of circulating adiponectin with estradiol and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in postmenopausal women. Menopause, 15, 536–541. doi:10.1097/gme.0b013e31815c85ed.
Liu, L.-Y., et al. (2013). The role of adiponectin in breast cancer: A meta-analysis. PloS One, 8(8), e73183. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0073183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhongming Jia and Yan Liu equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Z., Liu, Y. & Cui, S. Adiponectin Induces Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Growth Factor Expression. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 1239–1245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0047-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0047-9