Abstract
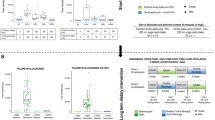
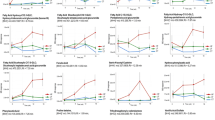
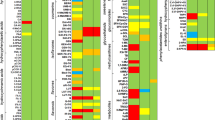
Fruit and vegetable consumption has been associated with several health benefits; however the mechanisms are largely unknown at the biochemical level. Our research aims to investigate whether plasma metabolome profiling can reflect biological effects after feeding rats with raw apple by using an untargeted UPLC–ESI–TOF–MS based metabolomics approach in both positive and negative mode. Eighty young male rats were randomised into groups receiving daily 0, 5 or 10 g fresh apple slices, respectively, for 13 weeks. During weeks 3–6 some of the animals were receiving 4 mg/ml 1,2-dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride (DMH) once a week. Plasma samples were taken at the end of the intervention and among all groups, about half the animals were 12 h fasted. An initial ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis with a three-factor or two-factor design was employed in order to isolate potential metabolic variations related to the consumption of fresh apples. Partial least squares-discriminant analysis was then applied in order to select discriminative features between plasma metabolites in control versus apple fed rats and partial least squares modelling to reveal possible dose response. The findings indicate that in laboratory rats apple feeding may alter the microbial amino acid fermentation, lowering toxic metabolites from amino acids metabolism and increasing metabolism into more protective products. It may also delay lipid and amino acid catabolism, gluconeogenesis, affect other features of the transition from the postprandial to the fasting state and affect steroid metabolism by suppressing the plasma level of stress corticosteroids, certain mineralocorticoids and oxidised bile acid metabolites. Several new hypotheses regarding the cause of health effects from apple intake can be generated from this study for further testing in humans.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. J., & Ter Braak, C. J. F. (2003). Permutation tests for multi-factorial analysis of variance. Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 73(2), 85–113.
Barri, T., Holmer-Jensen, J., Hermansen, K., & Dragsted, L. O. (2012). Metabolic fingerprinting of high-fat plasma samples processed by centrifugation- and filtration-based protein precipitation delineates significant differences in metabolite information coverage. Analytica Chimica Acta, 718, 47–57. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.12.065.
Bazzano, L. A., Serdula, M. K., & Liu, S. (2003). Dietary intake of fruits and vegetables and risk of cardiovascular disease (Review). Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 5(6), 492–499.
Block, G., Patterson, B., & Subar, A. (1992). Fruit, vegetables, and cancer prevention: a review of the epidemiological evidence (Review). Nutrition and Cancer, 18(1), 1–29.
Boyer, J., & Liu, R. (2004). Apple phytochemicals and their health benefits. Nutrition Journal, 3(1), 5.
Bremer, J. (1983). Carnitine–metabolism and functions (Review). Physiological Reviews, 63(4), 1420–1480.
Chyan, Y.-J., Poeggeler, B., Omar, R. A., Chain, D. G., Frangione, B., Ghiso, J., et al. (1999). Potent neuroprotective properties against the Alzheimer β-amyloid by an endogenous melatonin-related indole structure, indole-3-propionic acid. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274(31), 21937–21942. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.31.21937.
Creer, M., & Gross, R. (1985). Separation of isomeric lysophospholipids by reverse phase HPLC. Lipids, 20(12), 922–928. doi:10.1007/bf02534778.
Cunningham-Rundles, S., Ahrne, S., Bengmark, S., Johann-Liang, R., Marshall, F., Metakis, L., et al. (2000). Probiotics and immune response (Clinical Trial). American Journal of Gastroenterology, 95(1 Suppl), S22–S25.
Feigenbaum, J., & Neuberg, C. A. (1941). Simplified method for the preparation of aromatic sulfuric acid esters. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 63, 3529–3530.
Frey, F. J. (2006). Impaired 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase contributes to renal sodium avidity in cirrhosis: Hypothesis or fact? (Review). Hepatology, 44(4), 795–801.
Funder, J. W. (1997). Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors: Biology and clinical relevance. [Review]. Annual Review of Medicine, 48, 231–240. doi:10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.231.
Funder, J. W., Pearce, P. T., & Smith, A. I. (1988). Mineralocorticoid action: target tissue specificity is enzyme, not receptor, mediated (Research Support, Non-US Gov’t). Science, 242(4878), 583–585.
Goodhart, P. J., DeWolf, W. E, Jr, & Kruse, L. I. (1987). Mechanism-based inactivation of dopamine beta-hydroxylase by p-cresol and related alkylphenols. Biochemistry, 26(9), 2576–2583.
Gürdeniz, G., Kristensen, M., Skov, T., & D, L. O. (2012). The effect of LC–MS data preprocessing methods on the selection of plasma biomarkers in fed versus fasted rats. Metabolites, 2, 77–97. doi:10.3390/metabo2010077.
Heipieper, H. J., Keweloh, H., & Rehm, H. J. (1991). Influence of phenols on growth and membrane permeability of free and immobilized Escherichia coli. Applied and Environment Microbiology, 57(4), 1213–1217.
