Abstract
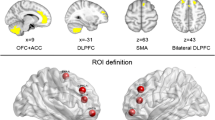
Behavioral studies have demonstrated visual attention bias and working memory deficits in individuals with internet gaming disorder (IGD). Neuroimaging studies demonstrated that individuals with IGD presented abnormalities in brain structures and functions including resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) disturbance. However, most previous studies investigated IGD-related rsFC alterations by using hypothesis-driven methods with priori selection of a region of interest, which cannot provide a full picture of the rsFC changes in IGD individuals. In this study, we recruited 27 male IGD adolescents and 35 demographically matched healthy controls (HCs) to investigate abnormal connective property of each voxel within whole brain of IGD adolescents using resting-state functional connectivity density (rsFCD) method, and further to evaluate the relationship between altered rsFCD and behavioral performances of visual attention and working memory. The results exhibited no significant intergroup difference in behavioral performance (visual working memory and attention). The IGD adolescents exhibited higher global/long-range rsFCD in the bilateral dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and the right inferior temporal cortex (ITC)/fusiform compared with the HCs. Although no significant correlation survived after Bonferroni correction, higher global/long-range rsFCD of the bilateral DLPFC was correlated with the Young’s internet addiction test (IAT) score and/or behavioral performance in IGD adolescents using an uncorrected threshold of P < 0.05. In conclusion, IGD adolescents demonstrated increased rsFCD in the brain regions involved in working memory, spatial orientation and attention processing, which indicated that increased rsFCD may reflect a compensatory mechanism for maintaining the normal behavioral performance in IGD adolescents compared with the HCs.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.007.
Bembich, S., Clarici, A., Vecchiet, C., Baldassi, G., Cont, G., & Demarini, S. (2014). Differences in time course activation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex associated with low or high risk choices in a gambling task. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 8, 464. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00464.
Beucke, J. C., Sepulcre, J., Talukdar, T., Linnman, C., Zschenderlein, K., Endrass, T., et al. (2013). Abnormally high degree connectivity of the orbitofrontal cortex in obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(6), 619–629. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.173.
Bharat Biswal, F. Z. Y., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using Echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34, 537–541.
Bolla, K. I., Eldreth, D. A., London, E. D., Kiehl, K. A., Mouratidis, M., Contoreggi, C., et al. (2003). Orbitofrontal cortex dysfunction in abstinent cocaine abusers performing a decision-making task. NeuroImage, 19(3), 1085–1094.
Carter, R. M., O'Doherty, J. P., Seymour, B., Koch, C., & Dolan, R. J. (2006). Contingency awareness in human aversive conditioning involves the middle frontal gyrus. NeuroImage, 29(3), 1007–1012. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.09.011.
Chang, C., Crottaz-Herbette, S., & Menon, V. (2007). Temporal dynamics of basal ganglia response and connectivity during verbal working memory. NeuroImage, 34(3), 1253–1269. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.056.
Charroud, C., Steffener, J., Le Bars, E., Deverdun, J., Bonafe, A., Abdennour, M., et al. (2015). Working memory activation of neural networks in the elderly as a function of information processing phase and task complexity. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 125, 211–223. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2015.10.002.
Ding, W. N., Sun, J. H., Sun, Y. W., Zhou, Y., Li, L., Xu, J. R., et al. (2013). Altered default network resting-state functional connectivity in adolescents with internet gaming addiction. PloS One, 8(3), e59902. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059902.
Dong, G., Zhou, H., & Zhao, X. (2010). Impulse inhibition in people with internet addiction disorder: electrophysiological evidence from a go/NoGo study. Neuroscience Letters, 485(2), 138–142. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.002.
Dong, G., Huang, J., & Du, X. (2012). Alterations in regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in internet gaming addicts. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 8, 41. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-8-41.
Dong, G., Shen, Y., Huang, J., & Du, X. (2013). Impaired error-monitoring function in people with internet addiction disorder: an event-related fMRI study. European Addiction Research, 19(5), 269–275. doi:10.1159/000346783.
