Abstract
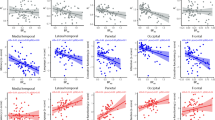
Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD) differs substantially from early-onset AD. In this cross sectional study we investigated brain perfusion changes after 18 months of treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors (ChEIs) donepezil or galantamine. Twenty-five drug-naïve late-onset AD patients were recruited from outpatient clinics. We examined brain perfusion using single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and used three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection (3D-SSP) and the stereotactic extraction estimation method (SEE) level 3 to analyze classified gyrus level segments. We assessed cognitive function using the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog) grouped into three subgroup domains, language, memory, and praxis. In the follow-up data, some regions were further hypoperfused, reflecting worsening of the disease, while other regions showed alleviated hypoperfusion, potentially related to the ChEIs treatment. Regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) decreased in the parietal cortex and increased in the frontal and the limbic cortices. Increased hypoperfusion significantly correlated with ADAS-cog scores changes were seen in the superior parietal lobule, inferior parietal lobule, angular gyrus, and supramarginal gyrus of the parietal cortex. Alleviated hypoperfusion significantly related to recovery of ADAS-cog scores were seen in the rectal and paracentral lobule of the frontal cortex, and the anterior cingulate of the limbic cortex. These regions showed significant relationships with total ADAS-cog and language, memory and praxis subscales scores. The current longitudinal study indicates prominent rCBF changes and their relationships with changes in ADAS-cog scores in late-onset AD patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994). Diagnostic and statistic manual of mental disorders (DSN-IV-TR), 4th edn., text rev). Washington DC: American Psychiatric Press.
Canu, E., Frisoni, G. B., Agosta, F., Pievani, M., Bonetti, M., & Filippi, M. (2012). Early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease patients have distinct patterns of white matter damage. Neurobiology of Aging, 33, 1023–1033.
Cavedo, E., Pievani, M., Boccardi, M., Galluzzi, S., Bocchetta, M., Bonetti, M., et al. (2014). Medial temporal atrophy in early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 35, 2004–2012.
Ceravolo, R., Volterrani, D., Toqnoni, G., Dell’Aqnello, G., Manca, G., Kiferie, L., et al. (2004). Cerebral perfusional effects of cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer disease. Clinical Neuropharmacology, 27, 166–170.
Chaudhart, S., Scouten, A., Schwindt, G., Janik, R., Lee, W., Sled, J. G., et al. (2013). Hemodynamic effects of cholinesterase inhibition in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 28, 26–35.
Desgranges, B., Baron, J. C., Giffard, B., Chételat, G., Lalevée, C., de la Sayette, V., et al. (2002). The neural basis of instruction in free recall and cued recall: a PET study in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage, 17, 1658–1664.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Cummings, J. L., DeKosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., et al. (2010). Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: a new lexicon. Lancet Neurology, 9, 1118–1127.
Fletcher, P. C., Frith, C. D., Grasby, P. M., Shallice, T., Frackowiak, R. S., & Dolan, R. J. (1995). Brain systems for encoding and retrieval of auditory-verbal memory. An in vivo study in humans. Brain, 118, 401–416.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). Mini-mental state. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinicians. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12, 189–198.
Frisoni, G. B., Pievani, M., Testa, C., Sabattoli, F., Bresciani, L., Bonetti, M., et al. (2007). The topography of grey matter involvement in early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 130, 720–730.
Giacobini, E. (2000). Cholinestrase inhibitor therapy stabilize symptoms of Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders, 14 suppl 1, S2-S10.
Grady, C. L., Haxby, J. V., Horwitz, B., Berg, G., & Rapoport, S. I. (1987). Neuropsychological and cerebral metabolic function in early vs late onset dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neuropsychologia, 25, 807–816.
Hachinski, V. C., Iliff, L. D., Zilhka, E., Du Boulay, G. H., McAllister, V. L., Marshall, J., et al. (1975). Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Archives of Neurology, 32, 632–637.
Hanyu, H., Sato, T., Hirao, K., Kanetaka, H., Iwamoto, T., & Koizumi, K. (2010). The progression of cognitive deterioration and regional cerebral blood flow patterns in Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal SPECT study. Journal of Neurological Sciences, 290, 96–101.
Hirano, K., Ohnishi, T., Hirata, Y., Yamashita, F., Mori, T., Moriguchi, Y., et al. (2005). The prediction of rapid conversion of Alzheimer’s disease in mild cognitive impairment using regional cerebral blood flow SPECT. Neuroimage, 28, 1014–1021.
