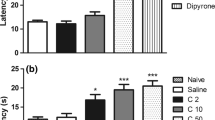
Abstract
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important nosocomial pathogen in civilian intensive care units. Recently the incidence has increased in wounded military personnel. Morphine is documented in numerous animal studies to be immunosuppressive and to sensitize to infection. The hypotheses were tested that morphine, administered for analgesia in the battlefield, predisposes to Acinetobacter infection, and that the opioid may have an additive or synergistic effect with trauma. To test these hypotheses, an intraperitoneal infection model was established in mice using several Acinetobacter strains. Morphine administered for 48 h by implantation of a slow-release morphine pellet increased mortality compared to animals receiving a placebo pellet, an effect that was blocked by the mu-opioid receptor antagonist, naltrexone. Acinetobacter burdens in the blood, spleens, livers, and lungs of morphine-treated mice, were significantly higher than those in placebo-treated animals, confirming that mortality was due to potentiated growth of the bacteria. There were also elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in morphine-treated versus placebo-treated mice. Morphine caused a reduction in the total number of cells in the peritoneal cavity, a decrease in the percentage and total numbers of neutrophils, and a decrease in the total number of macrophages. Morphine treatment also suppressed levels of the neutrophil-inducing molecules, IL-17A and KC/CXCL1. However, IL-17A−/− mice given morphine were not sensitized to Acintobacter infection to a greater degree than similarly treated wild-type mice. Trauma alone did not sensitize to Acinetobacter infection, and there was no additive effect between morphine and trauma. These results support the hypothesis that morphine potentiates Acinetobacter infection.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angele MK, Chaudry IH (2005) Surgical trauma and immunosuppression: pathophysiology and potential immunomodulatory approaches. Langenbecks Arch Surg 390:333–341
Asakura H, Kawamoto K, Igimi S, Yamamoto S, Makino S (2006) Enhancement of mice susceptibility to infection with Listeria monocytogenes by the treatment of morphine. Microbiol Immunol 50:543–547
Bernabeu-Wittel M, Pichardo C, Garcia-Curiel A, Pachon-Ibanez ME, Ibanez-Martinez J, Jimenez-Mejias ME, Pachon J (2005) Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic assessment of the in-vivo efficacy of imipenem alone or in combination with amikacin for the treatment of experimental multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia. Clin Microbiol Infect 11:319–325
Boucher HW, Talbo GH, Bradly JS, Edwards JE, Gilbert D, Rice LB, Scheld M, Spellberg B, Bartlett J (2009) Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 48:1–12
Breslow JM, Meissler JJ, Hartzell RH, Spence PB, Truant A, Gaughan J, Eisenstein TK (2011) Innate immune responses to systemic Acinetobacter baumannii infection in mice: neutrophils, but not IL-17, mediate host resistance. Infect Immun 79:3317–3327
Bryant HU, Bernton EW, Holaday JW (1988a) Morphine pellet-induced immunomodulation in mice: temporal relationships J. Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:913–920
Bryant HU, Yoburn BC, Inturrisi CE, Bernton EW, Holaday JW (1988b) Morphine-induced immunomodulation is not related to serum morphine concentrations Eur. J Pharmacol 149:165–169
Bussiere JL, Adler MW, Rogers TJ, Eisenstein TK (1993) Cytokine reversal of morphine-induced suppression of the antibody response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:591–597
Casellas AM, Guardiola H, Renaud FL (1991) Inhibition by opioids of phagocytosis in peritoneal macrophages. Neuropeptides 18:35–40
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006) HIV/AIDS Surveillance Report. Cases of HIV Infection and AIDS in the United States and Dependent Areas, 2005. US Dept. of Health and Human Services:Atlanta.