Dong, G., Lin, X., Zhou, H., & Lu, Q. (2014). Cognitive flexibility in internet addicts: fMRI evidence from difficult-to-easy and easy-to-difficult switching situations. Addictive Behaviors, 39(3), 677–683. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.11.028.
Dong, G., Lin, X., Hu, Y., Xie, C., & Du, X. (2015a). Imbalanced functional link between executive control network and reward network explain the online-game seeking behaviors in internet gaming disorder. Scientific Reports, 5, 9197. doi:10.1038/srep09197.
Dong, G., Lin, X., & Potenza, M. N. (2015b). Decreased functional connectivity in an executive control network is related to impaired executive function in internet gaming disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 57, 76–85. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.10.012.
du Boisgueheneuc, F., Levy, R., Volle, E., Seassau, M., Duffau, H., Kinkingnehun, S., et al. (2006). Functions of the left superior frontal gyrus in humans: a lesion study. Brain, 129(Pt 12), 3315–3328. doi:10.1093/brain/awl244.
Feil, J., Sheppard, D., Fitzgerald, P. B., Yucel, M., Lubman, D. I., & Bradshaw, J. L. (2010). Addiction, compulsive drug seeking, and the role of frontostriatal mechanisms in regulating inhibitory control. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(2), 248–275. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.03.001.
Femandes-serrrano, M. J., P.-g., M., & Verdejo-Garcia, A. (2011). What are the specific versus generalized effects of drugs of abuse on neuropsychological performance? Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35, 30.
Feng, Q., Chen, X., Sun, J., Zhou, Y., Sun, Y., Ding, W., et al. (2013). Voxel-level comparison of arterial spin-labeled perfusion magnetic resonance imaging in adolescents with internet gaming addiction. Behavioral and Brain Functions, 9(1), 33. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-9-33.
Goldstein, R. Z., & Volkow, N. D. (2011). Dysfunction of the prefrontal cortex in addiction: neuroimaging findings and clinical implications. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 12(11), 652–669. doi:10.1038/nrn3119.
Han, J. W., Han, D. H., Bolo, N., Kim, B., Kim, B. N., & Renshaw, P. F. (2015). Differences in functional connectivity between alcohol dependence and internet gaming disorder. Addictive Behaviors, 41, 12–19. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.09.006.
Hong, S. B., Zalesky, A., Cocchi, L., Fornito, A., Choi, E. J., Kim, H. H., et al. (2013). Decreased functional brain connectivity in adolescents with internet addiction. PloS One, 8(2), e57831. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057831.
Hong, S. B., Harrison, B. J., Dandash, O., Choi, E. J., Kim, S. C., Kim, H. H., et al. (2015). A selective involvement of putamen functional connectivity in youth with internet gaming disorder. Brain Research, 1602, 85–95. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.042.
Japee, S., Holiday, K., Satyshur, M. D., Mukai, I., & Ungerleider, L. G. (2015). A role of right middle frontal gyrus in reorienting of attention: a case study. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 9, 23. doi:10.3389/fnsys.2015.00023.
Jin Fan, B. D. M., Sommer, T., Raz, A., & Posner, M. I. (2002). Testing the efficiency and independence of attentional networks. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 14(3), 8.
Jin, C., Zhang, T., Cai, C., Bi, Y., Li, Y., Yu, D., et al. (2015). Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior. doi:10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8.
Jun., L. (2010). Increased regional homogeneity in internet addiction disorder: a resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Chinese Medical Journal. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0366-6999.2010.14.014.
Ko, C. H., Yen, J. Y., Chen, C. S., Yeh, Y. C., & Yen, C. F. (2009). Predictive values of psychiatric symptoms for internet addiction in adolescents: a 2-year prospective study. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 163(10), 937–943. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2009.159.
Ko, C. H., Hsieh, T. J., Wang, P. W., Lin, W. C., Yen, C. F., Chen, C. S., et al. (2015). Altered gray matter density and disrupted functional connectivity of the amygdala in adults with internet gaming disorder. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 57, 185–192. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.11.003.