Honda, H., Terada, S., Sato, S., Oshima, E., Ikeda, C., Nagao, S., et al. (2014). Subjective depressive mood and regional blood flow in mild Alzheimer’s disease. International Psychogeriatrics, 26, 817–823.
Hongo, J., Nakaaki, S., Shinagawa, Y., Murata, Y., Sato, J., Tatsumi, H., et al. (2008). SPECT-identified neuroanatomical predictor of the cognitive effects of donepezil treatment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 26, 556–566.
Ishii, K., Kawachi, T., Sasaki, H., Kono, A. K., Fukuda, T., Kojima, Y.,et al (2005). Voxel-based morphometric comparison between early- and late-onset mild Alzheimer’s disease and assessment of diagnostic performance of Z score images. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 26, 333–340.
Johnson, K. A., Jones, K., Holman, B. L., Spiers, P. A., Satllin, A., & Albert, M. S. (1998). Preclinical prediction of Altzheimer’s disease using SPECT. Neurology, 50, 1563–1571.
Joubert, S., Gour, N., Guedi, E., Didic, M., Guériot, C., Koric, L., et al. (2016). Early-onset and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease are associated with distinct patterns of memory impaiment. Cortex, 74, 217–232.
Kaiser, N. C., Melrose, R. J., Liu, C., Sultzer, D. L., Jimenez, E., Su, M., et al. (2012). Neuropsychological and neuroimaging markers in early versus late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias, 27, 520–529.
Keller, C., Kadir, A., Forsberg, A., Porras, O., & Noerberg, A. (2011). Long-term effects of galantamine treatment on brain functional activities as measured by PET in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 24, 109–123.
Kemp, P. M., Holmes, C., Hoffmann, S. M., Bolt, L., Holmes, R., Rowden, J., et al. (2003). Alzheimer’s disease: differences in technetium-99m HMPAO SPECT scan findings between early onset and late onset dementia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 74, 715–719.
Kimura, N., Kumamoto, T., Masuda, T., Hanaoka, T., Okazaki, T., & Arakawa, R. (2012). Evaluation of the cerebral blood flow changes during long-term donepezil therapy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease using 3DSRT. Journal of Neuroimaging, 22, 299–304.
Kogure, D., Matsuda, H., Ohnishi, T., Asada, T., Uno, M., Kunihiro, T., et al. (2000). Longitudinal evaluation of early Alzheimer’s disease using brain perfusion SPECT. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 41, 1155–1162.
Kouneiher, F., Charron, S., & Koechlin, E. (2009). Motivation and cognitive control in the human prefrontal cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 12, 939–945.
Kumar, A., Schapiro, M. B., Grady, C., Haxby, J. V., Wagner, E., Salerno, J. A., et al. (1991). High-resolution PET studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology, 4, 35–46.
Kume, K., Hanyu, H., Sato, T., Hirao, K., Shimizu, S., Kanetaka, H., et al. (2011). Vascular risk factors are associated with faster decline of Alzheimer disease: a longitudinal SPECT study. Journal of Neurology, 258, 1295–1303.
Lee, D. Y., Choo, I. H., Jhoo, J. H., Kim, K. W., Youn, J. C., Lee, D. S., et al. (2006). Frontal dysfunction underlie depressive syndrome in Alzheimer disease: a FDG-PET study. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 14, 625–628.
Li, W., Antuono, P. G., Xie, C., Chen, G., Jones, J. L., Ward, B. D., et al. (2012). Changes in regional cerebral blood flow and functional connectivity in the cholinergic pathway associated with cognitive performance in subjects with mild Alzheimer’s disease after 12-week donepezil treatment. Neuroimage, 60, 1083–1091.
McKhann, G., Drachman, D., Folstein, M., Katzman, R., Price, D., & Stadlan, E. M. (1984). Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology, 34, 939–944.
Minoshima, S., Frey, K. A., Koeppe, R. A., Foster, N. L., & Kuhl, D. E. (1995). A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 36, 1238–1248.
Mizumura, S., Kumita, S., Cho, K., Ishihara, M., Nakajo, H., Toba, M., et al. (2003). Development of quantitative analysis method for stereotactic brain image: assessment of reduced accumulation in extent and severity using anatomical segmentation. Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 17, 289–295.