Ikeda, S., Tohyama, T., & Yamashita, K. (2002). Dietary sesame seed and its lignans inhibit 2,7,8-trimethyl- 2(2′-carboxyethyl)-6-hydroxychroman excretion into urine of rats fed γ-tocopherol. Journal of Nutrition, 132(5), 961–966.
Joshipura, K. J., Hu, F. B., Manson, J. E., Stampfer, M. J., Rimm, E. B., Speizer, F. E., et al. (2001). The effect of fruit and vegetable intake on risk for coronary heart disease. Annals of Internal Medicine, 134(12), 1106–1114.
Kristensen, M., Engelsen, S. B., & Dragsted, L. O. (2012). LC–MS metabolomics top-down approach reveals new exposure and effect biomarkers of apple and apple-pectin intake. Metabolomics, 8(1), 64–73.
Kristensen, M., Savorani, F., Ravn-Haren, G., Poulsen, M., Markowski, J., Larsen, F. H., et al. (2010). NMR and interval PLS as reliable methods for determination of cholesterol in rodent lipoprotein fractions. Metabolomics, 6(1), 129–136.
Lascelles, P. T., & Taylor, W. H. (1966). The effect upon tissue respiration in vitro of metabolites which accumulate in uraemic coma (In Vitro). Clinical Science, 31(3), 403–413.
Li, Y.-J., Luo, S.-C., Lee, Y.-J., Lin, F.-J., Cheng, C.-C., Wein, Y.-S., et al. (2008). Isolation and identification of α-CEHC sulfate in rat urine and an improved method for the determination of conjugated α-CEHC. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 56(23), 11105–11113. doi:10.1021/jf802459d.
Licht, T. R., Hansen, M., Bergstrom, A., Poulsen, M., Krath, B. N., Markowski, J., et al. (2010). Effects of apples and specific apple components on the cecal environment of conventional rats: role of apple pectin. BMC Microbiology, 10, 13.
Liu, Z., & Franklin, M. R. (1984). Separation of four glucuronides in a single sample by high-pressure liquid chromatography and its use in the determination of UDP glucuronosyltransferase activity toward four aglycones. Analytical Biochemistry, 142(2), 340–346.
Liu, S., Manson, J. E., Lee, I. M., Cole, S. R., Hennekens, C. H., Willett, W. C., et al. (2000). Fruit and vegetable intake and risk of cardiovascular disease: The women’s health study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 72(4), 922–928.
Mammalian liver cytosol—guidline for use. (1996) TF000016 (Vol. Rev 1.0).
Marver, D., & Edelman, I. S. (1978). Dihydrocortisol: A potential mineralocorticoid. Journal of steroid biochemistry, 9(1), 1–7. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(78)90093-6.
McEwen, B. S. (1999). Stress and hippocampal plasticity (Review). Annual Review of Neuroscience, 22, 105–122. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.105.
McNamara, P. J., Lalka, D., & Gibaldi, M. (1981). Endogenous accumulation products and serum protein binding in uremia. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine, 98(5), 730–740.
Michals, K., & Matalon, R. (1985). Phenylalanine metabolites, attention span and hyperactivity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 42(2), 361–365.
Ministers, N. C. O. (2003). The NORBAGREEN 2002 study: Consumption of vegetables, potatoes, fruit, bread, and fish in the Nordic and Baltic countries. TemaNord, 556, 51–57.
Nelson, A. C., Huang, W., & Moody, D. E. (2001). Variables in human liver microsome preparation: impact on the kinetics of l-alpha-acetylmethadol (LAAM) n-demethylation and dextromethorphan O-demethylation. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 29(3), 319–325.
Pearson, D. J., & Tubbs, P. K. (1967). Carnitine and derivatives in rat tissues. Biochemical Journal, 105(3), 953–963.
Pete, M. J., & Exton, J. H. (1996). Purification of a lysophospholipase from bovine brain that selectively deacylates arachidonoyl-substituted lysophosphatidylcholine. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(30), 18114–18121.
Poulsen, M., Mortensen, A., Binderup, M. L., Langkilde, S., Markowski, J., & Dragsted, L. O. (2011). The effect of apple feeding on markers of colon carcinogenesis (Research Support, Non-US Gov’t). Nutrition and Cancer, 63(3), 402–409. doi:10.1080/01635581.2011.535961.
Rafter, J. (2003). Probiotics and colon cancer. Best Practice and Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 17(5), 849–859.
Ravn-Haren, G., Dragsted, L. O., Buch-Andersen, T., Jensen, E. N., Jensen, R. I., Nemeth-Balogh, M., et al. (2012). Intake of whole apples or clear apple juice has contrasting effects on plasma lipids in healthy volunteers. European Journal of Nutrition. doi:10.1007/s00394-012-0489-z.
Rosamond, W. D., Gorton, R. A., Hinn, A. R., Hohenhaus, S. M., & Morris, D. L. (1998). Rapid response to stroke symptoms: The delay in accessing stroke healthcare (DASH) study. Academic Emergency Medicine, 5(1), 45–51.