Kravitz, D. J., Saleem, K. S., Baker, C. I., Ungerleider, L. G., & Mishkin, M. (2013). The ventral visual pathway: an expanded neural framework for the processing of object quality. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17(1), 26–49. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2012.10.011.
Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2012). Internet and gaming addiction: a systematic literature review of neuroimaging studies. Brain Sciences, 2(3), 347–374. doi:10.3390/brainsci2030347.
Li, B., Friston, K. J., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Zhang, G., Cao, F., et al. (2014). Impaired frontal-basal ganglia connectivity in adolescents with internet addiction. Scientific Reports, 4, 5027. doi:10.1038/srep05027.
Lin, F., Zhou, Y., Du, Y., Zhao, Z., Qin, L., Xu, J., et al. (2015). Aberrant corticostriatal functional circuits in adolescents with internet addiction disorder. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 356. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2015.00356.
Liu, G. C., Yen, J. Y., Chen, C. Y., Yen, C. F., Chen, C. S., Lin, W. C., et al. (2014). Brain activation for response inhibition under gaming cue distraction in internet gaming disorder. The Kaohsiung Journal of Medical Sciences, 30(1), 43–51. doi:10.1016/j.kjms.2013.08.005.
Steven J. Luck, E. K. V. (1997). Thecapacityofvisualworking memoryfor featuresand conjunctions. Nature, 390(20), 3.
Luna, B., Minshew, N. J., Garver, K. E., Lazar, N. A., Thulborn, K. R., Eddy, W. F., et al. (2002). Neocortical system abnormalities in autism: an fMRI study of spatial working memory. Neurology, 59(6), 834–840.
McClernon, F. J., Froeliger, B., Rose, J. E., Kozink, R. V., Addicott, M. A., Sweitzer, M. M., et al. (2016). The effects of nicotine and non-nicotine smoking factors on working memory and associated brain function. Addiction Biology, 21(4), 954–961. doi:10.1111/adb.12253.
McNab, F., & Klingberg, T. (2008). Prefrontal cortex and basal ganglia control access to working memory. Nature Neuroscience, 11(1), 103–107. doi:10.1038/nn2024.
Patricia Gómez Salgado, A. R. B., Tobío, T. B., Mallou, J. V., & Couto, C. B. (2014). Evaluation and early detection of problematic internet use in adolescents. Psicothema, 26(1), 6. doi:10.7334/psicothema2013,109.
Qin, W., Xuan, Y., Liu, Y., Jiang, T., & Yu, C. (2015). Functional connectivity density in congenitally and late blind subjects. Cerebral Cortex, 25(9), 2507–2516. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhu051.
Schilling, C., Kuhn, S., Paus, T., Romanowski, A., Banaschewski, T., Barbot, A., et al. (2013). Cortical thickness of superior frontal cortex predicts impulsiveness and perceptual reasoning in adolescence. Molecular Psychiatry, 18(5), 624–630. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.56.
Song, J., Park, J. H., Han, D. H., Roh, S., Son, J. H., Choi, T. Y., et al. (2016). A comparative study of the effects of bupropion and escitalopram on internet gaming disorder. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. doi:10.1111/pcn.12429.
Tao, R., Huang, X., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y., & Li, M. (2010). Proposed diagnostic criteria for internet addiction. Addiction, 105(3), 556–564. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02828.x.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2010a). Functional connectivity density mapping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(21), 9885–9890. doi:10.1073/pnas.1001414107.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2010b). Ultrafast method for mapping local functional connectivity hubs in the human brain. 4274–4277, doi:10.1109/iembs.2010.5626180.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2011a). Association between functional connectivity hubs and brain networks. Cerebral Cortex, 21(9), 2003–2013. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq268.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2011b). Functional connectivity hubs in the human brain. NeuroImage, 57(3), 908–917. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.05.024.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2014). Mapping small-world properties through development in the human brain: disruption in schizophrenia. PloS One, 9(4), e96176. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096176.
Ungerleider, L. G., Courtney, S. M., & Haxby, J. V. (1998). A neural system for human visual working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95(3), 883–890.
