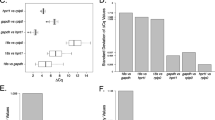
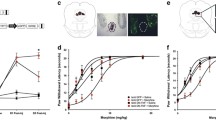
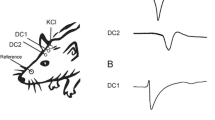
Abstract
Opioids significantly alter functional responses of lymphocytes following activation. The opiate Morphine, alters the Th1 to Th2 response and modulates functional responses such as cytolytic activity and T-cell proliferation. Although there has been extensive research involving morphine’s effects on lymphocytes, little is known about the effects morphine has on lymphocyte trafficking. The objective of the study was to use in vivo bioluminescent imaging to determine morphine’s effect on the trafficking pattern of splenocytes systemically and into the CNS either in a naïve state or following a neuroinflammatory stimulus. A neuroinflammatory response was induced by intracerebrally administering a DNA IFN-γ DNA plasmid into morphine-dependent or placebo wildtype mice. Mice with or without a neurostimulus received adoptively transferred firefly luciferase transgenic splenocytes and imaged. Morphine dependence significantly altered the inherent ability of splenocytes to traffic into the spleen, and lead to non-directed chaotic trafficking throughout the animal, including into the CNS. The morphine-mediated effects on trafficking were blocked by the antagonist naltrexone. Morphine dependence intensified splenocyte infiltration into the CNS following neuroinflammation induced by IFN-γ gene transfer. The study precented determined that morphine severely altered the ability of non-activated splenocytes to home to the spleen, inducing extrasplenic trafficking thoughout the animal. In addition to altering the ability of naive splenocyte to traffic to the spleen, this study demonstrated that morphine profoundly exacerbated lymphocyte infiltration into the CNS following a neurostimulus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benard A, Cavailles P, Boue J, Chapey E, Bayry J, Blanpied C, Meyer N, Lamant L, Kaveri S, Brousset P, Dietrich N (2010) μ-Opioid Receptor is induced by IL-13 within lymph nodes from patients with Sézary Syndrome. J Invest Dermatol 433:1–8
Borner C, Kraus J, Bedini A et al (2008) T-cell receptor/CD28-mediated activation of human T lymphocytes induces expression of functional mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol 74:496–504
Bryant HU, Bernton EW, Kenner JR, Holaday JW (1991) Role of adrenal cortical activation in the immunosuppressive effects of chronic morphine treatment. Endocrinology 128:3253–3258
Carriters MD, Visintin I, Viret C, Janeway CA (2002) Role of genetic back ground in P selection-dependent immune surveillance of the central nervous system. J Neuroimmunol 129:51–57
Chen Y, Mestek A, Liu J, Yu L (1993) Molecular cloning of a rat opioid receptor reveals sequence similar to the μ and opioid receptors. Biochem J 295:625–632
Donahoe R, Falck A (1990) Neuroimmunodulation by opiates and other drugs of abuse: relationship to HIV infection and AIDS. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 44:145–158
Eisenstein TK, Hilburger ME (1998) Opioid modulation of immune responses: effects on phagocyte and lymphoid cell populations. J Neuroimmunol 83:36–44
Flores LR, Wahl SM, Bayer BM (1995) Mechanisms of morphine-induced immunosuppression: effect of acute morphine administration on lymphocyte trafficking. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 3:1246–1251
Friedman H, Eisenstein TK (2004) Neurological basis of drug dependence and its effects on the immune system. J Neuroimmunol 147:106–108
Friedman H, Newton C, Klein TW (2003) Microbial infections, immunomodulation, and drugs of abuse. Clin Microbiol Rev 16:209–219
Gavériaux-Ruff C, Matthes HWD, Peluso J et al (1998) Abolition of morphine-immunosuppression in mice lacking the μ-opioid receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6326–6330
