Abstract
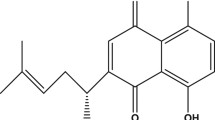
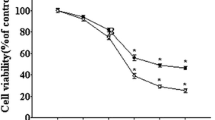
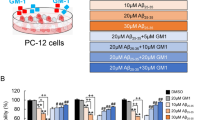
The accumulation of extracellular amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) has been considered as one of the important causes of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most prevalent form of dementia. Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA), a major active chemical component isolated from Carthamus tinctorius L., has been shown to possess neuroprotective actions in various ischemic models in vivo. The present study aimed to investigate the potential protective effect of HSYA against Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The PC12 cells were pretreated with different concentrations (20, 40 and 80 μM) of HSYA for 2 h and then further treated with Aβ (20 μM) for 24 h. The results showed that Aβ could significantly decrease cell viability, glutathione level, mitochondrial membrane potential and the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax protein expression, while elevate the release of lactate dehydrogenase, the formation of DNA fragmentation, the levels of malondialdehyde and intracellular reactive oxygen species in PC12 cells. However, pretreatment with HSYA could effectively reverse these changes induced by Aβ in PC12 cells. Our experimental results demonstrate that HSYA may be a potential neuroprotective agent warranting further development for treatment of AD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier M, Seabrook TJ, Lemere CA (2005) Developing novel immunogens for an effective, safe Alzheimer’s disease vaccine. Neurodegener Dis 2:267–272
Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2009) Advances in tau-focused drug discovery for Alzheimer’s disease and related tauopathies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:783–793
Smith DG, Cappai R, Barnham KJ (2007) The redox chemistry of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid beta peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:1976–1990
Varadarajan S, Kanski J, Aksenova M, Lauderback C, Butterfield DA (2001) Different mechanisms of oxidative stress and neurotoxicity for Alzheimer’s A beta(1–42) and A beta(25–35). J Am Chem Soc 123:5625–5631
Liu X, Xu K, Yan M, Wang Y, Zheng X (2010) Protective effects of galantamine against Abeta-induced PC12 cell apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurochem Int 57:588–599
Mattson MP, Partin J, Begley JG (1998) Amyloid beta-peptide induces apoptosis-related events in synapses and dendrites. Brain Res 807:167–176
Kim HS, Park CH, Cha SH, Lee JH, Lee S, Kim Y et al (2000) Carboxyl-terminal fragment of Alzheimer’s APP destabilizes calcium homeostasis and renders neuronal cells vulnerable to excitotoxicity. FASEB J 14:1508–1517
Eckert A, Marques CA, Keil U, Schüssel K, Müller WE (2003) Increased apoptotic cell death in sporadic and genetic Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:604–609
Choi SJ, Jeong CH, Choi SG, Chun JY, Kim YJ, Lee J et al (2009) Zeatin prevents amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity and scopolamine-induced cognitive deficits. J Med Food 12:271–277
Xian YF, Lin ZX, Mao QQ, Ip SP, Su ZR, Lai XP (2012) Protective effect of isorhynchophylline against β-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:353–360
Xian YF, Lin ZX, Mao QQ, Zhao M, Hu Z, Ip SP (2012) Bioassay-guided isolation of neuroprotective compounds from Uncaria rhynchophylla against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:802625
Greene LA, Tischler AS (1976) Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:2424–2428
Shafer TJ, Atchison WD (1991) Transmitter, ion channel and receptor properties of pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells: a model for neurotoxicological studies. Neurotoxicology 12:473–492
Mao QQ, Ip SP, Ko KM, Tsai SH, Zhao M, Che CT (2009) Peony glycosides protect against corticosterone-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:643–647
Zhang Z, Larner SF, Liu MC, Zheng W, Hayes RL, Wang KK (2009) Multiple alphaII-spectrin breakdown products distinguish calpain and caspase dominated necrotic and apoptotic cell death pathways. Apoptosis 14:1289–1298
Yang Z, Yang J, Jia Y, Tian Y, Wen A (2009) Pharmacokinetic properties of hydroxysafflor yellow A in healthy Chinese female volunteers. J Ethnopharmacol 124:635–638
