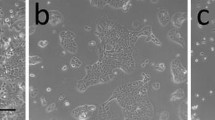
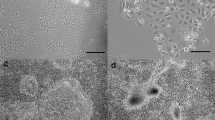
Summary
The ability of the murine mammary fat pad to directly stimulate the growth of mammary epithelial cells and to modulate the effects of various mammogenic agents has been investigated in a newly described, hormone- and serum-free coculture system. COMMA-1D mouse mammary epithelial cells were cultured for 5 or 7 d with various supplements in the absence or presence of epithelium-free mammary fat pad explants from virgin female BALB/c mice. Cocultured fat pad stimulated increases in the DNA content of COMMA-1D cultures by two- to threefold or six-to eightfold after 5 or 7 d, respectively. The mitogenic effect was additive to that of 10% fetal calf serum and could not be attributed to the release of prostaglandin E2 or synthesis of prostaglandins by epithelial cells. In addition, bovine serum albumin attenuated (P<0.05) the mitogenic effect of cocultured mammary fat pad. Added alone, insulinlike growth factor-I, epidermal growth factor, and insulin increased (P<0.05) total DNA of COMMA-1D cultures by 2.5-, 3.7-, and 2.3-fold, respectively. Cocultured mammary fat pad markedly interacted (P<0.01) with these mitogens to yield final DNA values that were 21.2-, 13.3-, and 22.1-fold greater than in basal medium only. Associated with this proliferation was the formation of numerous domes above the COMMA-1D monolayer. There was no proliferative response to growth hormone or prolactin in the absence or presence of cocultured fat pad (P>0.05). Whereas hydrocortisone did not alter cell number, it attenuated (P<0.05) the mitogenic effect of cocultured mammary fat pad. These results indicate that the murine mammary fat pad is not only a direct source of mitogenic activity, but also modulates the response of mammary epithelial cells to certain mammogens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandyopadhyay, G. K.; Hwang, S.-I.; Imagawa, W., et al. Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids as signal transducers: amplification of signals from growth factor receptors by fatty acids in mammary epithelial cells. Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Essent. Fatty Acids 48:71–78; 1993.
Bandyopadhyay, G. K.; Imagawa, W.; Wallace, D. R., et al. Linoleate metabolites enhance the in vitro proliferative response of mouse mammary epithelial cells to epidermal growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 262:2750–2756; 1987.
Bandyopadhyay, G. K.; Imagawa, W.; Wallace, D. R., et al. Proliferative effects of insulin and epidermal growth factor on mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Enhancement by hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids and synergism with prostaglandin E2. J. Biol. Chem. 263:7567–7573; 1988.
Beck, J. C.; Hosick, H. L. Growth of mouse mammary epithelium in response to serum-free media conditioned by mammary adipose tissue. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 12:85–97; 1988.
Beck, J. C.; Hosick, H. L.; Watkins, B. A. Growth of epithelium from a preneoplastic mammary outgrowth in response to mammary adipose tissue. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:409–418; 1989.
Carrington, C. A.; Hosick, H. L. Effects of dietary fat on the growth of normal, preneoplastic and neoplastic mammary epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 75:269–278; 1985.
Chakravorti, S.; Sheffield, L. G. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor mRNA and protein in mouse mammary glands. Endocrine 4:175–182; 1996.
Coleman, S.; Silberstein, G. B.; Daniel, C. W. Ductal morphogenesis in the mouse mammary gland: evidence supporting a role for epidermal growth factor. Dev. Biol. 127:304–315; 1988.
Danielson, K. G.; Oborn, C. J.; Durban, E. M., et al. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and functional differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3756–3760; 1984.
DeOme, K. B.; Faulkin, L. J., Jr.; Bern, H. A., et al. Development of mammary tumors from hyperplastic alveolar nodules transplanted into gland-free mammary fat pads of female C3H mice. Cancer Res. 19:515–520; 1959.
Dickson, R. B.; Lippman, M. E. Growth factors in breast cancer. Endocr. Rev. 16:559–589; 1995.
Eisenstein, R. S.; Rosen, J. M. Both cell substratum regulation and hormonal regulation of milk protein gene expression are exerted primarily at the posttranscriptional level. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:3183–3190; 1988.