Cerletti C, Keinath SH, Reidenberg MM, Adler MW (1976) Chronic morphine administration: plasma levels and withdrawal syndrome in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:323–327
Chao CC, Sharp BM, Pomeroy C, Filice GA, Peterson PK (1990) Lethality of morphine in mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:605–609
Cheney DL, Goldstein A (1971) Tolerance to opioid narcotics: time course and reversibility of physical dependence in mice. Nature 232:477–478
Clark JD, Shi X, Li X, Qiao Y, Liang DY, Angst MS, Yeomans DC (2007) Morphine reduces local cytokine expresssion and neutrophil infiltration after incision. Mol Pain 3:28–40
Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H (2007) An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:939–951
Feng P, Rahim RT, Cowan A, Liu-Chen L-Y, Peng X, Gaughan J, Meissler JJ Jr, Adler MW, Eisenstein TK (2006) Effects of mu, kappa or delta opioids administered by pellet or pump on oral Salmonella infection and gastrointestinal transit. Eur J Pharmacol 534:250–257
Grimm MC, Ben-Baruch A, Taub DD, Howard OMZ, Resau JH, Wang JM, Ali H, Richardson R, Snyderman R, Oppenheim JJ (1998) Opiates transdeactivate chemokine receptors: δ and μ opiate receptor-mediated heterologous desensitization. J Exp Med 188:317–325
Horsburgh CR, Anderson RA, Boyko EJ (1989) Increased incidence of infections in intravenous drug use. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 10:211–215
Hussey HH, Katz S (1950) Infections resulting from narcotic addiction. Am J Med 9:186–193
Joly-Guillou M-L, Wolff M, Pocidalo J-J, Walker F, Carbon C (1997) Use of a new mouse model of Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia to evaluate the post antibioic effect of imipenem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 41:345–351
Kang G, Hartzell JD, Howard R, Wood-Morris RN, Johnson MD, Fraser S, Wintrob A, Wortmann G (2010) Mortality associated with Acinetobacter baumannii complex bacteremia among patients with war-related trauma. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 31:92–94
Kimura F, Shimizu H, Yoshidome H, Ohtsuka M, Miyazaki M (2010) Immunosuppression following surgical and traumatic injury. Surg Today 40:793–808
Lenz A, Franklin GA, Cheadle WG (2007) Systemic inflammation after trauma. Injury 38:1336–1345
Lioy D, Sheridan PA, Hurley SD, Walton JR, Martin AM, Olschowka JA, Moynihan JA (2006) Acute morphine exposure potentiates the development of HSV-1-induced encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol 172:9–17
Lockhart EL, Green AM, Flynn JL (2006) IL-17 production is dominated by γδ T cells rather than CD4 T cells during Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. J Immunol 177:4662–4669
Louria DB, Hensle T, Rose J (1967) The major medical complications of heroin addiction. Ann Int Med 67:1–22
Ma J, Wang J, Wan J, Charboneau R, Chang Y, Barke RA, Roy S (2010) Morphine disrupts interleukin-23 (IL-23)/IL-17-mediated pulmonary mucosal host defense against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Infect Immun 78:830–837
MacFarlane AS, Peng X, Meissler JJ Jr, Rogers TJ, Geller EB, Adler MW, Eisenstein TK (2000) Morphine increases susceptibility to oral Salmonella typhimurium infection. J Infect Dis 181:1350–1358
Mack VE, McCarter MD, Naama HA, Calvano SE, Daly JM (1997) Candida infection following severe trauma exacerbates Th2 cytokines and increases mortality. J Surg Res 69:399–407
Mackrell PJ, Daly JM, Mestre JR, Stapleton PP, Howe LR, Subbaramaiah K, Dannerberg AJ (2001) Elevated expression of cyclooxygenase-2 contributes to immune dysfunction in a murine model of trauma. Surgery 130:826–833
Martin JL, Koodie L, Krishnan AG, Charboneau R, Barke RA, Roy S (2010) Chronic morphine administration delays wound healing by inhibiting immune cell recruitment to the wound site. Amer. J Path. 176:786–799
Matsuzaki G, Umemura M (2007) Interleukin-17 as an effector molecule of innate and acquired immunity against infections. Microbiol Immunol 51:1139–1147
McCarter MD, Mack VE, Daly JM, Naama HA, Calvano SE (1998) Trauma-induced alterations in macrophage function. Surgery 123:96–101