Lin XT (2012) The clinical application of Hydroxysafflor yellow. Chin J Health Care Med 14:332–333
Tian J, Li G, Liu Z, Fu F (2008) Hydroxysafflor yellow A inhibits rat brain mitochondrial permeability transition pores by a free radical scavenging action. Pharmacology 82:121–126
Ji DB, Zhang LY, Li CL, Ye J, Zhu HB (2009) Effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hypoxia. Vascul Pharmacol 50:137–145
Wang T, Fu F, Han B, Zhang L (2006) Mechanism of hydroxysafflor yellow A on protecting ischemic myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40:957
Nie PH, Zhang L, Zhang WH, Rong WF, Zhi JM (2012) The effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on blood pressure and cardiac function. J Ethnopharmacol 139:746–750
Zang BX, Jin M, Si N, Zhang Y, Wu W, Piao YZ (2002) Antagonistic effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on the platelet activating factor receptor. Yao Xue Xue Bao 37:696–699
Shi X, Ruan D, Wang Y, Ma L, Li M (2010) Anti-tumor activity of safflower polysaccharide (SPS) and effect on cytotoxicity of CTL cells, NK cells of T739 lung cancer in mice. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 35:215–218
Wu Y, Wang L, Jin M, Zang BX (2012) Hydroxysafflor yellow A alleviates early inflammatory response of bleomycin-induced mice lung injury. Biol Pharm Bull 35:515–522
Zhu H, Wang Z, Ma C, Tian J, Fu F, Li C et al (2003) Neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A: in vivo and in vitro studies. Planta Med 69:429–433
Wei X, Liu H, Sun X, Fu F, Zhang X, Wang J et al (2005) Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects rat brains against ischemia-reperfusion injury by antioxidant action. Neurosci Lett 386:58–62
Pan Y, Zheng DY, Liu SM, Meng Y, Xu HY, Zhang Q et al (2012) Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates lymphostatic encephalopathy-induced brain injury in rats. Phytother Res. doi:10.1002/ptr.4594
Zhu HB, Wang ZH, Tian JW, Fu FH, Liu K, Li CL (2005) Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on experimental cerebral ischemia in rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao 40:1144–1146
Fan L, Dang X, Shi Z, Zhang C, Wang K (2011) Hydroxysafflor Yellow A protects PC12 cells against the apoptosis induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31:1187–1194
Li G, Ma R, Huang C, Tang Q, Fu Q, Liu H et al (2008) Protective effect of erythropoietin on β-amyloid-induced PC12 cell death through antioxidant mechanisms. Neurosci Lett 442:143–147
Rosenberg JC, Rush BF (1966) An enzymatic-spectrophotometric determination of pyruvic and lactic acid in blood: methodologic aspects. Clin Chem 12:299–307
Xian YF, Lin ZX, Zhao M, Mao QQ, Ip SP, Che CT (2011) Uncaria rhynchophylla ameliorates cognitive deficits induced by D-galactose in mice. Planta Med 77:1977–1983
Xing QL, Chen JW, Ma RQ (2008) Protective effect of panaxatriol saponins on cerebral ischemia. J Sun Yat-sen Univ (Medical Sciences) 29:705–710
Li GS, Tian JW, Feng FH, Yang JQ (2006) Protective effect of ginsenoside Rb3 from rat cortex mitochondrial injuries due to cerebral ischemia. Chin J New Drug 15:518–522
Zhang Q, Chen ZY, Wu LB, Wang SC, Zheng QS (2005) Clinical nonferiority evaluation on the efficacy and safety of safflower yellow pigment lyophilized power and dripping solution in the treatment of patients with angina. Chinese J Evidence Based Med 5:276–285
Miao Y, Li LZ, Xu FQ, Chen KY, Wang XF, Zhang D et al (2010) A phase III trial of safflor yellow injection for the treatment of angina pectoris with heart-blood stagnation syndrome in patients with coronary heart disease. Chin New Drug J 19:584–589
Liu Y, Yu JD, Dai Z, Lin RC (2010) Study on quality control of Honghua injection. Chin J Pham Anal 30:1732–1734
Cheng WD (2011) Effect of Safflower Yellow and sodium chloride injection on acute exacerbation of chronic pulmonary heart disease at high altitude. Chin J New Drugs Clin Rem 30:208–210
Yang Q, Yang ZF, Liu SB, Zhang XN, Hou Y, Li XQ et al (2010) Neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A against excitotoxic neuronal death partially through down-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neurochem Res 35:1353–1360
Sul D, Kim HS, Lee D, Joo SS, Hwang KW, Park SY (2009) Protective effect of caffeic acid against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by the inhibition of calcium influx and tau phosphorylation. Life Sci 84:257–262
