Abstract
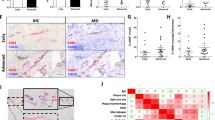
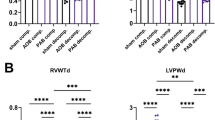
We previously showed that the expression of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC)6 ion channel elevated when TRPC1 was knocked down in A7r5 cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to explore whether TRPC6 is also upregulated in aging rat aorta comparable to that of TRPC1 in longitudinal in vivo aging model. We further investigated a possible causal relationship between altered phenylephrine-induced contractions and the expression levels of TRPC6, a purported essential component of alpha-adrenergic receptor signaling in aging aorta. Immunoblot analysis showed that TRPC1 protein levels significantly decreased whereas TRPC6 increased drastically in aorta from 16- to 20-month-old rats compared to that from 2 to 4 months. Immunohistochemical data demonstrated spatial changes in TRPC6 expression within the smooth muscle layers along with increased detection in the adventitia of the aged rat aorta. The phenylephrine-induced contractions were potentiated in aging aorta. In conclusion, based on this aging model, TRPC6 overexpression could be related with TRPC1 downregulation and might be responsible for the increased adrenoceptor sensitivity which contributes to the development of age-related vasospastic disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert AP, Large WA (2003) Store-operated Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels in smooth muscle cells. Cell Calcium 33:345–356
Albert AP, Saleh SN, Large WA (2009) Identification of canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) channel proteins in native vascular smooth muscle cells. Curr Med Chem 16:1158–1165
Anderson P, Kedersha N (2009) RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:430–436
Babich LG, Ku CY, Young HW, Huang H, Blackburn MR, Sanborn BM (2004) Expression of capacitative calcium TRPC proteins in rat myometrium during pregnancy. Biol Reprod 70:919–924
Barton M, Cosentino F, Brandes RP, Moreau P, Shaw S, Luscher TF (1997) Anatomic heterogeneity of vascular aging: role of nitric oxide and endothelin. Hypertension 30:817–824
Beech DJ (2005) TRPC1: store-operated channel and more. Pflugers Arch 451:53–60
Beech DJ, Xu SZ, McHugh D, Flemming R (2003) TRPC1 store-operated cationic channel subunit. Cell Calcium 33:433–440
Cayouette S, Lussier MP, Mathieu EL, Bousquet SM, Boulay G (2004) Exocytotic insertion of TRPC6 channel into the plasma membrane upon Gq protein-coupled receptor activation. J Biol Chem 279:7241–7246
Clarson LH, Roberts VH, Hamark B, Elliott AC, Powell T (2003) Store-operated Ca2+ entry in first trimester and term human placenta. J Physiol 550:515–528
Csiszar A, Ungvari Z, Edwards JG, Kaminski P, Wolin MS, Koller A, Kaley G (2002) Aging-induced phenotypic changes and oxidative stress impair coronary arteriolar function. Circ Res 90:1159–1166
Dietrich A, Mederos YSM, Gollasch M, Gross V, Storch U, Dubrovska G, Obst M, Yildirim E, Salanova B, Kalwa H, Essin K, Pinkenburg O, Luft FC, Gudermann T, Birnbaumer L (2005) Increased vascular smooth muscle contractility in TRPC6−/− mice. Mol Cell Biol 25:6980–6989
Dinenno FA, Tanaka H, Stauffer BL, Seals DR (2001) Reductions in basal limb blood flow and vascular conductance with human ageing: role for augmented alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction. J Physiol 536:977–983
Facemire CS, Mohler PJ, Arendshorst WJ (2004) Expression and relative abundance of short transient receptor potential channels in the rat renal microcirculation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F546–F551
Gonzalez MC, Arribas SM, Molero F, Fernandez-Alfonso MS (2001) Effect of removal of adventitia on vascular smooth muscle contraction and relaxation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:H2876–H2881
Gurdal H, Cai G, Johnson MD (1995) Alpha 1-adrenoceptor responsiveness in the aging aorta. Eur J Pharmacol 274:117–123
Inoue R, Jensen LJ, Shi J, Morita H, Nishida M, Honda A, Ito Y (2006) Transient receptor potential channels in cardiovascular function and disease. Circ Res 99:119–131
Inoue R, Okada T, Onoue H, Hara Y, Shimizu S, Naitoh S, Ito Y, Mori Y (2001) The transient receptor potential protein homologue TRP6 is the essential component of vascular alpha1-adrenoceptor-activated Ca2+-permeable cation channel. Circ Res 88:325–332
Jung S, Strotmann R, Schultz G, Plant TD (2002) TRPC6 is a candidate channel involved in receptor-stimulated cation currents in A7r5 smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 282:C347–C359