Gomez-Flores R, Weber RJ (1999) Inhibition of interleukin-2 production and down regulation of IL-2 and transferrin receptors on rat splenic lymphocytes following PAG morphine administration: a role in natural killer and T cell suppression. J Interferon Cytokine Res 6:625–630
Heagy W, Laurance M, Cohen E, Finberg R (1990) Neurohormones regulate T cell function. J Exp Med 171:1625–1633
Hickey WF (1999) Leukocyte traffic in the central nervous system: the participants and their roles. Semin Immunol 11:125–137
Hickey WF, Kimura H (1988) Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen. Science 239:290–292
Hickey WF, Hsu BL, Kimura H (1991) T Lymphocyte entry into the central nervous system. J Neurosci Res 28:254–260
Hilburger M, Adler M, Truant A, Meissler J, Satishchandran V, Rogers T, Eisenstein TK (1997) Morphine induces sepsis in mice. J Infect Dis 176:183–188
Jaume M, Laffont S, Chapey E et al (2007) Opioid receptor blockade increases the number of lymphocytes without altering T cell response in draining lymph nodes in vivo. J Neuroimmunol 188:95–102
Jordan CA, Watkins BA, Kufta C, Dubois-Dalcq M (1991) Infection of brain microglial cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is CD4 dependent. J Virol 65:736–742
Kraus J, Borner C, Giannini E et al (2001) Regulation of mu-opioid receptor gene transcription by interleukin-4 and influence of an allelic variation within a STAT6 transcription factor binding site. J Biol Chem 276:43901–43908
Lassmann H, Schmied M, Vass K, Hickey WF (1993) Bone marrow derived elements and resident microglia in brain inflammation. Glia 7:19–24
Li S, Zhu J, Chen C, Chen YW, Deriel JK, Ashby B, Liu-Chen LY (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of a rat opioid receptor. Biochem J 295:629–634
Mace G, Jaume M, Blanpied C et al (2002) Anti-mu-opioid-receptor IgG antibodies are commonly present in serum from healthy blood donors: evidence for a role in apoptotic immune cell death. Blood 100:3261–3268
Madden JJ, Whaley WL, Ketelsen D et al (2001) The morphine-binding site on human activated T-cells is not related to the mu opioid receptor. Drug Alcohol Depend 62:131–139
Nguyen K, Miller BC (2002) CD28 costimulation induces delta opioid receptor expression during anti-CD3 activation of T cells. J Immunol 168:4440–4445
Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J (1991) Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 108:193–199
Ohlfest JR, Lobitz PD, Perkinson SG, Largaespada DA (2004) Integration and long-term expression in xenografted human glioblastoma cells using a plasmid-based transposon system. Mol Ther 10:260–268
Ohlfest JR, Demorest ZL, Motooka Y, Vengco I, Oh S, Chen E, Scappaticci FA, Saplis RJ, Ekker SC, Low WC, Freese AB, Largaespada DA (2005) Combinatorial antiangiogenic gene therapy by nonviral gene transfer using the sleeping beauty transposon causes tumor regression and improves survival in mice bearing intracranial human glioblastoma. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther 12:778–788
Olin MR, Choi K, Lee J, Molitor TW (2004) gd T-lymphocytes cytolytic activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis analyzed by flow cytometry. J Immunol Meth 297:1–11
Olin MR, Choi K, Lee J, Peterson PK, Molitor TW (2007) Morphine modulates gammadelta lymphocytes cytolytic activity following BCG vaccination. Brain Behav Immun 21:195–201
Philippe D, Dubuquoy L, Groux H et al (2003) Anti-inflammatory properties of the mu-opioid receptor support its use in the treatment of colon inflammation. J Clin Invest 111:1329–1338
Rauch D, Gross S, Harding J, Bokhari S, Niewiesk S, Lairmore M, Plwnica-Worms D, Ratner L (2009) T-cell activation promotes tumorigenesis in inflammation-associated cancer. Retrovirology 6:116–126
Roy S, Ge BL, Ramakrishnan S, Lee NM, Loh HH (1991) 3H]morphine binding is enhanced by IL-1-stimulated thymocyte proliferation. FEBS Lett 287(1–2):93–96
Roy S, Cain KJ, Charboneau RG, Barke RA (1999) Morphine accelerates the progression of sepsis in an experimental sepsis model. Adv Exp Med Biol 437:21–31