Eling, T. E.; Glasgow, W. C. Cellular proliferation and lipid metabolism: importance of lipoxygenases in modulating epidermal growth factor-dependent mitogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 13:397–410; 1994.
Enami, J.; Enami, S.; Kawamura, K., et al. Growth of normal and neoplastic mammary epithelial cells of the mouse by mammary fibroblast-conditioned medium factor. In: Enami, J.; Ham, R. G., eds. Growth and differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in culture. Tokyo: Japan Scientific Societies Press; 1987:125–153.
Finch, P. W.; Cunha, G. R.; Rubin, J. S., et al. Pattern of keratinocyte growth factor and keratinocyte growth factor receptor expression during mouse fetal development suggests a role in mediating morphogenetic mesenchymal-epithelial interactions. Dev. Dyn. 203:223–240; 1995.
Haslam, S. Z. Mammary fibroblast influence on normal mouse mammary epithelial cells responses to estrogen in vitro. Cancer Res. 46:310–316; 1986.
Hoshino, K. Mammary transplantation and its histogenesis in mice. In: Yokoyama, A.; Mizuno, H.; Nagasawa, H., eds. Physiology of mammary glands. Tokyo: Japan Scientific Societies Press; 1978:163–228.
Imagawa, W.; Cunha, G. R.; Young, P., et al. Keratinocyte growth factor and acidic fibroblast growth factor are mitogens for primary cultures of mammary epithelium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 204:1165–1169; 1994a.
Imagawa, W.; Spencer, E. M.; Larson, L., et al. Somatomedin-C substitutes for insulin for the growth of mammary epithelial cells from normal virgin mice in serum-free collagen gel cell culture. Endocrinology 119:2695–2699; 1986a.
Imagawa, W.; Tomooka, Y.; Nandi, S. Serum-free growth of normal and tumor mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:4074–4077; 1982.
Imagawa, W.; Yang, J.; Guzman, R., et al. Control of mammary gland development. In: Knobil, E.; Neill, J. D., eds. The physiology of reproduction. 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press; 1994b:1033–1063.
Ip, M. M.; Darcy, K. M. Three-dimensional mammary primary culture model systems. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 1:91–110; 1996.
Keely, P. J.; Wu, J. E.; Santoro, S. A. The spatial and temporal expression of the α2β1 integrin and its ligands, collagen I, collagen IV, and laminin, suggest important roles in mouse mammary morphogenesis. Differentiation 59:1–13; 1995.
Kidwell, W. R.; Monaco, M. E.; Wicha, M. S., et al. Unsaturated fatty acid requirements for growth and survival of a rat mammary tumor cell line. Cancer Res. 38:4091–4100; 1978.
Labarca, C.; Paigen, K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal. Biochem. 102:344–352; 1980.
Levay-Young, B. K.; Bandyopadhyay, G. K.; Nandi, S. Linoleic acid, but not cortisol, stimulates accumulation of casein by mouse mammary epithelial cells in serum-free collagen gel culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:8448–8452; 1987.
Levine, J. F.; Stockdale, F. E. 3T3-L1 adipocytes promote the growth of mammary epithelium. Exp. Cell Res. 151:112–122; 1984.
Nilausen, K. Role of fatty acids in growth-promoting effect of serum albumin on hamster cells in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 96:1–14; 1978.
Nolan, R. D.; Danilowicz, R. M.; Eling, T. E. Role of arachidonic acid metabolism in the mitogenic response of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts to epidermal growth factor. Mol. Pharmacol. 33:650–656; 1988.
Pessin, J. E. Transmembrane signaling properties of the insulin and IGF-I tyrosine kinase receptors. In: Baxter, R. C.; Gluckman, P. D.; Rosenfeld, R. G., eds. The insulin-like growth factors and their regulatory proteins. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier Science Publishers; 1994:87–94.
Plaut, K.; Ikeda, M.; Vonderhaar, B. K. Role of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor-I in mammary development. Endocrinology 133:1843–1848; 1993.
Rahimi, N.; Saulnier, R.; Nakamura, T., et al. Role of hepatocyte growth factor in breast cancer: a novel mitogenic factor secreted by adipocytes. DNA Cell Biol. 13:1189–1197; 1994.