Kumar B, Dreja K, Shah SS, Cheong A, Xu SZ, Sukumar P, Naylor J, Forte A, Cipollaro M, McHugh D, Kingston PA, Heagerty AM, Munsch CM, Bergdahl A, Hultgardh-Nilsson A, Gomez MF, Porter KE, Hellstrand P, Beech DJ (2006) Upregulated TRPC1 channel in vascular injury in vivo and its role in human neointimal hyperplasia. Circ Res 98:557–563
Lin MJ, Leung GP, Zhang WM, Yang XR, Yip KP, Tse CM, Sham JS (2004) Chronic hypoxia-induced upregulation of store-operated and receptor-operated Ca2+ channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells: a novel mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res 95:496–505
Matz RL, Schott C, Stoclet JC, Andriantsitohaina R (2000) Age-related endothelial dysfunction with respect to nitric oxide, endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and cyclooxygenase products. Physiol Res 49:11–18
Minke B (2006) TRP channels and Ca2+ signaling. Cell Calcium 40:261–275
Najjar SS, Scuteri A, Lakatta EG (2005) Arterial aging: is it an immutable cardiovascular risk factor? Hypertension 46:454–462
Piascik MT, Hrometz SL, Edelmann SE, Guarino RD, Hadley RW, Brown RD (1997) Immunocytochemical localization of the alpha-1B adrenergic receptor and the contribution of this and the other subtypes to vascular smooth muscle contraction: analysis with selective ligands and antisense oligonucleotides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:854–868
Selli C, Erac Y, Kosova B, Tosun M (2009) Post-transcriptional silencing of TRPC1 ion channel gene by RNA interference upregulates TRPC6 expression and store-operated Ca2+ entry in A7r5 vascular smooth muscle cells. Vascul Pharmacol 51:96–100
Soboloff J, Spassova M, Xu W, He LP, Cuesta N, Gill DL (2005) Role of endogenous TRPC6 channels in Ca2+ signal generation in A7r5 smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 280:39786–39794
Strubing C, Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Clapham DE (2003) Formation of novel TRPC channels by complex subunit interactions in embryonic brain. J Biol Chem 278:39014–39019
Sweeney M, Yu Y, Platoshyn O, Zhang S, McDaniel SS, Yuan JX (2002) Inhibition of endogenous TRP1 decreases capacitative Ca2+ entry and attenuates pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283:L144–L155
Tabernero A, Vila E (1995) Effect of age on noradrenaline responses in rat tail artery and aorta: role of endothelium. J Auton Pharmacol 15:327–333
Tai K, Vandenberg G, Hamaide MC, Wibo M, Morel N (2009) Effect of organ culture on noradrenaline-evoked contraction, calcium signalling and TRPC expression in rat mesenteric artery. J Vasc Res 46:353–364
Tosun M, Erac Y, Selli C, Karakaya N (2007) Sarcoplasmic–endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase inhibition prevents endothelin A receptor antagonism in rat aorta. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H1961–H1966
Welsh DG, Morielli AD, Nelson MT, Brayden JE (2002) Transient receptor potential channels regulate myogenic tone of resistance arteries. Circ Res 90:248–250
Xu KM, Tang F, Han C (1997) Alterations of mRNA levels of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes with maturation and ageing in different rat blood vessels. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 24:415–417
Yu Y, Fantozzi I, Remillard CV, Landsberg JW, Kunichika N, Platoshyn O, Tigno DD, Thistlethwaite PA, Rubin LJ, Yuan JX (2004) Enhanced expression of transient receptor potential channels in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13861–13866
Yu Y, Sweeney M, Zhang S, Platoshyn O, Landsberg J, Rothman A, Yuan JX (2003) PDGF stimulates pulmonary vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by upregulating TRPC6 expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284:C316–C330
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK, SBAG-2735 to M.T. and graduate scholarship, BIDEB-2211 to C.S.). A partial support was also provided by the Ege University (BAP04ECZ011 and 05BIL016 to M.T.) and Bilkent University Research Grants. Authors thank Dr. R. M. Rapoport (University of Cincinnati, College of Medicine) for his critical comments on the study and I.T. Aydin (Bilkent University, Faculty of Science) for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Erac, Y., Selli, C., Kosova, B. et al. Expression levels of TRPC1 and TRPC6 ion channels are reciprocally altered in aging rat aorta: implications for age-related vasospastic disorders. AGE 32, 223–230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-009-9126-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-009-9126-z