Qu M, Li L, Chen C, Li M, Pei L, Chu F et al (2011) Protective effects of lycopene against amyloi β-induced neurotoxicity in cultured rat cortical neurons. Neurosci Lett 505:286–290
Zhang HY, Liu YH, Wang HQ, Xu JH, Hu HT (2008) Puerarin protects PC12 cells against β-amyloid-induced cell injury. Cell Biol Int 32:1230–1237
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1985) Oxygen radicals and the nervous system. Trends Neurosci 6:22–26
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P (1993) Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 262:689–695
Behl C (1999) Alzheimer’s disease and oxidative stress: implications for novel therapeutic approaches. Prog Neurobiol 57:301–323
Praticò D (2008) Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: a reappraisal. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:609–615
Bowen DM, Francis PT, Sims NR (1992) Beta-Amyloid increased neuronal susceptibility to injury by glucose deprivation. NeuroReport 3:733–734
Hensley K, Aksenova M, Carney JM, Harris M, Butterfield DA (1995) Amyloid beta-peptide spin trapping. II: evidence for decomposition of the PBN spin adduct. NeuroReport 6:493–496
Klegeris A, McGeer PL (1997) Beta-amyloid protein enhances macrophage production of oxygen free radicals and glutamate. J Neurosci Res 49:229–235
Canevari L, Abramov AY, Duchen MR (2004) Toxicity of amyloid beta peptide: tales of calcium, mitochondria, and oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 29:637–650
Takuma K, Yan SS, Stern DM, Yamada K (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Pharmacol Sci 97:312–316
Qian T, Herman B, Lemasters JJ (1999) The mitochondrial permeability transition mediates both necrotic and apoptotic death of hepatocytes exposed to Br-A23187. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 154:117–125
Bernardi P, Petronilli V, Di Lisa F, Forte M (2001) A mitochondrial perspective on cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 26:112–117
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6:513–519
Crompton M (2000) Mitochondrial intermembrane junctional complexes and their role in cell death. J Physiol 529:11–21
Li J, Li B, Zhou WJ, Zhao FG, Li DJ, Wang WJ (2010) Medicated rat serum containing Gengnianchun decoction reduces apoptosis of pheochromocytoma cells insulted by amyloid beta protein. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 8:472–479
Yamaguchi R, Andreyev A, Murphy AN, Perkins GA, Ellisman MH, Newmeyer DD (2007) Mitochondria frozen with trehalose retain a number of biological functions and preserve outer membrane integrity. Cell Death Differ 14:616–624
Antonsson B (2004) Mitochondria and the Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis signaling pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 256–257:141–155
McInnis J, Wang C, Anastasio N, Hultman M, Ye Y, Salvemini D et al (2002) The role of superoxide and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced necrosis and apoptosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:478–487
Schelman WR, Andres RD, Sipe KJ, Kang E, Weyhenmeyer JA (2004) Glutamate mediates cell death and increases the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio in a differentiated neuronal cell line. Mol Brain Res 128:160–169
Gu B, Nakamichi N, Zhang WS, Nakamura Y, Kambe Y, Fukumori R et al (2009) Possible protection by notoginsenoside R1 against glutamate neurotoxicity mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors composed of an NR1/NR2B subunit assembly. J Neurosci Res 87:2145–2156
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Yu-Feng Qiao for the generous donation of purified HSYA. This work was supported by grants from the Guangdong International Cooperation Projects in 2012, Guangdong Province, P.R. China (Project No. 2012B050300002), and International Cooperation Platform Construction for Chinese Medicine Innovation in Treating Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease (No.2011B050300021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Song-Zhi Kong and Yan-Fang Xian Contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, SZ., Xian, YF., Ip, SP. et al. Protective Effects of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A on β-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells. Neurochem Res 38, 951–960 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1002-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1002-7