Vuontela, V., Jiang, P., Tokariev, M., Savolainen, P., Ma, Y., Aronen, E. T., et al. (2013). Regulation of brain activity in the fusiform face and parahippocampal place areas in 7-11-year-old children. Brain and Cognition, 81(2), 203–214. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2012.11.003.
Wang, T., Li, Q., Guo, M., Peng, Y., Li, Q., Qin, W., et al. (2014). Abnormal functional connectivity density in children with anisometropic amblyopia at resting-state. Brain Research, 1563, 41–51. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.03.015.
Wang, Y., Yin, Y., Sun, Y. W., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., Ding, W. N., et al. (2015). Decreased prefrontal lobe interhemispheric functional connectivity in adolescents with internet gaming disorder: a primary study using resting-state FMRI. PloS One, 10(3), e0118733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0118733.
Wee, C. Y., Zhao, Z., Yap, P. T., Wu, G., Shi, F., Price, T., et al. (2014). Disrupted brain functional network in internet addiction disorder: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PloS One, 9(9), e107306. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107306.
Yen, J. Y., Ko, C. H., Yen, C. F., Wu, H. Y., & Yang, M. J. (2007). The comorbid psychiatric symptoms of internet addiction: attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, social phobia, and hostility. The Journal of Adolescent Health, 41(1), 93–98. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.02.002.
Young, K. S. (1998). Internet addiction: the emergence of a new clinical disorder. CyberPsychology and Behavior, 1(3), 8.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Wang, G., Zeng, F., Zhao, L., Yang, X., et al. (2011). Microstructure abnormalities in adolescents with internet addiction disorder. PloS One, 6(6), e20708. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020708.
Yuan, K., Qin, W., Yu, D., Bi, Y., Xing, L., Jin, C., et al. (2015). Core brain networks interactions and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder individuals in late adolescence/early adulthood. Brain Structure & Function. doi:10.1007/s00429-014-0982-7.
Zhang, Y., Du, G., Yang, Y., Qin, W., Li, X., & Zhang, Q. (2015a). Higher integrity of the motor and visual pathways in long-term video game players. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 9, 98. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2015.00098.
Zhang, B., Li, M., Qin, W., Demenescu, L. R., Metzger, C. D., Bogerts, B., et al. (2015b). Altered functional connectivity density in major depressive disorder at rest. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. doi:10.1007/s00406-015-0614-0.
Zhang, J. T., Yao, Y. W., Li, C. S., Zang, Y. F., Shen, Z. J., Liu, L., et al. (2015c). Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the insula in young adults with internet gaming disorder. Addiction Biology. doi:10.1111/adb.12247.
Zhang, Y., Lin, X., Zhou, H., Xu, J., Du, X., & Dong, G. (2016). Brain activity toward gaming-related cues in internet gaming disorder during an addiction Stroop task. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 714. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00714.
Zhou, Z., Li, C., & Zhu, H. (2013). An error-related negativity potential investigation of response monitoring function in individuals with internet addiction disorder. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 7, 131. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00131.
Zhou, Z., Zhu, H., Li, C., & Wang, J. (2014). Internet addictive individuals share impulsivity and executive dysfunction with alcohol-dependent patients. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 288. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00288.
Zhou, Z., Zhou, H., & Zhu, H. (2016). Working memory, executive function and impulsivity in internet-addictive disorders: a comparison with pathological gambling. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 28(2), 92–100. doi:10.1017/neu.2015.54.
Zhuo, C., Zhu, J., Qin, W., Qu, H., Ma, X., Tian, H., et al. (2014). Functional connectivity density alterations in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 8, 404. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00404.
Zikopoulos, B., & Barbas, H. (2006). Prefrontal projections to the thalamic reticular nucleus form a unique circuit for attentional mechanisms. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26(28), 7348–7361. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5511-05.2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have reported no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The protocol of this study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital, and all of the participants and their guardians provided written informed consent according to institutional guidelines.
Additional information
Xin Du and Yongxin Yang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, X., Yang, Y., Gao, P. et al. Compensatory increase of functional connectivity density in adolescents with internet gaming disorder. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1901–1909 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9655-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9655-x