Riss, T. L.; Sirbasku, D. A. Growth and continuous passage of COMMA-D mouse mammary epithelial cells in hormonally-defined serum-free medium. Cancer Res. 47:3776–3782; 1987.
Ruan, W.; Catanese, V.; Wieczorek, R., et al. Estradiol enhances the stimulatory effect of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) on mammary development and growth hormone-induced IGF-I messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology 136:1296–1302; 1995.
Rudland, P. S.; Twiston Davies, A. C.; Tsao, S.-W. Rat mammary preadipocytes in culture produce a trophic agent for mammary epithelia-prostaglandin E2. J. Cell. Physiol. 120:364–376; 1984.
Salomon, D. S.; Liotta, L. A.; Kidwell, W. R. Differential response to growth factor by rat mammary epithelium plated on different collagen substrata in serum-free medium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:382–386; 1981.
SAS system, version 6.1 The SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC; 1994.
Sasaki, M.; Nishio, M.; Sasaki, T., et al. Identification of mouse mammary fibroblast-derived mammary growth factor as hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199:772–779; 1994.
Shyamala, G.; Ferenczy, A. Mammary fat pad may be a potential site for initiation of estrogen action in normal mouse mammary glands. Endocrinology 115:1078–1081; 1984.
Singer, C.; Rasmussen, A.; Smith, H. S., et al. Malignant breast epithelium selects for insulin-like growth factor II expression in breast stroma: evidence for paracrine function. Cancer Res. 55:2448–2454; 1995.
Snedeker, S. M.; Brown, C. F.; DiAugustine, R. P. Expression and functional properties of transforming growth factor α and epidermal growth factor during mouse mammary gland ductal morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:276–280; 1991.
Spector, A. A. Structure and lipid binding properties of serum albumin. Methods Enzymol. 128:320–339; 1986.
Sylvester, P. W.; Birkenfeld, H. P.; Hosick, H. L., et al. Fatty acid modulation of epidermal growth factor-induced mouse mammary epithelial cell proliferation in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 214:145–153; 1994.
Topper, Y. J.; Freeman, C. S. Multiple hormone interactions in the developmental biology of the mammary gland. Physiol. Rev. 60:1049–1106; 1980.
Topper, Y. J.; Oka, T.; Vonderhaar, B. K. Techniques for studying development of normal mammary epithelial cells in organ culture. Methods Enzymol. 39:443–454; 1975.
Ulich, T. R.; Yi, E. S.; Cardiff, R., et al. Keratinocyte growth factor is a growth factor for mammary epithelium in vivo: the mammary epithelium of lactating rats is resistant to the proliferative action of keratinocyte growth factor. Am. J. Pathol. 144:862–868; 1994.
Wang, S.; Haslam, S. Z. Serum-free primary culture of normal mouse mammary epithelial and stromal cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30A:859–866; 1994.
Weber-Hall, S. J.; Phippard, D. J.; Niemeyer, C. C., et al. Developmental and hormonal regulation of Wnt gene expression in the mouse mammary gland. Differentiation 57:205–214; 1994.
Wicha, M. S.; Liotta, L. A.; Kidwell, W. R. Effects of free fatty acids on the growth of normal and neoplastic rat mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 39:426–435; 1979.
Wilson, S. E.; Weng, J.; Chwang, E. L., et al. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), keratinocyte growth factor (KGF), and their receptors in human breast cells and tissues: alternative receptors. Cell & Mol. Biol. Res. 40:337–350; 1994.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Guzman, R., et al. Sustained growth in primary culture of normal mammary epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:2088–2092; 1980.
Zor, U.; Her, E.; Harell, T., et al. Arachidonic acid release by basophilic leukemia cells and macrophages stimulated by Ca2+ ionophores, antigen and diacylglycerol: essential role for protein kinase C and prevention by glucocorticosteroids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1091:385–392; 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hovey, R.C., MacKenzie, D.D.S. & McFadden, T.B. The proliferation of mouse mammary epithelial cells in response to specific mitogens is modulated by the mammary fat pad in vitro . In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 34, 385–392 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-998-0020-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-998-0020-2