Abstract
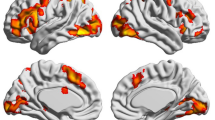
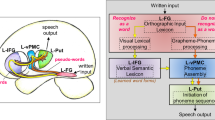
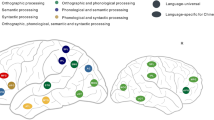
Functional imaging studies have established cortical networks for reading alphabetic, syllabic and logographic scripts. There is little information about the different cortical areas that participate in reading an alphasyllabary. We use functional brain imaging to study the reading network for Devanagari, an alphasyllabary. Similar to syllabic scripts, the basic phonological unit that corresponds to a grapheme in Devanagari, called an akshara, is a syllable but the component consonant and vowel within akshara can always be visually analyzed giving it the appearance of an alphabetic system. Unlike an alphabetic system wherein arrangement of consonants and vowels is linear, in Devanagari, vowels can also be placed linearly in a sequential manner or non-linearly, above or below, making it visuospatially complex. In this study we used functional neuroimaging to ascertain the cortical reading network when 10 native speakers of Hindi, read linear words in Devanagari. Akin to other word reading studies, we find activation in the mid-fusiform gyrus (visual word form area, BA 37). Region of interest analysis shows involvement of left superior temporal gyrus (BA 41), inferior (BA 40) and superior parietal (BA 7) lobules. These findings suggest that the reading network for Devanagari, an alphasyllabary encompasses cortical areas involved in reading both alphabetic and syllabic writing systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolger, D. J., Perfetti, C. A., & Schneider, W. (2005). Cross-cultural effect on the brain revisited: Universal structures plus writing system variation. Human Brain Mapping, 25, 92–104.
Bright, W. (2000). A matter of typology: Alphasyllabaries and abugidas. Studies in the Linguistic Sciences, 30, 63–71.
Clarke, M. A. (1980). The short circuit hypothesis of ESL reading or when language competence interferes with reading performance. Journal of Modern Language, 64, 203–209.
Das, T., Kumar, U., Bapi, R. S., Padakannaya, P., & Singh, N. C. (2009). Neural representation of an alphasyllabary—The story of Devanagari. Current Science, 97, 1033–1038.
Dehaene, S., & Cohen L. (2007). Cultural recycling of cortical maps. Neuron, 56, 384–398.
Friston, K. J., Frith, C. D., Frackowiak, R. S., & Turner, R. (1995a). Characterizing dynamic brain responses with fMRI: A multivariate approach. Neuroimage, 2, 166–172.
Friston, K. J., Holmes, A. P., Worsley, K. J., Poline, J.-B., Frith, C. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. J. (1995b). Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach. Human Brain Mapping, 4, 189–210.
Goodman, K. S. (1973). Psycholinguistic universals in the reading process. In F. Smith (Ed.), Psycholinguistics and reading. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Hagoort, P., Indefrey, P., Brown, C., Herzog, H., Steinmetz, H., & Seitz, R. J. (1999). The neural circuitry involved in the reading of German words and pseudo words: A PET study. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 11, 383–398.
Howard, D., Patterson, K., Wise, R., Brown, W. D., Friston, K., Weiller, C., et al. (1992). The cortical localization of the lexicons. Brain, 115, 1769–1782.
Ino, T., Nakai, R., Azuma, T., Kimura, T., & Fukuyama, H. (2009). Recognition and reading aloud of Kana and Kanji words: An fMRI study. Brain Research Bulletin, 78, 232–239.
Jobard, G., Crivello, F., & Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. (2003). Evaluation of the dual route theory of reading: A metanalysis of 35 neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage, 20, 693–712.
Kumar, U., Das, T., Bapi, R. S., Padakannaya, P., Joshi, R. M., & Singh, N. C. (2010). Reading different orthographies: An fMRI study of phrase reading in Hindi-English bilinguals. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 23, 239–255.
McCandliss, B. D., Cohen, L., & Dehaene, S. (2003). The visual word form area: Expertise for reading in the fusiform gyrus. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7, 293–299.
Meschyan, G., & Hernandez, A. E. (2006). Impact of language proficiency and orthographic transparency on bilingual word reading: An fMRI investigation. Neuroimage, 29, 1135–1140.
Moore, C. J., & Price, C. J. (1999). Three distinct ventral occipitotemporal regions for reading and object naming. Neuroimage, 10, 181–192.
Nakamura, K., Dehaene, S., Jobert, A., Bihan, D. L., & Kouider, S. (2005). Subliminal convergence of Kanji and Kana words: Further evidence for functional parcellation of the posterior temporal cortex in visual word perception. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17, 954–968.
Oldfield, R. C. (1971). The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia, 9, 97–113.
Paulesu, E., McCrory, E., Fazio, F., Menoncello, L., Brunswick, N., Cappa, S. F., et al. (2000). A cultural effect on brain function. Nature Neuroscience, 3, 91–96.
Pelgrims, B., Andres, M., & Olivier, E. (2009). Double dissociation between motor and visual imagery in the posterior parietal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 19, 2298–2307.
Penny, W. D., Holmes, A. P., & Friston, K. J. (2003). Random effects analysis. In R. S. J. Frackowiak, K. J. Friston, C. D. Frith, R. Dolan, C. J. Price, S. J. Zeki, et al. (Eds.), Human brain function. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Perfetti, C. A. (2003). The universal grammar of reading. Scientific Studies of Reading, 8, 3–24.
Perfetti, C. A., & Liu, Y. (2005). Orthography to phonology and meaning: Comparisons across and within writing systems. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 18, 193–210.
Perfetti, C. A., Liu, Y., Fiez, J., Nelson, J., & Bolger, D. J. (2007). Reading in two writing systems: Accomodation and assimilation of the brain’s reading network. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition, 10, 131–146.
Perfetti, C. A., Zhang, S., & Berent, I. (1992). Reading in english and Chinese: Evidence for a “universal” phonological principle. In R. Frost & L. Katz (Eds.), Orthography, phonology, morphology and meaning. Amsterdam.
Poldrack, R. A., Desmond, J. A., Glover, G. H., & Gabrielei, J. D. (1998). The neural basis of visual skill learning: An fMRI study of mirror reading. Cerebral Cortex, 8, 1–10.
Price, C. J. (2000). The anatomy of language: Contributions from functional neuroimaging. Journal of Anatomy, 197, 335–359.
Talairach, J., & Tournoux, P. (1988). Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. New York: Thieme.
Tan, L. H., Spinks, J. A., Feng, C.-M., Siok, W. T., Perfetti, C. A., Xiong, J., et al. (2003). Neural systems of second language reading are shaped by native language. Human Brain Mapping, 18, 158–166.
Vaid, J., & Gupta, A. (2002). Exploring word recognition in a semi-alphabetic script: The case of Devanagari. Brain and Language, 81, 679–690.
Yoon, H. W., Cho, K., Chung, J., & Park, H. W. (2005). Neural mechanisms of Korean word reading: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroscience Letters, 373, 206–211.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge J. Ahlawat for their support in image acquisition. This research was supported by funding from the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India and intramural funding from the National Brain Research Centre, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, T., Bapi, R.S., Padakannaya, P. et al. Cortical network for reading linear words in an alphasyllabary. Read Writ 24, 697–707 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9241-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9241-3