McCoy CB, Metsch LR, Chitwood DD, Shapshak P, Comerford ST (1998) Parenteral transmission of HIV among injection drug users: assessing the frequency of multiperson use of needles, syringes, cookers, cotton, and water. JAIDS 18(Suppl 1):S25–S29
Meeks KD, Sieve AN, Kolls JK, Ghilardi N, Berg RE (2009) IL-23 is required for protection against systemic infection with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol 183:8026–8034
Mojadadi S, Jamali A, Khansarinejad B, Soleimanjahi H, Bamdad T (2009) Acute morphine adminstration reduces cell-mediated immunity and induces reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus type 1 in BALB/c mice. Cell Mol Immunol 6:111–116
Monroy MA, Opperman KK, Pucciarelli M, Yerrum S, Berg DA, Daly JM (2007) The PPARγ ligand 15D-PGJ2 modulates macrophage activation after injury in a murine trauma model. Shock 28:186–191
Moore FA, Moore EE (1995) Evolving concepts in the pathogenesis of postinjury multiple organ failure. Surg Clin N Amer 75:257–277
Nakae S, Komiyama Y, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwase M, Homma I, Sekikawa K, Asano M, Iwakura Y (2002) Antigen-specific T cell sensitization is impared in IL-17-deficient mice, causing suppression of allergic cellular and humoral responses. Immunity 17:375–387
Ni X, Gritman KR, Eisenstein TK, Adler MW, Arfors KE, Tuma RF (2000) Morphine attenuates leukocyte/endothelial interactions. Microvasc Res 60:121–130
Petersen K, Riddle MS, Danko JR, Blazes DL, Hayden R, Tasker SA, Dunne JR (2007) Trauma-related infections in battlefield casualties from Iraq. Ann Surg 245:803–811
Rachitskaya AV, Hansen AM, Horai R, Li Z, Villasmil R, Luger D, Nussenblatt RB, Caspi RR (2008) Cutting edge: NKT cells constitutively express IL-23 receptor and RORγt and rapidly produce IL-17 upon receptor ligation in an IL-6-independent fashion. J Immunol 180:5167–5171
Renckens R, Roelofs JJ, Knapp S, deVos AF, Florquin S, van der Poll T (2006) The acute-phase response and serum amyloid A inhibit the inflammatory response to Acinetobacter baumannii pneumonia. J Infect Dis 193:187–195
Riol-Blanco L, Lazarevic V, Awasthi A, Mitsdoerffer M, Wilson BS, Croxford A, Waisman A, Kuchroo VK, Glimcher LH, Oukka M (2010) IL-23 receptor regulated unconventional IL-17-producing T cells that control bacterial infection. J Immunol 184:1710–1720
Rogers TJ, Bednar F, Kaminsky DE, Davey PC, Meissler JJ Jr, Eisenstein TK (2005) Laboratory model systems of drug abuse and their relevance to HIV infection and dementia. In: Gendelman HE, Grant I, Everall IP, Lipton SA, Swindells S (eds) The neurology of AIDS. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 310–320
Roumen RM, Hendriks T, van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, Nieuwenhiujzen GAP, Sauerwein RW, van der Meer JW, Goris RJA (1993) Cytokine patterns in patients after major surgery, hemorrhagic shock, and severe blunt trauma. Ann Surg 6:769–776
Russo TA, Beanan JM, Olson R, MacDonald U, Luke NR, Gill SR, Campagnari AA (2008) Rat pneumonia and soft-tissue infection models for the study of Acinetobacter baumannii biology. Infect Immun 76:3577–3586
Scott PT (2004) Acinetobacter baumannii infections among patients at military medical facilities treating injured U.S. service members, 2002–2004 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly. Report 53:1064–1065
Scott P, Deye G, Srinivasan A, Murray C, Moran K, Hulten E, Fishbain J, Craft D, Riddell S, Lindler L, Mancuso J, Milstrey E, Bautista CT, Patel J, Ewell A, Hamilton T, Geddy C, Tenney M, Christopher G, Peterson K, Endy T, Petruccelli B (2007) An outbreak of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex infection in the US military health care system associated with military operations in Iraq. Clin Infect Dis 44:1577–1584
Shavit Y, Terman GW, Lewis JW, Zane CJ, Gale RP, Liebeskind JC (1986) Effects of footshock stress and morphine on natural killer lymphocytes in rats: studies of tolerance and cross-tolerance. Brain Res 372:382–385
Shibata K, Yamata H, Hara H, Kishihara K, Yoshikai Y (2007) Resident Vγ1+ γδ T cells control early infiltration of neutrophils after Escherichia coli infection via IL-17 production. J Immunol 178:4466–4472