Smilde, A. K., Jansen, J. J., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Lamers, R.-J. A. N., van der Greef, J., & Timmerman, M. E. (2005). ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): A new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics, 21(13), 3043–3048.
Smit, S., van Breemen, M. J., Hoefsloot, H. C., Smilde, A. K., Aerts, J. M., & de Koster, C. G. (2007). Assessing the statistical validity of proteomics based biomarkers. Analytica Chimica Acta, 592(2), 210–217.
Souci, S.W., Fachmann, W., Kraut, H., Senser, F., & Scherz, H. (1991). Lebensmitteltabelle für die Praxis: Wissenschaftliche Verlagsges.
Stanimirova, I., Michalik, K., Drzazga, Z., Trzeciak, H., Wentzell, P. D., & Walczak, B. (2011). Interpretation of analysis of variance models using principal component analysis to assess the effect of a maternal anticancer treatment on the mineralization of rat bones. Analytica Chimica Acta, 689(1), 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.01.008.
Steinmetz, K. A., & Potter, J. D. (1996). Vegetables, fruit, and cancer prevention: A review (Review). Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 96(10), 1027–1039.
Stewart, P., Valentino, R., Wallace, A. M., Burt, D., Shackleton, C. L., & Edwards, C. W. (1987). Mineral corticoid activity of liquorice: 11-Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency comes of age. The Lancet, 330(8563), 821–824.
Subbaiah, P. V., & Liu, M. (1996). Comparative studies on the substrate specificity of lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase towards the molecular species of phosphatidylcholine in the plasma of 14 vertebrates. Journal of Lipid Research, 37(1), 113–122.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics, 3(3), 211–221. doi:10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2.
Sun, J., Chu, Y.-F., Wu, X., & Liu, R. H. (2002). Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of common fruits. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 50(25), 7449–7454.
Swain, M. G., & Maric, M. (1996). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates adrenal glucocorticoid secretion in cholestatic rats. American Journal of Physiology—Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 270(6), G987–G991.
Ten Berge, J. M. F., Khal, & Van der Stel, V. (1992). Simultaneous components analysis. Statistica Applicata, 4(4), 277–392.
Thompson, D. C., Perera, K., Fisher, R., & Brendel, K. (1994). Cresol isomers: Comparison of toxic potency in rat liver slices. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 125(1), 51–58.
Thomson, R. Y., Scotto, G. T., & Brown, G. B. (1962). On the conversion of cytidine to deoxycytidine in the rat. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 237, 3510–3512.
Touma, C., Sachser, N., Möstl, E., & Palme, R. (2003). Effects of sex and time of day on metabolism and excretion of corticosterone in urine and feces of mice. General and Comparative Endocrinology, 130(3), 267–278. doi:10.1016/s0016-6480(02)00620-2.
Turnbaugh, P. J., Ley, R. E., Mahowald, M. A., Magrini, V., Mardis, E. R., & Gordon, J. I. (2006). An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature, 444(7122), 1027–1031. doi:10.1038/nature05414.
Van Duijnhoven, F. J., Bueno-De-Mesquita, H. B., Ferrari, P., Jenab, M., Boshuizen, H. C., Ros, M. M., et al. (2009). Fruit, vegetables, and colorectal cancer risk: the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (Research Support, Non-US Gov’t). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(5), 1441–1452.
Vanholder, R., Glorieux, G., De Smet, R., & Lameire, N. (2003). New insights in uremic toxins. Kidney International Supplements, 84, S6–10.
Wikoff, W. R., Anfora, A. T., Liu, J., Schultz, P. G., Lesley, S. A., Peters, E. C., et al. (2009). Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science USA, 106(10), 3698–3703. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812874106.
Windey, K., De Preter, V., & Verbeke, K. (2012). Relevance of protein fermentation to gut health (Review). Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 56(1), 184–196.
Yokoyama, M. T., Tabori, C., Miller, E. R., & Hogberg, M. G. (1982). The effects of antibiotics in the weanling pig diet on growth and the excretion of volatile phenolic and aromatic bacterial metabolites. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 35(6), 1417–1424.
Zhao, Y., Lee, M. J., Cheung, C., Ju, J. H., Chen, Y. K., Liu, B., et al. (2010). Analysis of multiple metabolites of tocopherols and tocotrienols in mice and humans. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 58(8), 4844–4852. doi:10.1021/Jf904464u.
Zwanenburg, G., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Westerhuis, J. A., Jansen, J. J., & Smilde, A. K. (2011). ANOVA–principal component analysis and ANOVA–simultaneous component analysis: A comparison. Journal of Chemometrics, 25(10), 561–567. doi:10.1002/cem.1400.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rago, D., Mette, K., Gürdeniz, G. et al. A LC–MS metabolomics approach to investigate the effect of raw apple intake in the rat plasma metabolome. Metabolomics 9, 1202–1215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0534-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-013-0534-9