Roy S, Wang JH, Sumandeep G, Charboneau RG, Loh HH, Barke RA (2004) Chronic Morphine treatment differentiates T helper cells to Th2 effector cells by modulating transcription factors GATA 3 and T bet. J Neuroimmunol 147:78–81
Roy S, Wang J, Charboneau R, Loh HH, Barke RA (2005) Morphine induces CD4+ T cell IL-4 expression through an adenylyl cyclase mechanism independent of the protein kinase A pathway. J Immunol 175:6361–6367
Shacklett BL, Cox CA, Wilkens DT, Karl Karlsson R, Nilsson A, Nixon DF, Price RW (2004) Increased adhesion molecule and chemokine receptor expression on CD8+ T cells trafficking to cerebrospinal fluid in HIV-1 infection. J Infect Dis 189:2202–2212
Shavit Y, Lewis J, Terman G et al (1984) Opioid peptides mediate the suppressive effect of stress on natural killer cell cytotoxicity. Science 223:188–190
Svenningsson A, Anderson O, Edsbagge M, Stemme S (1995) Lymphocyte phenotype and subset distribution in normal cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 63:39–46
Sweeney TJ, Mailander V, Tucker AA, Olomu AB, Zhang W, Cao Y, Negrin RS, Contag CH (1999) Visualizing the kinetics of tumor-cell clearance in living animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:12044–12049
Szabo I, Rojavin M, Bussiere J, Eisenstein TK, Alder MW, Rogers TJ (1995) Suppression of peritoneal macrophage phagocytes of Candida albicans by opioids. J Pharmacol Expt Therap 267:703–706
Von Andrian UH, Mackay CR (2000) T-cell function and migration—two sides of the same coin. N Engl J Med 343:1020–1026
Wang JB, Johnson PS, Imai Y, Persico AM, Ozenberger BA, Eppler CM, Uhl GR (1994) cDNA cloning of an orphan opiate receptor gene family member and its splice variant. FEBS Lett 348:75–79
Wang J, Charboneau R, Barke RA et al (2002a) Mu-opioid receptor mediates chronic restraint stress-induced lymphocyte apoptosis. J Immunol 169:3630–3636
Wang J, Charboneau R, Balasubramanian S et al (2002b) The immunosuppressive effects of chronic morphine treatment are partially dependent on corticosterone and mediated by the mu-opioid receptor. J Leukoc Biol 71:782–790
Wekerle H, Fierz W (1985) T cell approach to demyelinating diseases. Springer Semin Immunopathol 8:97–110
Wiley CA, Schrier RD, Nelson JA, Lampert PW, Oldstone MBA (1986) Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7089–7093
Wu DY, Woodman SE, Weiss JM, McManus CM, D’Aversa TG, Hesselgesser J, Major EO, Nath A, Berman JW (2000) Mechanisms of leukocyte trafficking into the CNS. J Neurovirol Suppl 1:S82–85
Wu A, Oh S, Ericson K, Demorest ZL, Vengco I, Gharagozlou S, Chen W, Low WC, Ohlfest JR (2007) Transposon-based interferon gamma gene transfer overcomes limitations of episomal plasmid for immunogene therapy of glioblastoma. Canc Gene Ther 14:550–560
Yasuda K, Raynor K, Kong H, Breder CD, Takeda J, Reisine T, Bell GI (1993) Cloning and functional comparison of and opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:6736–6748
Yin D, Mufson A, Wang R et al (1999) Fas-mediated cell death promoted by opioids. Nature 397:218
Yokota T, Uehara K, Nomota Y (2000) Intrathecal morphine suppresses NK cell activity following abdominal surgery. Can J Anaesth 47:303–308
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Dr. Maxim Cheeran for his assistance in the laboratory and Dr. Ohlfest for his assistance with plasmid inoculation. Michael Olin was supported by the National Institute of Health, National Research Service Award T32 DA07097 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse, support for this study was provided by the National Institute of Health R21DA023543-01 Opiate Modulate lymphocyte Trafficking into the CNS in TB meningitis
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olin, M., Oh, S., Roy, S. et al. Morphine Induces Splenocyte Trafficking into the CNS. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7, 436–443 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9307-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9307-2