Shirzad H, Shahrani M, Rafieian-Kopaei M (2009) Comparison of morphine and tramadol effects on phagocytic activity of mice peritoneal phagocytes in vivo. Int Immunopharm 9:968–970
Singal P, Kinhikar AG, Singh S, Singh PP (2002) Neuroimmunomodulatory effects of morphine in Leishmania donovani-infected hamsters. Neuroimmunomod 10:261–269
Singh PP, Singal P (2007) Morphine-induced neuroimmunomodulation in murine visceral leishmaniasis: the role(s) of cytokines and nitric oxide. J Neuroimm Pharmacol 2:338–351
Singh PP, Singh S, Dutta GP, Srimal RC (1993) Immunomodulation by morphine in Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Life Sci 54:331–339
Singhal PC, Bhaskaran M, Patel J, Patel K, Kasinath BS, Duraisamy S, Franki N, Reddy K, Kapasi AA (2002) Role of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase phophorylation and Fas-Fas ligand interaction in morphine-induced macrophage apoptosis. J Immunol 168:4025–4033
Szabo I, Rojavin M, Bussiere JL, Eisenstein TK, Adler MW, Rogers TJ (1993) Suppression of peritoneal macrophage phagocytosis of Candida albicans by opioids. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:703–706
Szabo I, Wetzel MA, Zhang N, Steele AD, Kaminsky DE, Chen C, Liu-Chen L-Y, Bednar F, Henderson EE, Howard OMZ, Oppenheim JJ, Rogers TJ (2003) Selective inactivation of CCR5 and decreased infectivity of R5 HIV-1 strains mediated by opioid-induced heterologous desensitization. J Leukoc Biol 74:1074–1082
Towner KJ (2009) Acinetobacter: an old friend but a new enemy. J Hosp Infect 73:355–363
Tubaro E, Borelli G, Croce C, Cavallo G, Santiangeli C (1983) Effect of morphine on resistance to infection. J Infect Dis 148:656–666
Van Faassen H, KuoLee R, Harris G, Zhao X, Conlan JW, Chen W (2007) Neutrophils play an important role in host resistance to respiratory infection with Acinetobacter baumannii in mice. Infect Immun 75:5597–5608
Vassou D, Badogeorgou E, Kampa M, Dimitriou H, Hatzoglou A, Castanas E (2008) Opioids modulate constitutive B-lymphocyte secretion. Int Immunopharm 8:634–644
Vincent JL, Bello J, Marshall J, Silva E, Anzueto A, Martin CD, Moreno R, Lipman J, Gomersall C, Sakr Y, Reinhart K (2009) International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in Intensive Care Units. JAMA 302:2323–2329
Wang J, Barke RA, Charboneau R, Roy S (2005) Morphine impairs host innate immune response and increases susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae lung infection. J Immunol 174:426–434
Wang J, Barke RA, Charboneau R, Schwendener R, Roy S (2008) Morphine induces defects in early response of alveolar macrophages to Streptococcus pneumoniae by modulating TLR9-NFkB signaling. J Immunol 180:3594–3600
Weber RJ, Pert A (1989) The periaqueductal gray matter mediates opiate-induced immunosuppression. Science 245:188–190
Wendt C, Dietze B, Dietz E, Ruden H (1997) Survival of Acinetobacter baumannii on dry surfaces. J Clin Microbiol 35:1394–1397
Wisplinghoff H, Bischoff T, Tallent M, Seifert H, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB (2004) Nosocomial bloodstream infections in US hospitals: analysis of 24,179 cases from a prospective nationwide surveillance study. Clin Infect Dis 39:309–317
Witowski J, Ksiazek K, Jorres A (2004) Interleukin-17: a mediator of inflammatory responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:567–572
Yin D, Mufson A, Wang R, Shi Y (1999) Fas-mediated cell death promoted by opioids. Nature 397:218
Acknowledgements
We thank Col. Craft for providing the Acinetobacter strains. We are grateful to Dr. Iwakura for giving us permission to obtain the IL-17a −/− mice, and to Dr. Kolls for supplying us with breeding stock of the IL-17a −/− mice.
Disclosure
There is no financial or other relationship that might lead to a conflict of interest in regard to the data being reported.
These studies were supported by USAMRMC grant W81XWH-06-1-0147, NIDA grant DA13429, and NIDA Training Grant T32DA07237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breslow, J.M., Monroy, M.A., Daly, J.M. et al. Morphine, but Not Trauma, Sensitizes to Systemic Acinetobacter baumannii Infection. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 6, 551–565 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9303-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9303-6