Möller, C., Vrenken, H., Jiskoot, L., Versteeg, A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., et al. (2013). Different patterns of gray matter atrophy in early-and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 34, 2014–2022.
Nagahama, Y., Nabatame, H., Okina, T., Yamauchi, H., Narita, M., Fujimoto, N., et al. (2003). Cerebral correlations of the cognitive decline in probable Alzheimer’s disease. European Neurology, 50, 1–9.
Nakano, S., Asada, T., Matsuda, H., Uno, M., & Takasaki, M. (2001). Donepezil hydrochloride preserves regional cerebral blood flow in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 41, 1441–1445.
Nobili, F., Vitali, P., Canfora, M., Girtler, N., De Leo, C., Mariani, G., et al. (2002). Effects of long-term Donepezil therapy on rCBF of Alzheimer’s patients. Clinical Neurophysiology, 113, 1241–1248.
Potkin, S. G., Anand, R., Fleming, K., Alva, G., Keator, D., Carreon, D., et al. (2001). Brain metabolic and clinical effects of rivastigmine in Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 4, 223–230.
Reisberg, B., Ferris, S. H., Anand, R., de Leon, M. J., Schneck, M. K., Buttinger, C., et al. (1984). Functional staging of dementia of the Alzheimer’s type. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 435, 481–483.
Roeltgen, D. P., & Heilman, K. M. (1984). Lexical agraphia. Further support for the two-system hypothesis of linguistic agraphia. Brain, 107, 811–827.
Rosen, W. G., Mohs, R. C., & Davis, K. L. (1984). A new rating scale for Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Psychiatry, 141, 1356–1364.
Rushworth, M. F., Buckley, M. J., Behrens, T. E., Walton, M. E., & Bennerman, D. M. (2007). Functional organization of the medial frontal cortex. Current Opinion of Neurobiology, 17, 220–227.
Sá, F., Pinto, P., Cunha, C., Lemos, R., Letra, L., Simões, M., et al. (2012). Differences between early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in neuropsychological tests. Frontiers in Neurology, 14, 81.
Shimizu, S., Kanetake, H., Hirose, D., Sakurai, H., & Hanyu, H. (2015). Differential effects of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on clinical responses and cerebral blod flow changes in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a 12-month, randomized, and open-label trial. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders Extra, 5, 135–146.
Stefanova, E., Wall, A., Almkvist, O., Nilsson, A., Forsberg, A., Långström, B., et al. (2006). Longitudinal PET evaluation of cerebral glucose metabolism in rivastigmine treated patients with mild Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neural Transmission, 113, 205–218.
Takahashi, M., Oda, Y., Okubo, T., & Shirayama, Y. (2017). Relationships between cognitive impairment on ADAS-cog and regional cerebral blood flow using SPECT in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neural Transmission, 124, 1109–1121.
Tateno, M., Kobayashi, S., Utsumi, K., Morii, H., & Fujii, K. (2008). Quantitative analysis of the effects of donepezil on regional cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease by using an automated program, 3DSRT. Neuroradiology, 50, 723–727.
Ushijima, Y., Okuyama, C., Mori, S., Kubota, T., Nakai, T., & Nishimura, T. (2006). Regional cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease: comparison between short and long-term donepezil therapy. Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 20, 425–429.
Verma, N., Beretvas, S. N., Pascual, B., Masdeu, J. C., & Markey, M. K. (2015). New scoring methodology improves the sensitivity of the Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) in clinical trials. Alzheimers Research & Therapy, 7, 64.
Waldemar, G., Bruhn, P., Kristensen, M., Johnson, A., Paulson, O. B., & Lassen, N. A. (1994). Heterogeneity of neocortical cerebral blood flow deficits in dementia of the Alzheimer type: a [99Tc]-d,l-HMPAO SPECT study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 57, 285–295.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Shirayama has received research support from Eli Lilly, Eisai, MSD, Pfizer, Takeda and Mitsubishi-Tanabe. Dr. Iyo has received consultant fees from Eli Lilly, Sumitomo, Dainippon, Pfizer and Abbott.
Drs. Takahashi, Oda, Yoshino and Sato have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ehical standards of the institutional research committee and with 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the ehics committee of Teikyo University Chiba Medical Center.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shirayama, Y., Takahashi, M., Oda, Y. et al. rCBF and cognitive impairment changes assessed by SPECT and ADAS-cog in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease after 18 months of treatment with the cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil or galantamine. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 75–86 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9803-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9803-y